LightSpeed Fastq to Somatic Variants Tumor Normal
The LightSpeed Fastq to Somatic Variants Tumor Normal tool is designed to provide somatic variant calls from a tumor and a normal sample within a very short timeframe.
The tool can perform read trimming, mapping, deduplication, local realignment and variant calling. For a description of each step, see LightSpeed Methods.
LightSpeed Fastq to Somatic Variants Tumor Normal can only analyze one sample per analysis start (see Batching).
To run the tumor normal LightSpeed tool go to:
Tools | LightSpeed (![]() ) | LightSpeed Fastq to Somatic Variants Tumor Normal (
) | LightSpeed Fastq to Somatic Variants Tumor Normal (![]() )
)
If you are connected to a CLC Server via your Workbench, you will be asked where you would like to run the analysis. We recommend that you run the analysis on a CLC Server when possible.
In the first wizard step, specify tumor and normal fastq files and a reference sequence (figure 11.1):
- Input data
- Tumor reads (fastq) Tumor fastq files for analysis. At least two fastq files representing R1 and R2 reads must be provided.
- Normal reads (fastq) Normal fastq files for analysis. At least two fastq files representing R1 and R2 reads must be provided.
- References
- References The reference sequence that reads will be mapped to.
- Reference masking
- No masking Reads are mapped to the full reference sequence.
- Exclude annotated Reads are mapped to the full reference sequence except regions specified in the masking track.
- Include annotated only Reads are only mapped to the regions specified in the masking track.
- Masking track The track specifying the masking regions.
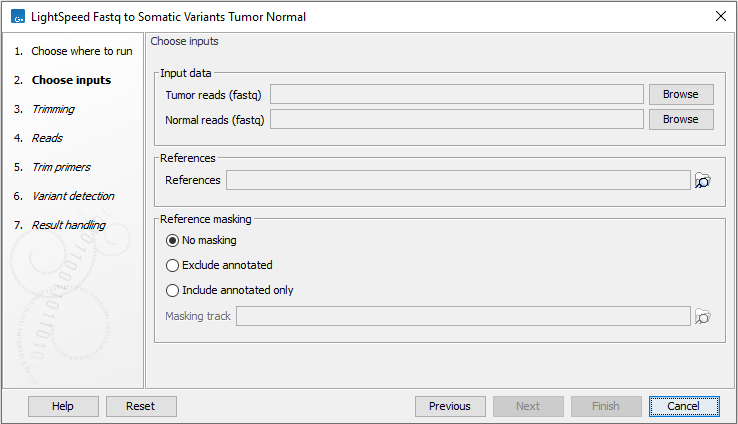
Figure 11.1: Input fastq files and references, and, optionally, a track for reference masking.
Next, options are available for trimming (figure 11.2):
- Quality trimming
- Quality trim Reads are trimmed for low quality nucleotides.
- Quality trim limit Adjust the quality trim limit for softer or harder trimming. Read more about the quality trim limit here: https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Quality_trimming.html.
- Minimum read length after quality trim Trimmed reads shorter than this length are removed.
- Only quality trim from 3' end When checked, only the 3' ends of reads are trimmed for low quality nucleotides. This option is recommended for analyses where deduplication is included, because deduplication relies on the 5' positions of R1 and R2.
- Adapter trimming
- Adapter trim Reads are trimmed for read-through adapter sequence.
- Minimum read length after adapter trim Trimmed reads shorter than this length are removed.
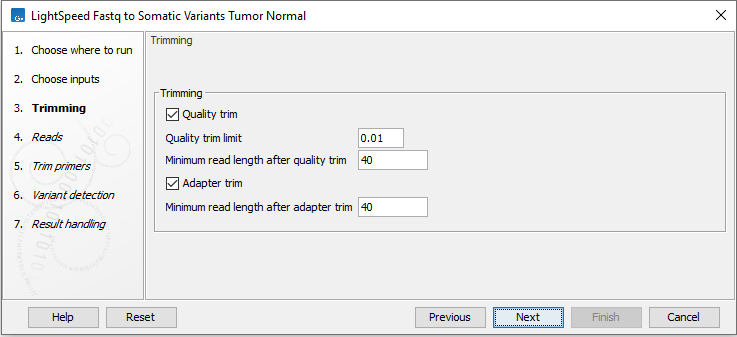
Figure 11.2: Options for trimming.
Next, options are available for UMI and duplicate reads (figure 11.3):
- UMI read structure
- UMI preset Specify where the UMI is placed in the reads. If a preset for a specific panel type is selected, the UMI and common sequence position and length are automatically adjusted to match the panel design.
- No UMI Select for reads that do not have UMIs.
- Custom Select to specify a protocol-specific read and UMI structure.
- QIAseq Targeted DNA Select if you are analyzing data from a QIAseq Targeted DNA panel.
- QIAseq Targeted DNA Pro Select if you are analyzing data from a QIAseq Targeted DNA Pro panel.
- QIAseq Multimodal DNA/RNA Library Kit Select if you are analyzing data generated with the QIAseq Multimodal DNA/RNA Library Kit.
- TSO500 Select if you are analyzing data from a TSO500 protocol utilizing duplex UMIs.
- Twist UMI Select if you are analyzing data from a Twist protocol utilizing duplex UMIs.
- Roche KAPA UMI Select if you are analyzing data from a KAPA protocol utilizing duplex UMIs.
- Agilent MBC Select if you are analyzing data from an Agilent protocol utilizing duplex UMIs.
- UMI length (Read 1) The number of nucleotides at the start of read 1 that are part of the UMI.
- Common sequence length (Read 1) The number of nucleotides between the UMI and the biological sequence in read 1. These nucleotides are discarded.
- UMI length (Read 2) The number of nucleotides at the start of read 2 that are part of the UMI.
- Common sequence length (Read 2) The number of nucleotides between the UMI and the biological sequence in read 2. These nucleotides are discarded.
- Calculate duplex consensus reads Check this option to collapse simplex UMI reads sharing a UMI and mapping position, that originate from different strands, to a duplex UMI read.
- UMI preset Specify where the UMI is placed in the reads. If a preset for a specific panel type is selected, the UMI and common sequence position and length are automatically adjusted to match the panel design.
- UMI settings
- Retrieve UMI from fastq header Check this option if the UMI sequence is present in the fastq file read headers instead of being part of the sequencing reads. UMI and common sequence lengths must be specified below when this option is used.
- Minimum UMI group size Only UMI groups consisting of at least this number of input read pairs will be merged to consensus UMI reads. UMI groups with fewer input read pairs than this number will be discarded. A UMI group is a group of input read pairs with the same UMI sequence that maps to the same genomic position.
- Minimum size of a big UMI group Define the number of read pairs required for a UMI group to be considered a big UMI group. When variants are called, they are annotated with the number of big UMI groups supporting them.
- Maximum UMI differences Add input read pairs to the same UMI group when their UMI sequence have at most this number of mismatches. If UMIs are present on both read 1 and read 2 (duplex), this threshold operates on the sum of mismatches from the two UMIs.
- UMI window size Add input read pairs to the same UMI group when they map to genomic positions at most this number of bases apart.
- Keep duplex consensus reads only For duplex UMI protocols, check this option if only duplex reads should be retained. Simplex reads will be discarded.
- Duplicate read handling
- Discard duplicate mapped reads Reads likely representing PCR duplicates are collapsed. This option is disabled when UMIs are used to group reads.
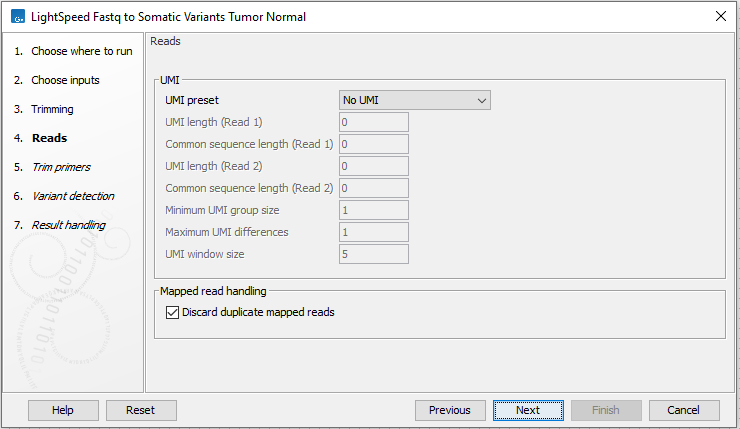
Figure 11.3: Options for UMI and duplicate reads.
Next options are available for removing ligation artifacts and for realignment (see (figure 11.4)):
- Mapped read handling
- Remove ligation artifacts When enabled, reads identified as ligation artifacts are removed from the mapping.
- Minimum mismatches The number of mismatches required between a read and the reference for a read to be considered a potential ligation artifact.
- Ligation artifact recognition length The length of the window where the number of mismatches defined under Minimum mismatches must be present in a read, for that read to be considered a potential ligation artifact.
- Allow mismatch Enable to allow a single mismatch when comparing the read sequence to nearby reference sequence.
- Optimize realignment for targeted data When enabled, realignment can process complex regions with high coverage that may be present in targeted data. Enabling can cause an increase in processing time, and is not recommended for WGS data.
- Remove ligation artifacts When enabled, reads identified as ligation artifacts are removed from the mapping.
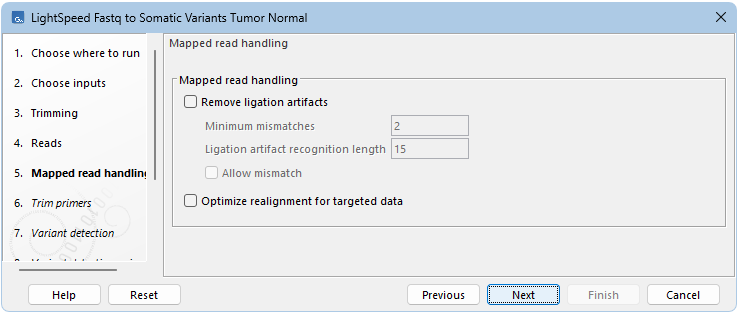
Figure 11.4: Options for removing ligation artifacts and for realignment.
Next, options are available for primer trimming (figure 11.5):
- Trim primers
- No primer trim Disable the trim primers step.
- Start of read 1 Primers are at the start of read 1.
- Start of read 2 Primers are at the start of read 2.
- Primers track Annotation track with location and strand of primers. Unalign parts of mapped reads that overlap a primer.
- Discard reads without primer Discard reads that do not overlap with a primer in the primers track.
- Minimum read length after primer trim Reads that are shorter than this number of nucleotides after primer trim are discarded.
- Additional bases to trim Unalign this number of additional mapped bases in reads matching a primer. Bases are unaligned at the beginning of the mapped read downstream from the primer.
- Minimum primer overlap (%) Reads overlap a primer when the expected part of the read (start of read 1 or read 2) maps to a genomic location that overlaps at least this percentage of a primer. Reads that do not meet the threshold are discarded.
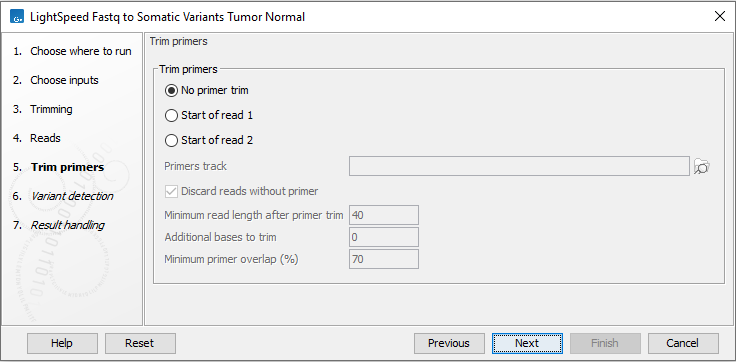
Figure 11.5: Options for primer trimming.
Next, options are available for variant detection (figure 11.6).
- Variant detection
- Restrict calling to target regions Optional: A track providing the regions to be inspected when calling variants. When no track is provided, all positions in the mapping are considered.
- Ignore non-specific matches When enabled, reads that map to more then one genomic position equally well are not considered when calling variants.
- Variant detection general filters, see figure 11.6
- Minimum frequency (%) Minimum frequency for detected variants.
- SNV minimum allele count Minimum allele count required for SNVs and MNVs to be called.
- SNV minimum per-strand allele count Minimum allele count required on each strand for SNVs and MNVs to be called.
- Indel minimum allele count Minimum allele count required for indels to be called.
- Indel minimum per-strand allele count Minimum allele count required on each strand for indels to be called.
- SNV significance threshold using global error rate p-value threshold for SNVs and MNVs. The p-value is calculated from a binomial test given count, coverage and an error rate of 0.005. Allowed range: 0 - 1.0.
- Indel significance threshold using global error rate p-value threshold for indels. The p-value is calculated from a binomial test given count, coverage and an error rate of 0.005. Allowed range: 0 - 1.0.
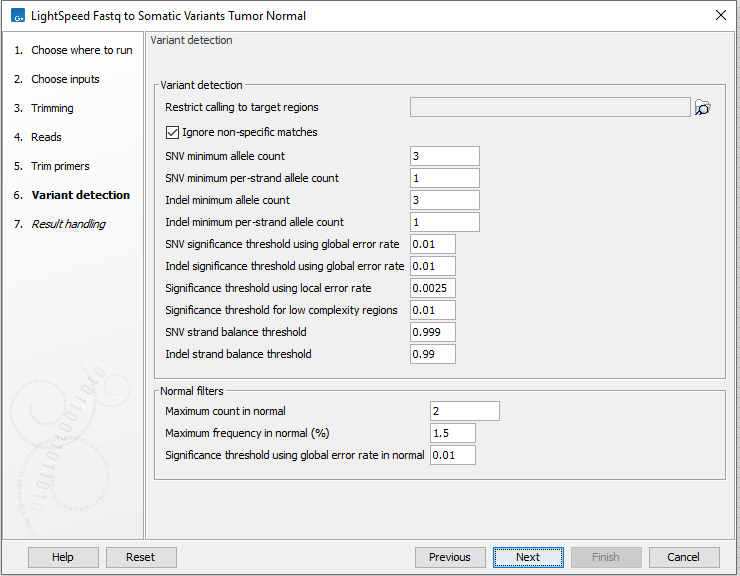
Figure 11.6: Options for variant detection.
Next, options are available for variant detection noise filters (figure 11.7).
- Variant detection noise filters
- SNV minimum average quality The minimum average quality of detected SNVs and MNVs.
- Indel minimum average quality The minimum average quality of detected indels.
- Significance threshold using local error rate p-value threshold for all variants. The p-value is the minimum p-value from two individual tests: 1. A binomial test given forward count, forward coverage and a local error rate for forward reads estimated from the data. 2. A binomial test given reverse count, reverse coverage and a local error rate for reverse reads estimated from the data. Allowed range: 0 - 0.1.
- SNV strand balance threshold Threshold for a strand balance score for SNVs and MNVs. The score is calculated as 1 - (p-value from binomial test given forward count, count, and forward count/coverage). Allowed range: 0.9 - 1.
- Indel strand balance threshold Threshold for a strand balance score for indels. The score is calculated as 1 - (p-value from binomial test given forward count, count, and forward count/coverage). Allowed range: 0.9 - 1.
- STR annotations and filter Annotate and filter variants that change the number of repeats in short tandem repeat (STR) regions, excluding homopolymers.
- Minimum repeat count The minimum number of repeats, excluding the variant, that an allele must have to be annotated as an STR variant. For example if a reference allele "AGAGAGAG" is called, and a low frequent stutter insertion allele is called "AGAGAGAGAG", the repeat count is 4.
- Minimum repeat region length The minimum length of all repeats combined, excluding the variant, that an allele must have to be annotated as an STR variant. For example if a reference allele "AGAGAGAG" is called, and a low frequent stutter insertion allele "AGAGAGAGAG" is called, the repeat region length is 8.
- Maximum repeat element length The maximum length of a repeat unit, that an allele can have to be annotated as an STR variant. For example, for the dinucleotide repeat "AGAGAGAG", the repeat unit length is 2.
- STR filter Enable to remove variants annotated as STR "Yes" from the results, provided that they are below the frequency threshold defined under "Remove STR variants with frequency below".
- Remove STR variants with frequency below Specify the frequency threshold below which STR variants will be removed from the results.
For the options under Variant detection general filters and Variant detection noise filters
- All of the options, except "SNV minimum allele count" and "Indel minimum allele count" only removes alleles with a frequency of less than 30%.
- For all of the options that include threshold in the name, lowering the value will reduce the number of called variants.
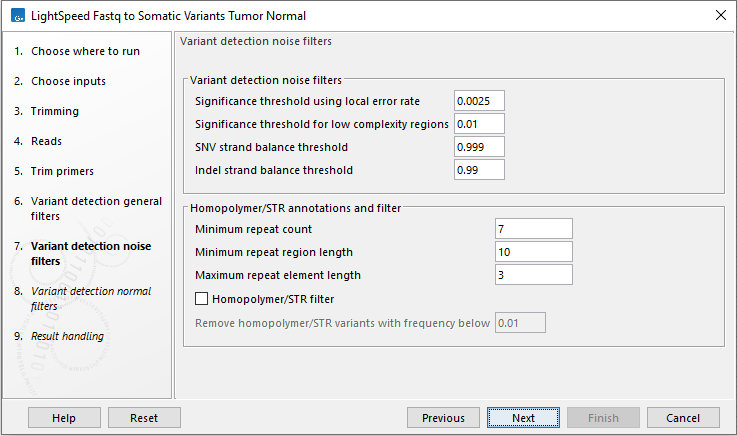
Figure 11.7: Options for variant detection noise filters.
In the following wizard step, specify the maximum variant count, frequency and significance in the normal read mapping (figure 11.8).
- Normal filters
- Maximum count in normal Somatic variants are not reported when the variant count in the normal is equal to or higher than this threshold.
- Maximum frequency in normal (%) Somatic variants are not reported when the variant frequency in the normal is equal to or higher than this threshold.
- Significance threshold using global error rate in normal Somatic variants are not reported when the variant p-value in the normal is lower than this threshold. Allowed range: 0 - 1.0.
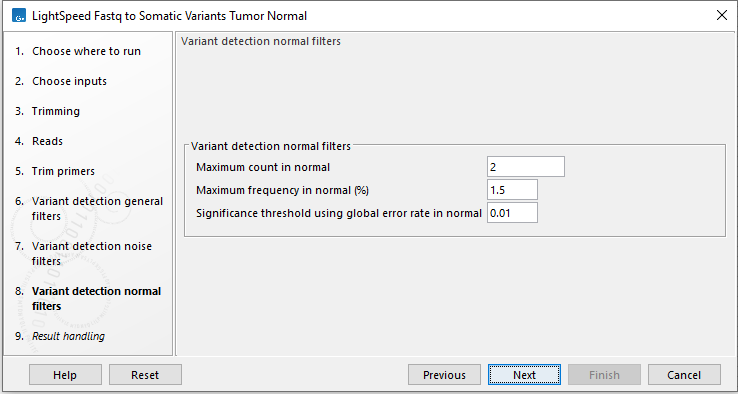
Figure 11.8: Options for variant detection normal filters.
In the final wizard step, choose which outputs should be generated and whether results should be saved or opened. If a reads track is selected as output, runtime will increase.
Subsections
