Identify DNA Germline Variants workflow
When running an analysis to detect variants in DNA-seq data it is essential to include tools that allow detection of variants with high accuracy. Here we provide a basic workflow for identification of germline variants in DNA-seq data which includes the minimal number of tools that should be used for variant detection as well as a few tools to provide reports and visualization.Please note that the tools in this workflow have not been optimized for any specific application. It is recommended that samples with known variants are used to test the secondary analysis workflow to confirm that settings in the individual tools are appropriate.
The workflow must be configured with a reference sequence. When the workflow is started, any available reference can be chosen, including reference sequences in the reference data sets that are available for download under References (QIAGEN Sets). Alternatively, the reference sequence can be specified in a copy of the workflow. All species can be used as long as the reference sequence is available.
The tools and outputs provided by this workflow are:
- QC for Sequencing Reads performs basic QC on the sequencing reads and outputs a report that can be used to evaluate the quality of the sequencing reads. The tool can be configured to output the report directly, but in this workflow the report is instead included in a combined report together with other reports QC for Sequencing Reads.
- Trim Reads is used to trim reads for adapter sequences and low quality nucleotides. A trim report created by this tool is outputted as part of the combined report. It is important that Trim Reads is configured to trim reads correctly. The specific settings depend on the protocol used to generate the reads. Note that the workbench is able to trim automatically read-through adapters, but if you are not sure you have read-through reads, you will need to provide a Trim Adapter List. To learn how to create an adapter trim list, Trim adapter list. See NGS Trim Reads tool for more details about the Trim Reads tool.
- Map Reads to Reference maps reads to the provided reference sequence Map Reads to Reference.
- Indels and Structural Variants is used to predict InDels. Identified InDels are used to improve the read mapping during the realignment step in the workflow. The tool also outputs identified InDels in the track Indels-indirect_evidence which can be inspected if relevant. Note that with default settings of this tool, only reads with 3 or fewer mismatches to the reference are considered when the tool identifies potential breakpoints from unaligned ends. This may need to be adjusted if long and/or low quality reads are used as input. See InDels and Structural Variants for more information about InDels and Structural Variants.
- Local Realignment uses the predicted indels from Indels and Structural Variants to realign reads and hence improve the read mapping Local Realignment. The tool outputs the read mapping track Mapped_reads.
- Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection calls variants in the read mapping that are present at germline frequencies. In this workflow, the coverage threshold for variant detection has been set to 10, meaning that no variants will be called in regions where the coverage is below 10. Similarly, a frequency threshold of 20 percent has been defined. If variants should be called at lower frequencies or lower coverages, the thresholds must be adjusted. For more details about Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection see section Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection. See also the note about low frequency variant detection below.
- Remove Marginal Variants allows post-filtering of detected variants based on frequency, forward/reverse balance and minimum average base quality (see Remove Marginal Variants for further details). The tool outputs the final variant list Variants_passing_filters. Note that decreasing the thresholds in Remove Marginal Variants below the thresholds set in Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection will not result in detection of additional variants.
- Create Track List outputs the track list Genome_browser_view which contains the reference sequence, read mapping and identified variants (see Track lists as workflow outputs).
- Create Sample Report compiles reports from other tools and outputs the Combined_report. It is possible to set QC thresholds in the tool, which will trigger an additional section in the combined report showing whether QC thresholds were met (see Report types supported).
You find the workflow here:
Toolbox | Template Workflow | Basic Workflow Designs (![]() )
| Identify DNA Germline Variants (
)
| Identify DNA Germline Variants (![]() )
)
To run the workflow use the start button and follow the steps that are provided in the wizards.
- Select the reads and click Next.
- Select your reference data set or select "Use the default reference data" if you want to specify a reference in the next wizard step, see figure 12.47. Read more about creating reference data in Custom Sets.
- Specify how the reads should be trimmed.
- If the data is from a targeted sequencing experiment, you can choose restrict to InDels and Structural Variants to call variants in target regions by providing a target regions file, see figure 12.48.
- If the data is from a targeted sequencing experiment, you can choose restrict Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection to call variants in target regions by providing a target regions file and click Next.
- Specify threshold for filtering variants, see figure 12.49.
- Finally select a save location and press Finish.
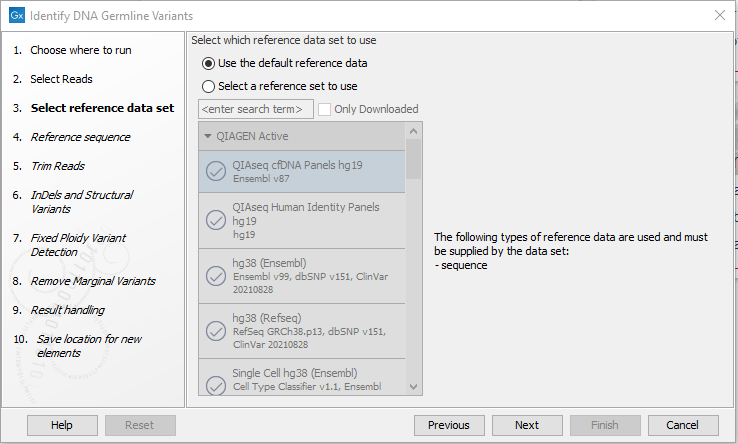
Figure 12.47: Wizard step for specifying reference data.
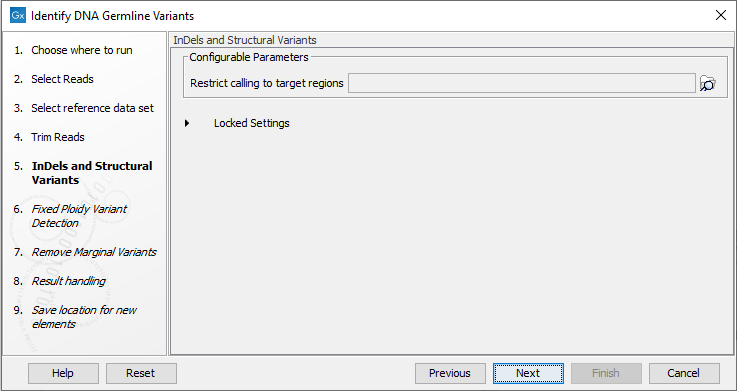
Figure 12.48: Optional wizard step for selecting a target region.
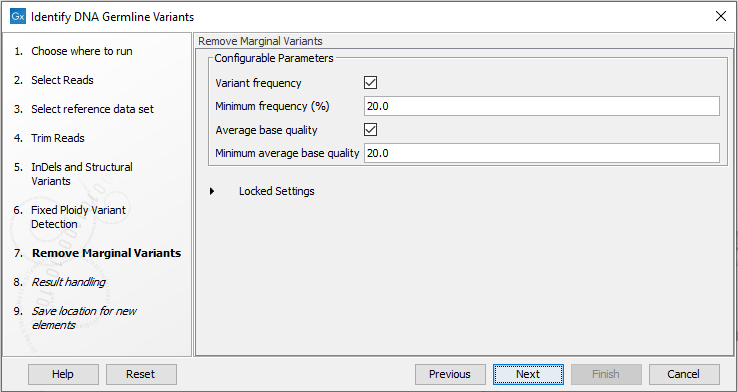
Figure 12.49: Wizard step for specifying variant filtering criteria.
Identify DNA Germline Variants represents the minimal number of tools that should be used for variant detection. Depending on the application, additional steps or alternative configurations may be helpful. To adapt the workflow, you must create your own copy of the workflow by right clicking on the workflow name and choosing Open Copy of Workflow. Read about creating and modifying workflows in Creating a workflow and the following sections.
- Low frequency variant detection If you want to detect low frequency variants, Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection should be replaced with Low Frequency Variant Detection (section Low Frequency Variant Detection).
- Targeted sequencing If a targeted protocol was used to generate the sequencing data, several of the tools can be configured to only analyze defined target regions. This typically reduces the runtime of the analysis significantly. The target regions can be configured in a copy of the workflow or can be selected in the wizard when the workflow is started. Also, it can be useful to incorporate the tool QC for Targeted Sequencing which outputs a report that for example includes the percentage of reads mapped in the target regions QC for Targeted Sequencing.
- PCR duplicates For protocols where PCR bias is expected, it can be useful to remove PCR duplicates from the read mapping. This can be achieved with the tool Remove Duplicate Mapped Reads (Algorithm details and parameters). For inspiration, take a look at the workflow Identify Variants (WES-HD) that is available when the Biomedical Genomics Analysis plugin is installed in the Genomics Workbench https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/biomedicalgenomicsanalysis/current/index.php?manual=Identify_Variants_WES_HD.html.
- Annotation of variants It is possible to annotate variants with different types of information such as which gene they occur in and whether the variant changes the coding sequence of a protein. For inspiration, see the workflow Annotate Variants (WGS) that is available when the Biomedical Genomics Analysis plugin is installed https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/biomedicalgenomicsanalysis/current/index.php?manual=Annotate_Variants_WES.html.
- Filtering of variants It is possible to filter variants by their annotations such as their quality and their position relative to a gene, see Variant filtering. In many of the template workflows in the Biomedical Genomics Analysis plugin, extensive filtering cascades have been set up in order to remove false positive variants from the final variant list. See for example the Identify QIAseq DNA Variants workflows https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/biomedicalgenomicsanalysis/current/index.php?manual=_Identify_QIAseq_DNA_Variants_ready_to_use_workflows.html.
- Other Template Workflows The plugins that can be installed in the QIAGEN CLC Genomics Workbench often contain additional workflow templates. For example, in the Biomedical Genomics Analysis plugin, a wealth of template workflows are available that can be used for different applications including whole exome sequencing (WES), whole genome sequencing (WGS) and targeted amplicon sequencing (TAS).
