VCF compatibility
Structure
The genotype track uses concepts similar to those in the VCF specification to facilitate import and export of the commonly used format (https://samtools.github.io/hts-specs/VCFv4.3.pdf). Genotype tracks exist in either sample or database form, corresponding to VCF files with or without the FORMAT column, respectively.
Databases such as ClinVar, dbSNP, and Cosmic are usually made available in VCFs without the FORMAT and sample specific columns. Database variants are without genome context, in the sense that it varies from sample to sample if they are heterozygous or homozygous and which alleles at other loci they form haplotypes with. These variants are also referred to as conceptual variants, and the annotations they posses (VCF INFO column) are typically database or population specific as opposed to specific for a single sample.
Sample genotype tracks describe the genome of a single sample. Sample variants can have both database and sample specific annotations and genome context is provided in genotypes and haplotypes.
Genome model
The genotype track genome model consists of four elements as shown in figure 13.13. A variant locus and an allele variant always have a database component and may have a sample specific component. Haplotype alleles represent instances of allele variants in a sample, and when haplotype alleles are present in the same DNA molecule they form a haplotype together (i.e. the haplotype alleles are phased).
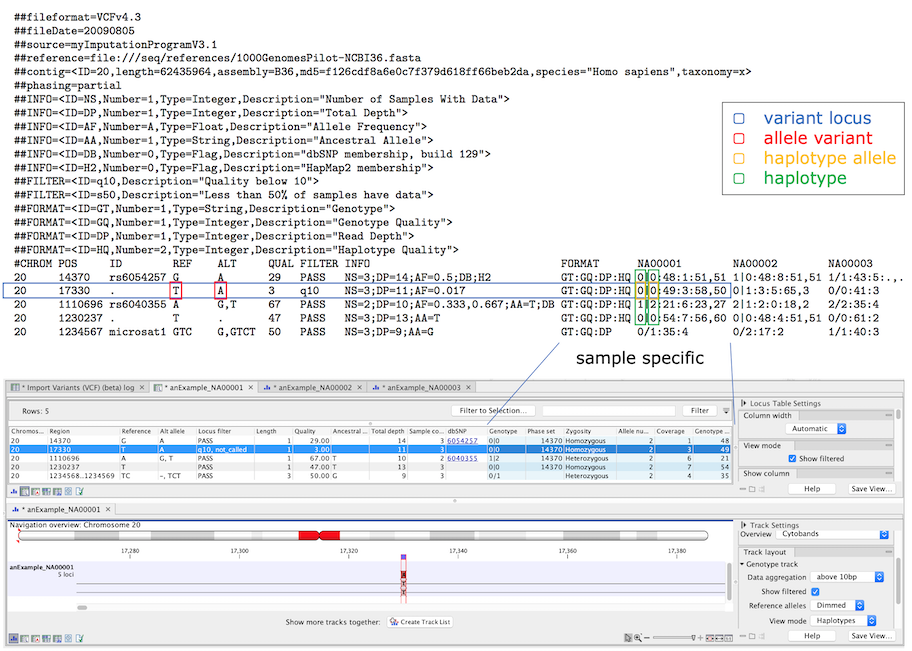
Figure 13.13: The four elements in the genome model and their relation to VCF. The variant locus has a number of allele variants that in a sample has a number of haplotype alleles, and phased haplotype alleles at several loci form a haplotype. In the lower part, the VCF has been imported and a genotype track locus table and track view are showing a filtered locus. Sample specific annotations are colored blue in the genotype track tables.
