Batch processing
The tools LightSpeed Fastq to Germline Variants, LightSpeed Fastq to Somatic Variants, LightSpeed Fastq to Somatic Variants Tumor Normal, and LightSpeed Long Reads to Germline Variants (beta) have limited batch processing functionality.
For each of the four tools, batch processing is only possible when they are run as part of a workflow.
The sections below describe additional limitations that apply to each of the tools.
LightSpeed Fastq to Germline Variants and LightSpeed Fastq to Somatic Variants
When running the tools as part of a workflow, it is possible to batch over fastq files (figure 6.1), if not batching over other inputs to the LightSpeed tools. When batching over the fastq files, the names of the fastq files are used to determine which fastq files are analyzed together (see Default rules for determining pairs of files here https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Illumina.html).
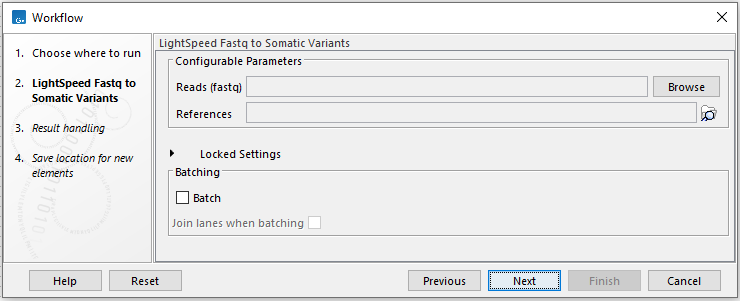
Figure 6.1: When running LightSpeed Fastq to Germline Variants or LightSpeed Fastq to Somatic Variants in a workflow, it is possible to batch over fastq files. Check "Batch" in the wizard step where "Reads (fastq)" files are selected.
When not batching over fastq files, it is possible to batch over the references, masking track, primers track and target regions tracks, when the tracks are added as input elements in a workflow (figure 6.2).
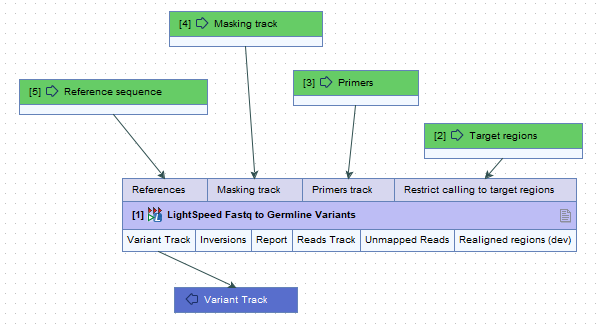
Figure 6.2: When running LightSpeed Fastq to Germline Variants and LightSpeed Fastq to Somatic Variants in a workflow, and not batching over fastq files, it is possible to batch over the inputs references, masking track, primers track and target regions when they are added as input elements in a workflow.
LightSpeed Fastq to Somatic Variants Tumor Normal
It is not possible to batch over fastq files, whereas batching over references, masking track, primers track and target regions tracks is possible when they are added as input elements in a workflow.
LightSpeed Long Reads to Germline Variants (beta)
When running the tool as part of a workflow, it is possible to batch over fastq files or unaligned bam files, if not batching over other inputs to the LightSpeed tool similar to LightSpeed Fastq to Germline Variants and LightSpeed Fastq to Somatic Variants.When not batching over fastq files or unaligned bam files, it is possible to batch over the references, masking track, and target regions tracks, when the tracks are added as input elements in a workflow.
