Remove Ligation Artifacts
During the adapter ligation step of the library preparation, it can happen that two different DNA sequences also get ligated together. These ligation artifacts are more prone to occur between short DNA fragments, such as the ones generated from FFPE samples. The tool Remove Ligation Artifacts removes reads which are likely the result of ligation artifacts. In addition, in cases of short fragments, a remnant of the common sequence can be found at the end of R1 reads. The tool will also remove these common sequence artifacts.
The tool can be found in the Toolbox here:
Toolbox | Biomedical Genomics Analysis (![]() ) | Biomedical Utility Tools (
) | Biomedical Utility Tools (![]() ) | Remove Ligation Artifacts (
) | Remove Ligation Artifacts (![]() )
)
In the first dialog (figure 6.8), select a read mapping (it can also be an rna-seq read mapping).
Figure 6.8: Select a read mapping.
In looking for ligation artifact, for each read:
- The tool looks at a window of a specific size (set by the option "Ligation artifact recognition length").
- The tool counts mismatches in the window. If there are less than 2 mismatches (value set by the "Minimum mismatches" parameter), the read is accepted. Note that any unaligned end counts as mismatches, i.e., if we have an unaligned end of size 3 that counts as 3 mismatches and the read will be subjected to the following steps.
- If there are at least 2 mismatches, the tool reverse complements the part of the read and tries to find a match within 250 bp on each side in the reference sequence.
- If a match is found, the read is deemed a ligation artifact and removed. It is possible to allow a single mismatch compared to the main sequence while still calling it a match ("Allow mismatch" under "Ligation artifacts").
- If the option "Remove entire Unique Molecular Index" is checked, all reads in a UMI group are removed if at least one ligation artifact read is found in the group.
In looking for common sequence artifact, for single reads and broken pairs:
- The tool looks at the 23 first and last bases (the window) in the read (defined by the "Full length common sequence search limit" parameter) and searches for the common sequence and the reverse complemented common sequence in the window. It is possible to allow a single mismatch between the common sequence and the read window and still call it a match (check "Allow mismatch" in the Common sequence artifacts section of the dialog).
- If no match is found, the tool searches for sub-strings down to a minimum of 4 bases ("Minimal partial common sequence length" parameter) on the read: When searching the first bases of a read, the tool checks if suffixes of the common sequence match the start of the read. When searching for the last bases of a read, the tool checks if prefixes of the common sequence match the end of the read. It is here again possible to allow a single SNP in the common sequence sub-string and the read and still call them a match.
- The tool then counts mismatches in the window (the window is from the match (including the common sequence) out to the end of the read). If the percentage of mismatches in the window is less than 50% (defined by the "Minimum mismatch percentage" parameter), the read is accepted.
- If there are more than 50% mismatches in the window, the read is trimmed from the bases in the read in the window. Both unaligned and aligned bases will be removed. If there are no aligned bases left after trimming, the read is removed.
In looking for common sequence artifact for paired reads, the tool will trim the overhang of the read that extends further than the beginning of the paired read carrying the UMI.
The setting options for the Remove Ligation Artifacts tools are as follow (figure 6.9).
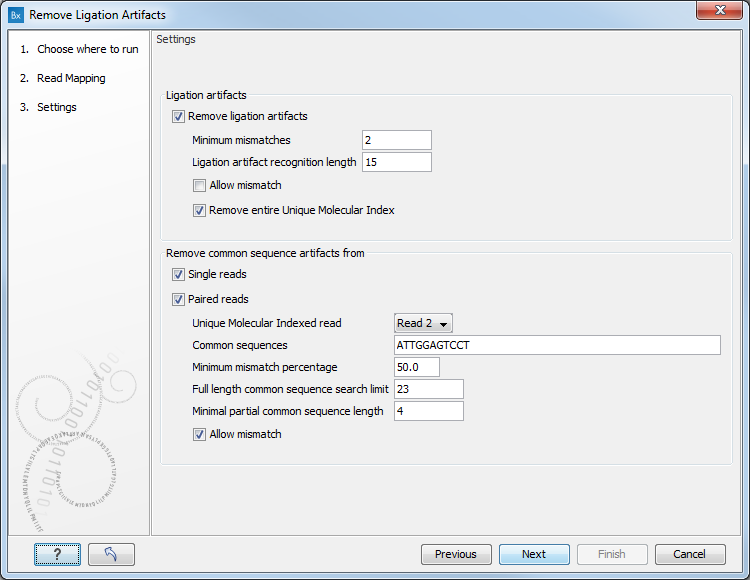
Figure 6.9: Set the parameters for the remove Ligation Artifacts tool.
- Ligation artifacts
- Remove ligation artifacts: uncheck this option to keep ligation artifacts in your data.
- Minimum mismatches: define the thresholds of mismatching characterizing a potential ligation artifact.
- Ligation artifact recognition length: defines the size of the window being searched for mismatches.
- Allow mismatch: checking this option will allow a single mismatch between the sequence window and the main sequence while still calling it a match.
- Remove entire Unique Molecular Index: remove all reads in a UMI group if at least one ligation artifact read is found in the group.
- Remove common sequence artifacts from
- Single reads
- Paired reads
- Unique Molecular Indexed read: can be set to Read 1 or Read 2 if you wish to restrict the removal of the common sequence artifacts to only one read in the pair.
- Common sequences defined by the QIAseq DNA Panel kit. It can be one or several sequences separated by commas.
- Minimum mismatches percentage: defines the thresholds of mismatching characterizing a potential common sequence artifact.
- Full length common sequence search limit: size of the sequence window in which the tool will search for the common sequence.
- Minimal partial common sequence length: size of a sub-string to look for matches between the beginning and the end of a read and the common sequence.
- Allow mismatch: allows a single mismatch between the sequence window and the read sequence while still calling it a match.
Click Next to choose to Open or Save the tool output, i.e., the read mapping where the ligation and sequences artifacts have been removed. It is also possible to generate a read mapping containing the ligation artifacts, and a report.
This report can be used together with the Combine Reports tool (see http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Combine_Reports.html)
