Create K-mer Tree
The Create K-mer Tree tool may be helpful for identification of the closest common reference across samples. The tool uses reads, single sequences or sequence list as input and creates a distance-based phylogenetic tree. If a sequence list has a read-group it will be treated as a set of reads, otherwise the tool will group the sequences in a sequence list based on their "Assembly ID" annotation or treat the sequences individually when no "Assembly ID" annotation has been assigned. To find out how to assign Assembly ID annotation, please see Using the Assembly ID annotation. There are two ways to initiate creation of a k-mer tree: either from the Result Metadata Table (see the section on Running analysis directly from the Result Metadata Table), or from the Toolbox.
To run the Create K-mer Tree from the toolbox:
Toolbox | Microbial Genomics Module (![]() ) | Typing and Epidemiology (
) | Typing and Epidemiology (![]() ) | Create K-mer Tree (
) | Create K-mer Tree (![]() )
)
Input files can be specified step-by-step like shown in figure 11.15 or by selecting data recursively by right-clicking on the folder name and selecting Add folder contents (recursively). If using the recursive option, remember to double check that files relevant for the downstream analysis are selected.
Figure 11.15: Selection of individual reads and single sequences or sequence list to be included in the K-mer tree analysis.
Specify the following parameters (figure 11.16):
- K-mer parameters
- K-mer length is the fixed number (k) of DNA bases to search across.
- Only index k-mers with prefix allows specification of the initial bases of the k-mer sequence to limit the search space. Reduction of prefix size increases the RAM requirements, and therefore decrease the search speed.
- Method may be specified by either of the two statistical methods: Jaccard Distance or Feature Frequency Profile via Jensen-Shannon divergences (FFP). You can read more about the Jaccard Distance and FFP at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jaccard_index and https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alignment-free_sequence_analysis, respectively.
- Strand may be specified as either only the Plus strand or Both strands.
- Result metadata. Specify location of the Result metadata table file.
- Tree view. Select a standard tree setting (i.e., None, K-mer Tree Default or SNP Tree Default) or your own custom tree setting. Read more on creating your customized tree settings: http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Tree_Settings.html.
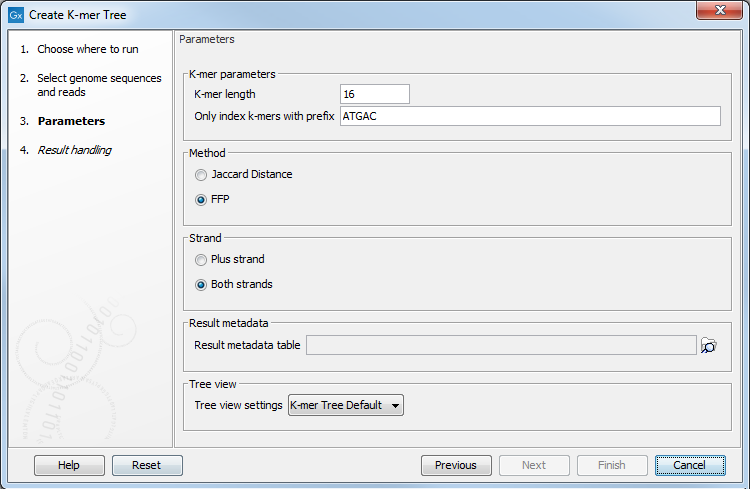
Figure 11.16: Various parameters may be set before generation of a K-mer tree.
The K-mer trees are constructed using a Neighbour Joining method, which makes use of a distance function, either Jaccard Distance or Feature Frequency Profile via Jensen-Shannon divergences (FFP). In both cases, the distance can assume values between 0 (exactly same k-mer distribution) and 1 (completely different k-mer distribution).
Branch lengths depend on the distance function used. Specifically, if one sums up all the branch length of all the branches connecting two leaves, one can get the distance between the two organisms the leaves represent.
Subsections
