Convert Metadata to Cell Annotations
Metadata is often present at both the sample and cell level. However, it is always possible to convert sample level metadata into cell level metadata. For example, the knowledge that a sample comes from `Lab A' can be captured by annotating the entire sample with `Lab A', or alternatively by annotating all the cells in the sample with `Lab A'.For simplicity, most tools in the CLC Single Cell Analysis Module only accept cell level metadata. Convert Metadata to Cell Annotations is provided to easily transform sample level metadata in the form of Metadata Tables (see http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Metadata.html for more details) into cell level metadata in the form of Cell Annotations. Convert Metadata to Cell Annotations can be found in the Toolbox here:
Utility Tools (![]() ) | Convert Metadata to Cell Annotations (
) | Convert Metadata to Cell Annotations (![]() )
)
The tool can take an Expression Matrix (![]() ) / (
) / (![]() ), Velocity Matrix (
), Velocity Matrix (![]() ), or Peak Count Matrix (
), or Peak Count Matrix (![]() ) as input and produces a single Cell Annotations (
) as input and produces a single Cell Annotations (![]() ) element. An example of this process is shown in figure 14.1.
) element. An example of this process is shown in figure 14.1.
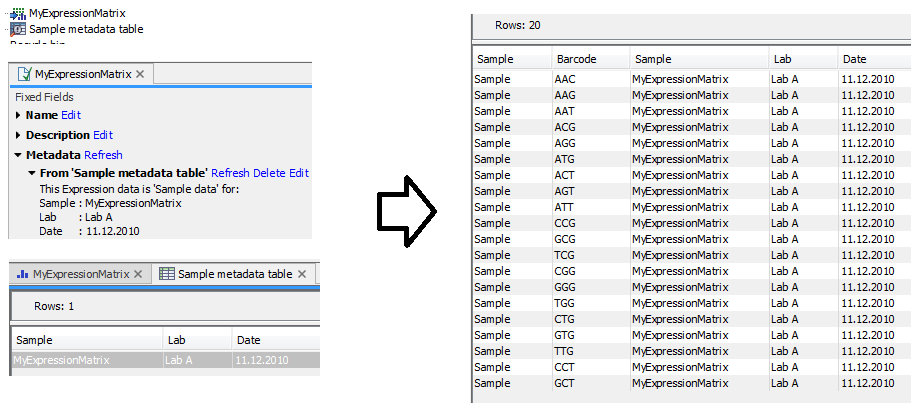
Figure 14.1: A Metadata Table (left) annotates a sample as being produced by `Lab A' on `11.12.2010'. Convert Metadata to Cell Annotations converts this metadata into Cell Annotations (right) where each cell in the sample is annotated with the same information.
The tool does not require the sample level metadata to be explicitly provided. Instead:
- In a workflow
- the sample level metadata is taken from a Metadata Table provided to the workflow, if present.
- Otherwise
- the sample level metadata is collated from all the Metadata Tables that reference the input Expression Matrix. If multiple such tables exist, their annotations are combined. If the annotations are in conflict, for example one table says the sample has `Lab = Lab A' and another says `Lab = Lab B', then the Lab will be missing (and hence unknown) in the combined table. Note that after connecting to a CLC Server, additional metadata tables, only present on the server, may be found by the tool.
