Table for Clonotypes
TCR clonotypes (- Clonotype #: A unique number identifying the clonotype.
- Chain:
Which chain type the clonotype belongs to: TRA (
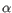 ), TRB (
), TRB (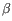 ), TRG (
), TRG (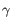 ) and TRD (
) and TRD (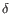 ) for TCR, or IGH (heavy), IGK (light
) for TCR, or IGH (heavy), IGK (light 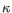 ), and IGL (light
), and IGL (light 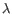 ) for BCR. Note that other light BCR chain types are currently not supported.
) for BCR. Note that other light BCR chain types are currently not supported.
- V, D, J and C: The identified V, D, J and C reference segment(s). If a single unambiguous V / D / J / C segment could not be identified, the segments will be listed separated by a comma.
- CDR3 nucleotide sequence: The nucleotide sequence for CDR3 including the V and J segment-encoded conserved amino acids.
- CDR3 amino acid sequence: The translated amino acid sequence for the CDR3 nucleotide sequence provided that it is in-frame.
- CDR3 length: The length of the CDR3 nucleotide sequence.
- Count: The number of times the specific clonotype was detected.
- Frequency (%): The count given as a percentage relative to the sum of all counts. Note that filtering can affect frequencies, see Filter Immune Repertoire.
- Productive:
One of three categories are used to characterize the CDR3 nucleotide sequences:
- Productive: sequences that are in frame and do not contain a premature stop codon;
- Out-of-frame: sequences that have a length that is not a multiple of three;
- Premature stop codon: sequences that are in-frame but contain a premature stop codon.
The clonotypes are sorted by count in decreasing order.
At the bottom of the table, a button labeled Create Clonotypes from Selection is available. Select the relevant rows in the table and click the button to create new TCR clonotypes (![]() ) or BCR clonotypes (
) or BCR clonotypes (![]() ) that only include the selected clonotypes. When the button is clicked, a dialog with the following options is shown:
) that only include the selected clonotypes. When the button is clicked, a dialog with the following options is shown:
- Recalculate frequencies. If ticked, frequencies in the output clonotypes are recalculated such that they add up to 100% across all chains. Otherwise, the original frequencies found in the input are used.
It can be useful to recalculate frequencies when removing noise (for example, removing clonotypes with a count of 1), but if a subset of clonotypes is created for the purpose of comparing clonotypes between samples, it might be more relevant to preserve the original frequencies.
- Set frequencies per chain. If ticked, the frequencies are recalculated to add up to 100% for each individual chain. This option is enabled only when Recalculate frequencies is ticked.
