Refine Read Mapping
Different sequencing technologies have different advantages and disadvantages and this is also the case when it comes to accuracy. The tool Refine Read Mapping can remove problematic mapped reads with many mismatches in close proximity and mapped reads with an unaligned end of a certain length. Removal of these types of mapped reads can minimize the number of potential false positive variants being reported. Note: The tool considers single end mapped reads. When analyzing paired end mapped reads the tool considers each mapped read in the pair separately.
The tool can be found in the Toolbox here:
Toolbox | Resequencing Analysis (![]() ) | Refine Read Mapping (
) | Refine Read Mapping (![]() )
)
In the first dialog (figure 11.12), select a read mapping.
Figure 11.12: Select a read mapping.
In the second dialog (figure 11.13) the following parameters can be specified:
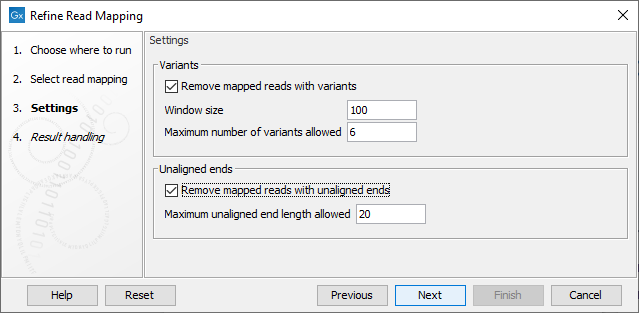
Figure 11.13: Specify the settings for when to remove mapped reads with variants and when to remove mapped reads with unaligned ends.
- Variants
- Remove mapped reads with variants: When enabled, the Window size and Maximum variants can be specified.
- Window size: The length of a region to be considered when counting the number of allowed variants specified under Maximum variants.
- Maximum number of variants allowed: A mapped read with this number of variants found within a stretch of nucleotides of the length specified under Window size will be removed. Insertions, deletions, SNVs and MNVs each count as one variant. As the tool works on single end mapped reads, both mapped reads in a pair will be removed if this number of variants are found in any of the two single end mapped reads making up the pair.
- Unaligned ends
- Remove mapped reads with unaligned ends: When enabled, the Maximum unaligned end length can be specified.
- Maximum unaligned end length allowed: The maximum allowed number of nucleotides that are unaligned in a mapped read. If the number of unaligned nucleotides in a mapped read exceeds the specified Maximum unaligned end length, the mapped read is removed. A paired mapped read is removed if any of the two single end mapped reads making up the pair has an unaligned end longer than the specified maximum number of unaligned bases.
An example of a read mapping before and after using the Refine Read Mapping is shown in figure 11.14. In this example the mapped reads contain sequencing artifacts that can result in potential false positive calls.
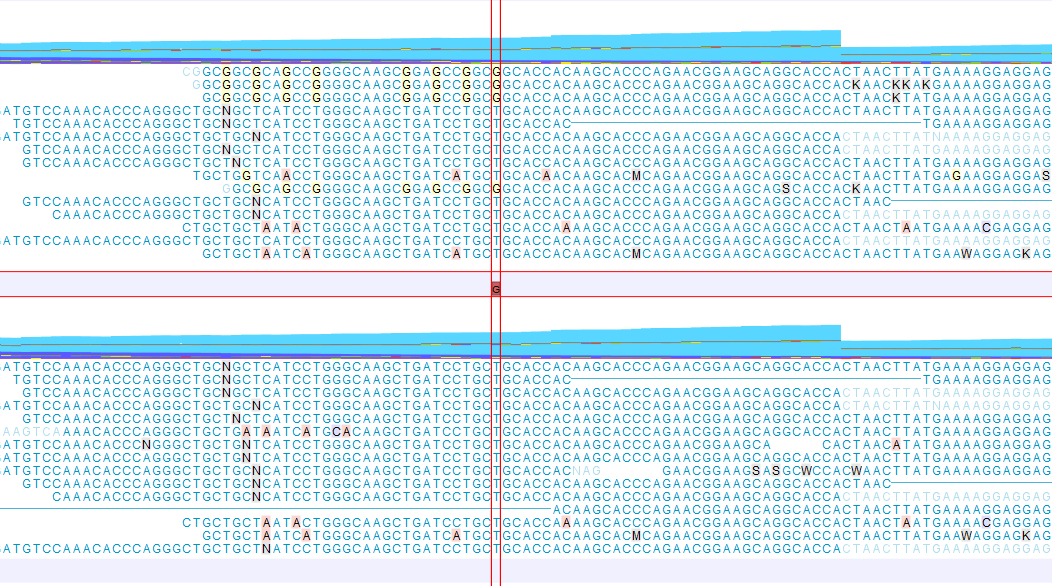
Figure 11.14: A read mapping before (top) and after (bottom) using the tool Refine Read Mapping on the read mapping using default settings for Variants of Window size = 100 and Maximum variants = 6. A false positive variant was reported for one of the G positions before using the tool Refine Read Mapping. The variant is not reported after the mapped reads containing the G artifacts have been removed.
The data used in this example are from a patient sample that were sequenced twice using two different sequencing technologies. Only one sequencing technology had problems with the G pattern shown in figure 11.14.
