Find QIAseq xHYB AMR Markers
The Find QIAseq xHYB AMR Markers template workflow trims reads and detects antimicrobial resistance (AMR) markers.
It is suitable for data generated with the QIAseq xHYB AMR Panel.
QIAGEN reference data set
The QIAseq xHYB AMR Panel reference data set is available from QIAGEN Sets Reference Data Library accessible via References (![]() ) in the top Toolbar.
) in the top Toolbar.
Launching the workflow
The QIAseq xHYB AMR Markers workflow is at:
Toolbox | Template Workflows (![]() ) | Microbial Workflows (
) | Microbial Workflows (![]() ) | QIAseq Analysis (
) | QIAseq Analysis (![]() ) | Find QIAseq xHYB AMR Markers (
) | Find QIAseq xHYB AMR Markers (![]() )
)
Launch the workflow and step through the wizard.
- Select the sequence list(s) containing the reads to analyze and click on Next.
- Select a reference data set or select "Use the default reference data" to configure the reference data elements individually in subsequent wizard steps (figure 3.86). Click on Next.
- Choose whether batch units should be defined based on organization of the input data, or by provided metadata (figure 3.87). For information on how to use metadata when running part of a workflow multiple times, see http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Running_part_workflow_multiple_times.html.
- Next, you can review the batch units resulting from your selections above. Click on Next.
- Verify or select the reference marker database (figure 3.88). Click on Next.
- Verify or select control genes (figure 3.89). Click on Next.
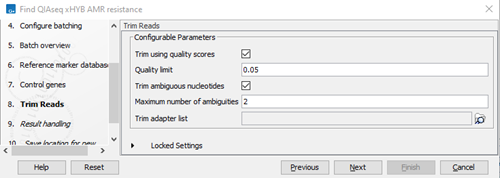
- Specify the trim settings (figure 3.90) and click on Next.
- Finally, select a location to save outputs to and click on Finish.
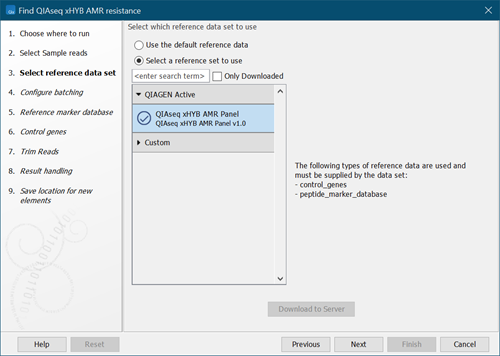
Figure 3.86:
Select reference data set.
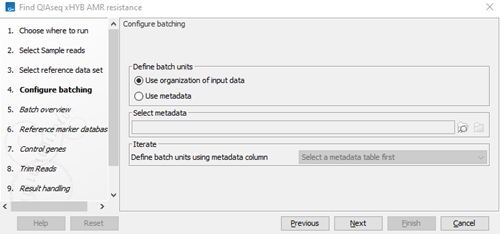
Figure 3.87:
Define batch units.
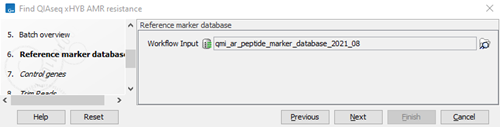
Figure 3.88:
Select the reference marker database.
Figure 3.89:
Select control genes.
Tools in the workflow and outputs generated
The workflow Find QIAseq xHYB AMR Resistance consists of the below mentioned tools. See figure 3.91 for a full overview of the workflow.
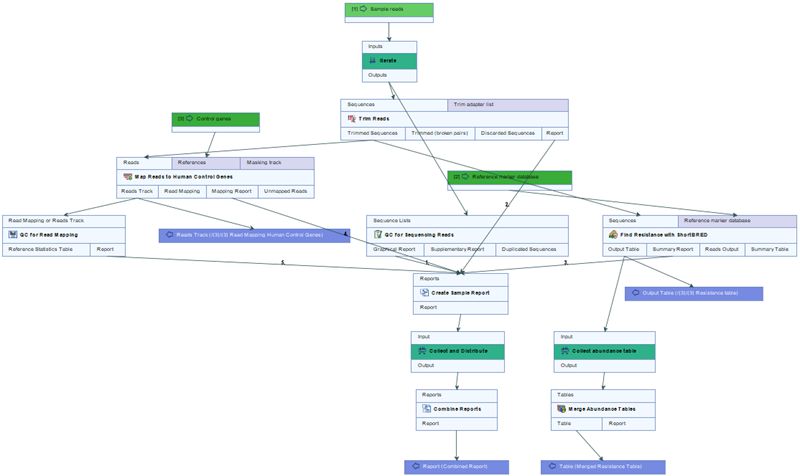
Figure 3.91:
Layout of the QIAseq xHYB AMR Markers workflow.
The tools included in the workflow are:
- QC for Sequencing Reads performs basic QC on the sequencing reads. The output, which here is included in a combined report, can be used to evaluate the quality of the sequencing reads. See http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=QC_Sequencing_Reads.html.
- Trim Reads removes adapter sequences and low quality nucleotides. The appropriate settings for the Trim Reads tool depends on the protocol used to generate the reads.
See http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Trim_Reads.html.
- Map Reads to Human Control Genes maps the input reads to a reference of human control genes. See http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Map_Reads_Reference.html.
- QC for Read Mapping performs QC of the read mapping. See http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=QC_Read_Mapping.html.
Together, Map Reads to Human Control Genes and QC for Read Mapping serve to verify mapping to the human control genes.
- Find Resistance with ShortBRED detects and quantifies the presence of antimicrobial resistance marker genes of interest. See Find Resistance with ShortBRED.
- Merge Abundance Tables merges the sample-specific abundance tables to one combined abundance table. See Merge Abundance Tables.
The outputs provided by this workflow are:
- Resistance table is the result table from Find Resistance with ShortBRED. The sample-specific output provides the abundance of each detected AMR marker. See Resistance abundance table.
- Read Mapping Human Control Genes is a sample-specific reads track containing the reads that mapped to the human control genes.
- Combined Report contains information on the results from the individual tools for all the samples included in the workflow run.
- Merged Resistance Table provides the abundances of the detected AMR marker across samples. See Resistance abundance table.