Customized attributes on data locations
Location-specific attributes can be set on all elements stored in a given data location. Attributes could be things like company-specific information such as LIMS id, freezer position etc. Attributes are set using a CLC Workbench acting as a client to the CLC Server.
Note that the attributes scheme belongs to a particular data location, so if there are multiple data locations, each will have its own set of attributes.
To configure which fields that should be available3.1 go to the Workbench:
right-click the data location | Location | Attribute Manager
This will display the dialog shown in figure 3.13.
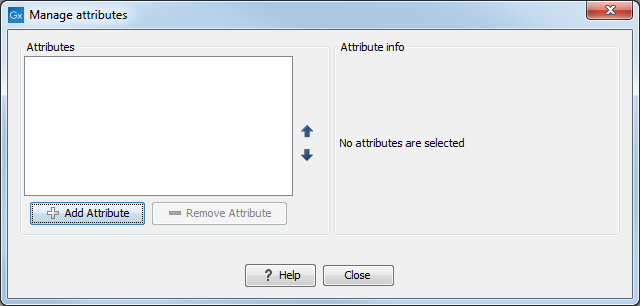
Figure 3.13: Adding attributes.
Click the Add Attribute (![]() ) button to create a new attribute. This will display the dialog shown in figure 3.14.
) button to create a new attribute. This will display the dialog shown in figure 3.14.
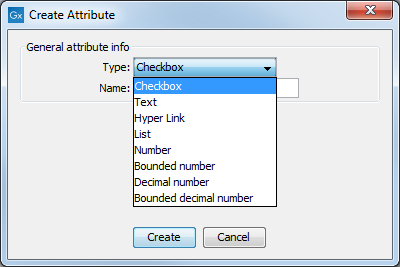
Figure 3.14: The list of attribute types.
First, select what kind of attribute you wish to create. This affects the type of information that can be entered by the end users, and it also affects the way the data can be searched. The following types are available:
- Checkbox. This is used for attributes that are binary (e.g. true/false, checked/unchecked and yes/no).
- Text. For simple text with no constraints on what can be entered.
- Hyper Link. This can be used if the attribute is a reference to a web page. A value of this type will appear to the end user as a hyper link that can be clicked. Note that this attribute can only contain one hyper link. If you need more, you will have to create additional attributes.
- List. Lets you define a list of items that can be selected (explained in further detail).
- Number. Any positive or negative integer.
- Bounded number. Same as number, but you can define the minimum and maximum values that should be accepted. If you designate some kind of ID to your sequences, you can use the bounded number to define that it should be at least 1 and max 99999 if that is the range of your IDs.
- Decimal number. Same as number, but it will also accept decimal numbers.
- Bounded decimal number. Same as bounded number, but it will also accept decimal numbers.
When you click OK, the attribute will appear in the list to the left. Clicking the attribute will allow you to see information on its type in the panel to the right.
Lists are a little special, since you have to define the items in the list. When you choose to add the list attribute in the left side of the dialog, you can define the items of the list in the panel to the right by clicking Add Item (![]() ) (see figure 3.15).
) (see figure 3.15).
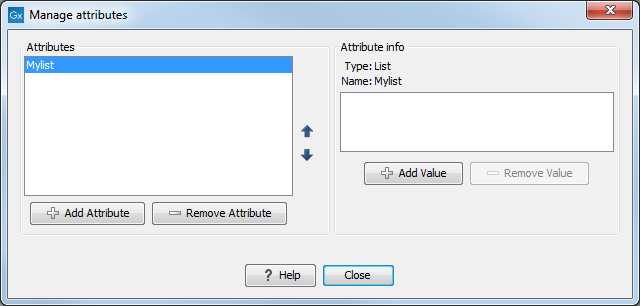
Figure 3.15: Defining items in a list.
Remove items in the list by pressing Remove Item (![]() ).
).
Removing attributes
To remove an attribute, select the attribute in the list and click Remove Attribute (If you accidentally removed an attribute and wish to restore it, this can be done by creating a new attribute of exactly the same name and type as the one you removed. All the "static" values will now become editable again.
When you remove an attribute, it will no longer be possible to search for it, even if there is "static" information on elements in the data location.
Renaming and changing the type of an attribute is not possible - you will have to create a new one.
Changing the order of the attributes
You can change the order of the attributes by selecting an attribute and click the Up and Down arrows in the dialog. This will affect the way the attributes are presented for the user.Footnotes
- ... available3.1
- If the data location is a server location, you need to be a server administrator to do this.
Subsections
