Annotate CDS with Best DIAMOND Hit
The Annotate CDS with Best DIAMOND Hit tool will allow you to annotate a set of contigs containing CDS annotations with their best DIAMOND hit. This tool is particularly useful for large data sets, as an alternative to Annotate CDS with Best BLAST Hit.
DIAMOND is a sequence aligner for protein and translated DNA searches, designed for high performance analysis of big sequence data. The key features are:
- Pairwise alignment of proteins and translated DNA at 500x-20,000x speed of BLAST.
- Frameshift alignments for long read analysis.
- Low resource requirements and suitable for running on standard desktops or laptops.
The version of the DIAMOND binaries bundled with the tool is v0.9.26.127. For questions or comments about DIAMOND, see https://github.com/bbuchfink/diamond.
To start the tool, go to:
Toolbox | Microbial Genomics Module (![]() ) | Functional Analysis (
) | Functional Analysis (![]() ) | Annotate CDS with Best DIAMOND Hit (
) | Annotate CDS with Best DIAMOND Hit (![]() )
)
Several parameters are available (figure 13.9):
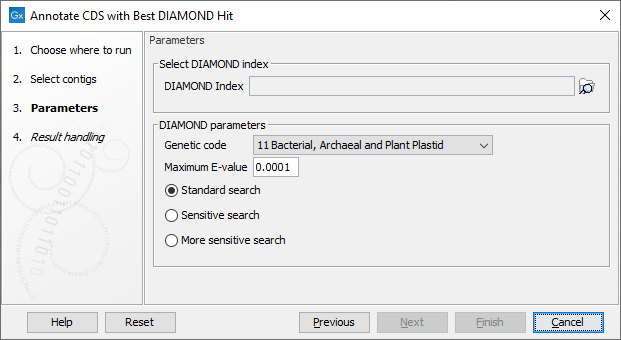
Figure 13.9: BLAST Best Hit annotations added to gene cds4 of h. pylori.
- Genetic code parameters. The genetic code used for translating CDS to proteins.
- DIAMOND parameters.
- Maximum E-value. Maximum expectation value (E-value) threshold for saving hits.
- DIAMOND Index. Select the relevant indexes. Indexes are generated by 1/ downloading a database with the Download Protein Database tool (section Download Protein Database) and 2/ building the index using the Create DIAMOND Index tool (see section Create DIAMOND Index).
- Standard search, mainly designed for short reads alignments, i.e., for finding significant matches of >50 bits on 30-40aa fragments.
- Sensitive search, for longer sequences.
- More sensitive search, where results in DIAMOND come close to the quality of BLAST searches.
The tool will output a copy of the input file with the DIAMOND Hit annotations. The tool can also output an annotation table summarizing information about the annotations added to the sequence list. Finally it is possible to generate a report containing information about the input file, the DIAMOND database and the amount of CDS annotated with a DIAMOND hit.
If a DIAMOND index was created from a protein sequence list containing metadata (such as GO terms or taxonomy information), the original metadata will be transferred to the annotations created by this tool.
