Filter Immune Repertoire
The Filter Immune Repertoire tool can be used to restrict clonotypes to only a specific subset, for example, only productive clonotypes, or clonotypes with a specific chain. Alternatively, clonotypes can be filtered by creating a new element from a selection in the clonotypes table (Table for Clonotypes) or the clonotype sample comparison table (Table for Clonotype Sample Comparison).
To run Filter Immune Repertoire go to the Toolbox and select:
Toolbox | Biomedical Genomics Analysis (![]() ) | Immune Repertoire Analysis (
) | Immune Repertoire Analysis (![]() ) | Filter Immune Repertoire (
) | Filter Immune Repertoire (![]() )
)
This opens a dialog where a single TCR clonotypes (![]() ), BCR clonotypes (
), BCR clonotypes (![]() ), or Clonotype Sample Comparison (
), or Clonotype Sample Comparison (![]() ) element can be selected. The following filtering options can then be configured (see figures 7.9, 7.10, and 7.11). Note that the filters are applied independently.
) element can be selected. The following filtering options can then be configured (see figures 7.9, 7.10, and 7.11). Note that the filters are applied independently.
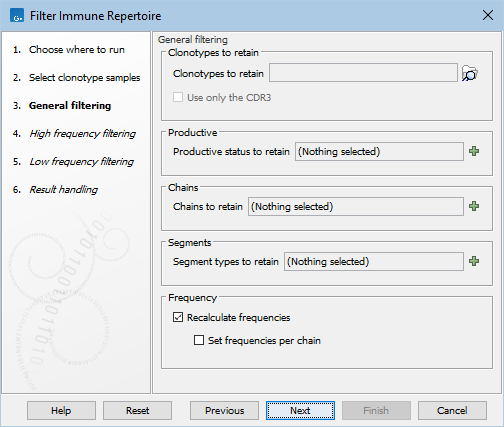
Figure 7.9: General filtering options for Filter Immune Repertoire.
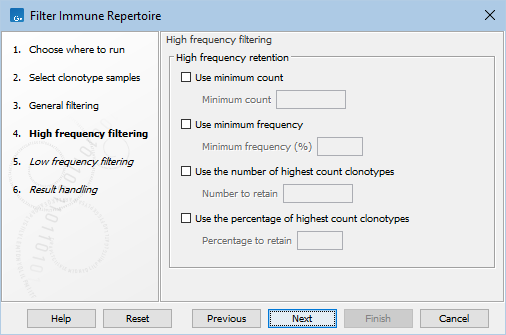
Figure 7.10: High frequency filtering options for Filter Immune Repertoire.
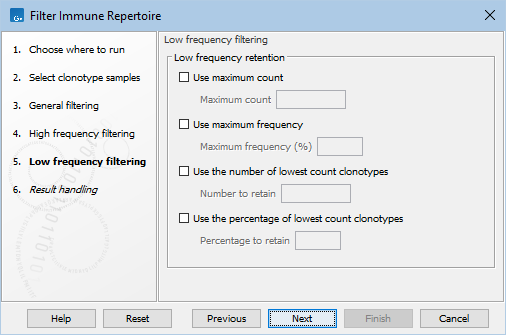
Figure 7.11: Low frequency filtering options for Filter Immune Repertoire.
- Clonotypes to retain. Retain clonotypes that are found in all provided TCR clonotypes (
 ), BCR clonotypes (
), BCR clonotypes ( ), or Clonotype Sample Comparison (
), or Clonotype Sample Comparison ( ) elements. If left empty, no filter is applied.
) elements. If left empty, no filter is applied.
- Use only the CDR3. When comparing the clonotypes in the input with those in the elements from Clonotypes to retain, only the CDR3 is used if this is ticked. Otherwise, the V and J segments together with the CDR3 are used to determine if two clonotypes are the same.
- Productive status to retain. A combination of 'Productive', 'Out of frame' and 'Premature stop codon' can be chosen and only the clonotypes with the respective productive status will be retained. If left empty, no filter is applied.
- Chains to retain. A combination of 'TRA', 'TRB', 'TRG' and 'TRD' for TCR data, or 'IGH', 'IGK' and 'IGL' for BCR data, can be chosen and only the clonotypes with the respective chains will be retained. If left empty, no filter is applied.
- Segment types to retain. A combination of 'V', 'D', 'J' and 'C' can be chosen and only the clonotypes that have identified segments for all respective segment types will be retained. This means that, for example, if 'D' is chosen, only chains for which the D segment is used will be retained, and for those chains, only the clonotypes for which the identification of the D segment was successful will be retained. If left empty, no filter is applied.
- Recalculate frequencies. If ticked, frequencies in the output clonotypes are recalculated such that they add up to 100% across all chains. Otherwise, the original frequencies found in the input are used.
It can be useful to recalculate frequencies when removing noise (for example, removing clonotypes with a count of 1), but if a subset of clonotypes is created for the purpose of comparing clonotypes between samples, it might be more relevant to preserve the original frequencies.
- Set frequencies per chain. If ticked, the frequencies are recalculated to add up to 100% for each individual chain. This option is enabled only when Recalculate frequencies is ticked.
- High frequency retention. The following filters for removing clonotypes with low frequencies can be enabled:
- Use minimum count. Retain clonotypes with a count greater than or equal to Minimum count.
- Use minimum frequency. Retain clonotypes with a frequency greater than or equal to Minimum frequency (%).
- Use the number of highest frequency clonotypes. Retain Number to retain clonotypes from each sample that have highest frequency.
- Use the percentage of highest frequency clonotypes. Retain Percentage to retain percentage of clonotypes from each sample that have highest frequency.
- Low frequency retention. These filters can be used to remove clonotypes that have high frequencies:
- Use maximum count. Retain clonotypes with a count less than or equal to Minimum count.
- Use maximum frequency. Retain clonotypes with a frequency less than or equal to Minimum frequency (%).
- Use the number of lowest frequency clonotypes. Retain Number to retain clonotypes from each sample that have lowest frequency.
- Use the percentage of lowest frequency clonotypes. Retain Percentage to retain percentage of clonotypes from each sample that have lowest frequency.
The tool outputs the filtered clonotypes and a report summarizing statistics of the filtered clonotypes. See Output from the Immune Repertoire Analysis for TCR clonotypes (![]() ) and BCR clonotypes (
) and BCR clonotypes (![]() ), or Output from Compare Immune Repertoires tool for Clonotype Sample Comparison (
), or Output from Compare Immune Repertoires tool for Clonotype Sample Comparison (![]() ).
).
