QC, Assemble and Bin Pangenomes
This workflow guides the investigator through the key steps to analyze whole-genome shotgun metagenomic reads and deconstruct them into clusters of sequences (bins) using the tools Bin Pangenomes by Taxonomy and Bin Pangenomes by Sequence. The inputs to the workflow are short reads belonging to a single metagenome sample (also split in multiple sequence objects). The outputs are two sequence lists objects: one for reads and one for assembled contigs, labelled for bin association. Reports are also output at each step.
To run the workflow, go to:
Toolbox | Template Workflows (![]() ) | Microbial Workflows (
) | Microbial Workflows (![]() ) | Metagenomics (
) | Metagenomics (![]() ) | Taxonomic Analysis (
) | Taxonomic Analysis (![]() ) | QC, Assemble and Bin Pangenomes (
) | QC, Assemble and Bin Pangenomes (![]() )
)
In the first step, one or more reads sequence objects are selected (figure 3.19).
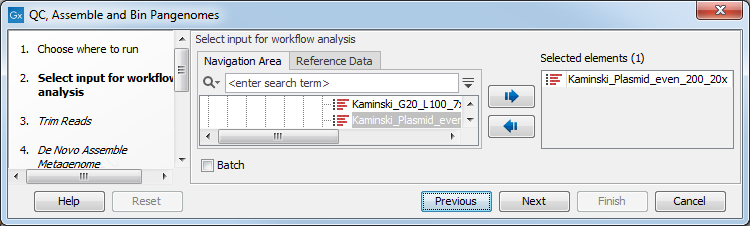
Figure 3.19: Select the reads.
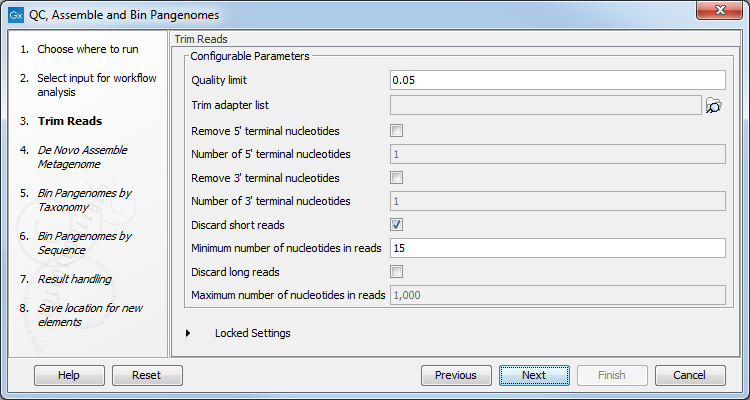
The workflow first performs QC of raw reads using basic quality-based trimming, but fixed-length trimming can also be added. In the "Trim Reads" dialog, you can specify a trim adapter list and set up parameters if you would like to trim your sequences from adapters. Specifying a trim adapter list is optional but recommended to ensure the highest quality data for your typing analysis (figure 3.20).
In the next step, QC-processed reads are assembled in contigs using the De novo Assemble Metagenome tool. Specify minimum contig length, the type of de novo assembly you wish to perform (fast, or optimized for longer contigs), and whether you wish to perform scaffolding (figure 3.21).
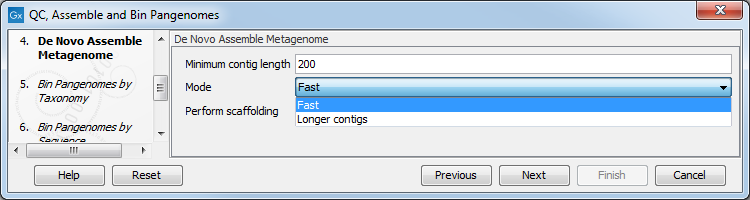
Figure 3.21: Parameters for the De Novo Assembly Metagenome tool.
Reads and contigs are then first binned according to taxonomic association and then based on sequence similarity. The tool is designed to work on contigs assembled from the same set of reads used as input (as in the workflow, see QC, Assemble and Bin Pangenomes). The tool will use the result of the De novo assembly configured here, but you can set the minimum contig length needed in the next dialog (figure 3.22).
As reference databases, one or two Taxonomic Profiling index files can be provided:
- the file provided as "Reference indexes" is used to find taxonomic information for the reads
- the file provided as "Plasmid reference index" (once the "Find plasmid information option is checked) is used to distinguish genomic reads from plasmid reads.
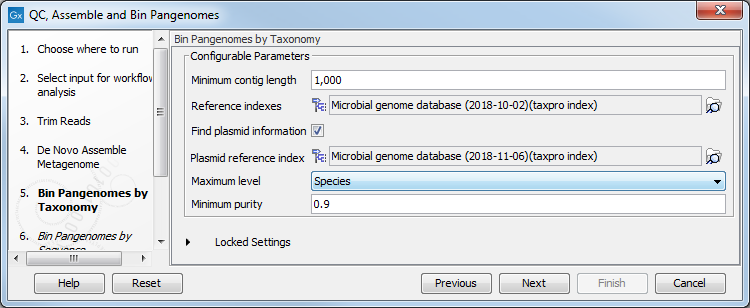
Figure 3.22: Select the references and configure the Bin Pangenomes by Taxonomy.
Depending on the dataset, it may be necessary to adapt the contig purity settings, where "Maximum level" refers to a maximum level in the taxonomic tree and where a specific "Minimum purity" per contig needs to be reached in order for it to be considered a part of a bin. For example, if Maximum level = Genus and Minimum purity = 0.8 and 512 reads map to a given contig, at least 0.8 * 512 = 410 reads need to have the same Genus level taxonomy in order for the contig to become part of the respective bin. If more precise taxonomic information is available (e.g., on Species level) with the requested minimum purity, this information will be used instead.
In the next dialog (figure 3.23), configure the parameters for the Bin Pangenomes by Sequence: once again you can set the minimum contig length of the contigs generated by the De Novo Assembly Metagenome tool. You can also choose the maximum of iterations that should be performed, and how to label singletons (bins with only one genome).
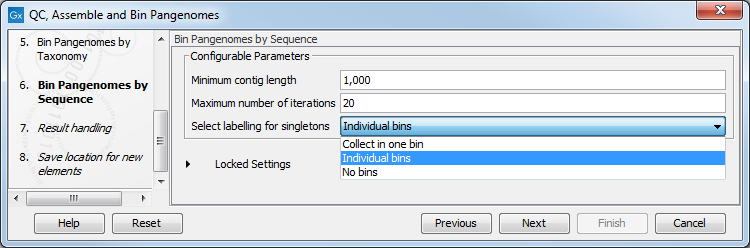
Figure 3.23: Configure the Bin Pangenomes by Sequence.
The tool will produce the following outputs:
- QC graphic report and QC supplementary report. For a detailed description of the QC reports and indication on how to interpret the different values, see http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=QC_Sequencing_Reads.html.
- An assembly summary report (see
http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=De_novo_assembly_report.html.
- A Bin Pangenomes by Taxonomy report (figure 3.24). Sequences with the same TaxBin label should have very similar, if not identical, taxonomy.
- A Bin Pangenomes by Sequence (figure 3.25). Sequences with same Bin label are closely related in sequence space.
- A list of reads, and a list of contigs, listing binned (and unbinned) reads and contigs from both binning steps.
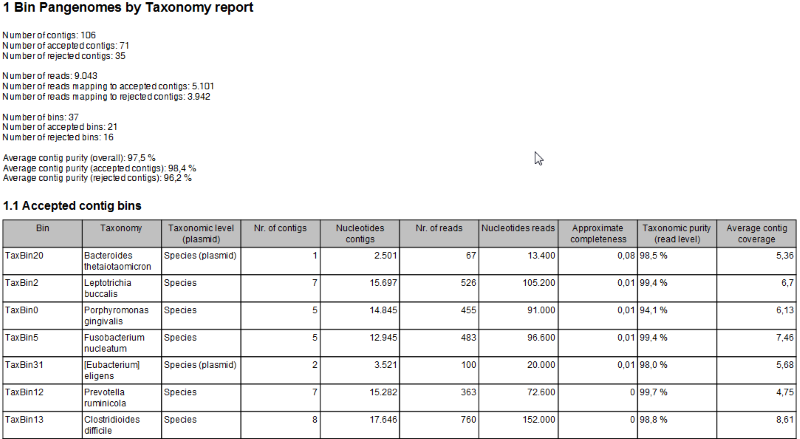
Figure 3.24: The Bin Pangenomes by Taxonomy report. Sequences with the same TaxBin label should have very similar, if not identical, taxonomy.
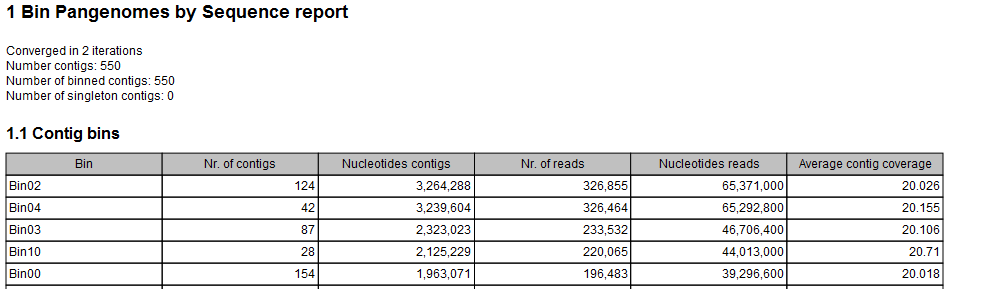
Figure 3.25: The Bin Pangenomes by Sequence report. Sequences with same Bin label are closely related in sequence space.
Individual bins can be extracted from the sequence and contig lists (when seen as tables, you can find the bin label inthe Assembly_ID column) and used for downstream analysis such as reference-based assembly (or re-assembly), functional analysis, typing etc.