Sequence web info
CLC Main Workbench provides direct access to web-based search in various databases and on the Internet using your computer's default browser. You can look up a sequence in the databases of NCBI and UniProt, search for a sequence on the Internet using Google and search for Pubmed references at NCBI. This is useful for quickly obtaining updated and additional information about a sequence.
The functionality of these search functions depends on the information that the sequence contains. You can see this information by viewing the sequence as text (see View as text). In the following sections, we will explain this in further detail.
The procedure for searching is identical for all four search options (see also figure 10.5):
Open a sequence or a sequence list |
Right-click the name of the sequence | Web
Info (![]() ) | select the desired search function
) | select the desired search function
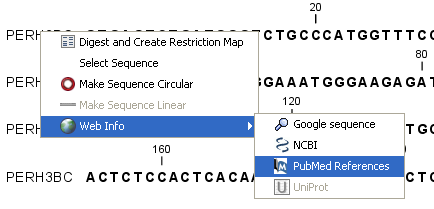
Figure 10.8: Open webpages with information about this sequence.
This will open your computer's default browser searching for the sequence that you selected.
Google sequence
The Google search function uses the accession number of the sequence which is used as search term on http://www.google.com. The resulting web page is equivalent to typing the accession number of the sequence into the search field on http://www.google.com.
NCBI
The NCBI search function searches in GenBank at NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) using an identification number (when you view the sequence as text it is the "GI" number). Therefore, the sequence file must contain this number in order to look it up at NCBI. All sequences downloaded from NCBI have this number.
PubMed References
The PubMed references search option lets you look up Pubmed articles based on references contained in the sequence file (when you view the sequence as text it contains a number of "PUBMED" lines). Not all sequence have these PubMed references, but in this case you will se a dialog and the browser will not open.
UniProt
The UniProt search function searches in the UniProt database (http://www.ebi.uniprot.org) using the accession number. Furthermore, it checks whether the sequence was indeed downloaded from UniProt.
Additional annotation information
When sequences are downloaded from GenBank they often link to additional information on taxonomy, conserved domains etc. If such information is available for a sequence it is possible to access additional accurate online information. If the db_xref identifier line is found as part of the annotation information in the downloaded GenBank file, it is possible to easily look up additional information on the NCBI web-site.
To access this feature, simply right click an annotation and see which databases are available. For tracks, these links are also available in the track table.
