Copy Number Variant Detection (WGS) (beta)
The Copy Number Variant Detection (WGS) (beta) tool is designed to identify copy number variants (CNVs) from whole genome sequencing (WGS) data including low-pass WGS data.
The tool takes a read mapping as input and is designed to not rely on control samples. This is achieved by estimating the expected coverage for diploid regions via the following steps:
- The mean and standard deviation for the coverage is calculated for each chromosome. Only coverage values between the 10th and 90th percentile are included.
- Chromosomes are clustered based on their mean and standard deviation for the coverage.
- The cluster with the greatest density and highest number of chromosomes is selected using a weighted density value.
- Finally, the mean coverage for the selected cluster of chromosomes is calculated and used as the expected coverage for diploid regions.
If the tool is unable to find a suitable cluster, the median coverage for all chromosomes will be used as the expected coverage for diploid regions.
The presence of XX or XY chromosomes is automatically determined by the tool based on the observed coverage.
The tool defines non-overlapping windows that mapped reads are divided into, and calculates a coverage in each window that is adjusted for mapping quality and GC content. The resulting coverage in each window is normalized using the expected coverage for diploid regions. If any masking tracks are provided, the coverage will be ignored in the regions defined by these.
CNVs are detected using the normalized window coverage values with a hidden Markov model (HMM). The HMM consists of five different states for diploid chromosomes that each represent a copy number (0, 1, 2, 3, or 4). Only four states (0, 1, 2, or 3) are used for haploid chromosomes, i.e. when there is both an X and a Y chromosome. For each window, we calculate a probability for each state based on the normalized coverage value and the sample purity. The HMM considers each window as an event, and then tries to find the most likely sequence of copy number states that explains these events. The boundaries of detected CNVs are refined by using a window of half the size of the original window.
A coefficient of variation is calculated based on the coverage windows across all chromosomes. This is used to set the copy number state transition probabilities in the HMM. This serves the purpose of making it less likely to detect a CNV when using noisy data. The coefficient of variation is also used for automatically determining the window size.
The HMM calculates a CNV score by initially obtaining the probability of the sequence of events that occurred (i.e. the states it traversed). Next, the probability that there is no CNV is found using the same calculations, but where only copy neutral states are traversed. The CNV score is finally calculated as the log-ratio between these two probabilities.
To run Copy Number Variant Detection (WGS) (beta):
Tools | LightSpeed (![]() ) | Copy Number Variant Detection (WGS) (beta) (
) | Copy Number Variant Detection (WGS) (beta) (![]() )
)
If you are connected to a CLC Server via your Workbench, you will be asked where you would like to run the analysis. We recommend that you run the analysis on a CLC Server when possible.
In the first wizard step, select a read mapping (figure 3.27).
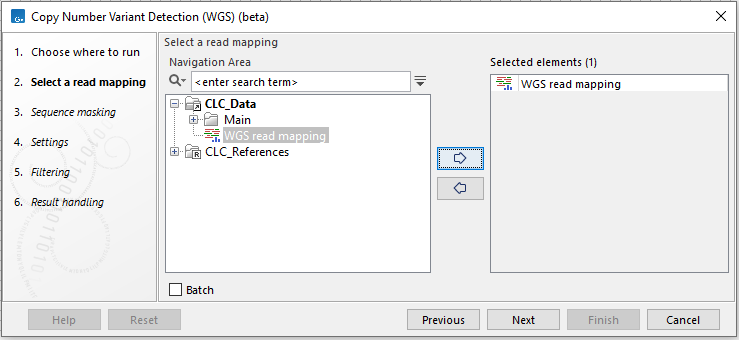
Figure 3.27: Select a read mapping.
Next, specify regions that should be masked (figure 3.28). You can choose to mask centromeres, pseudoautosomal regions, and/or regions included in a blacklist masking track. Windows with more than 25% ambiguous nucleotides, i.e. N, will automatically be masked.
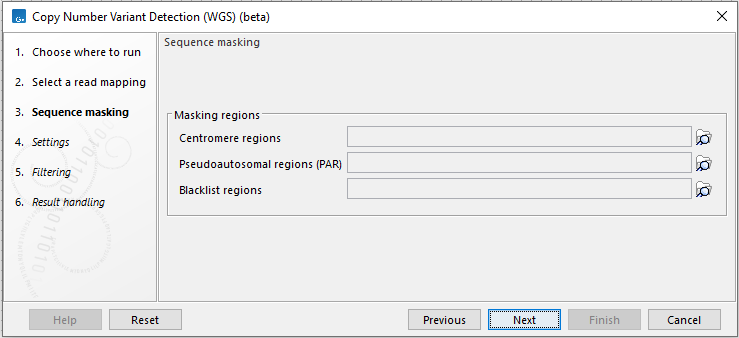
Figure 3.28: Provide tracks for sequence masking.
Centromere regions are repetitive which can result in the detection of false positive CNVs. Pseudoautosomal regions (PAR) are homologous between the X and Y chromosome which similarly can result in the detection of false positive CNVs. Tracks containing centromere regions and PAR are available for hg19 and hg38_no_alt_analysis_set in the Reference Data Manager. Excluding these regions is beneficial for estimating the expected coverage for diploid regions. Identified CNVs cannot overlap with centromere regions and/or PAR. We recommend masking centromere regions and PAR for CNV detection.
Blacklist regions can be used to mask regions where false positive CNVs are often detected, e.g. in regions with high or low mappability. See for example the ENCODE Blacklist described in (regions are available for download in the Data Availability section of the paper):
- Amemiya et al., The ENCODE Blacklist: Identification of Problematic Regions of the Genome, Sci Rep 9, 9354 (2019)[Amemiya et al., 2019].
In the settings step, the following options are available (figure 3.29):
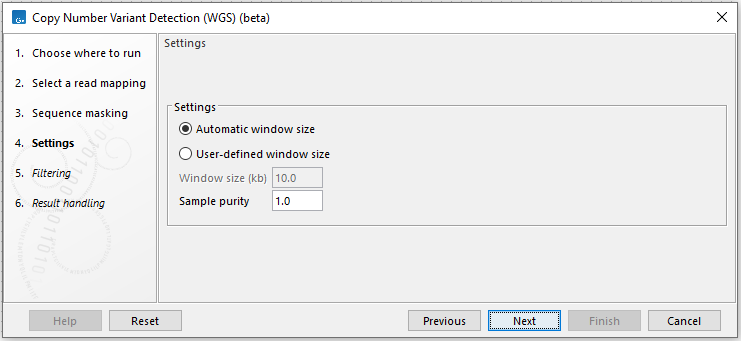
Figure 3.29: Specify settings for CNV detection.
- Automatic window size or User-defined window size. Choose whether the tool should estimate the optimal window size based on the data or use a pre-specified window size.
- Window size (kb) Manually specify the window size. This affects the size of CNVs that can be detected. The lower the coverage, the larger the window size should be. CNVs typically need to span at least 2-3 consecutive windows to be called.
- Sample purity Provide the purity of the sample. The value must be provided as a fraction. Purity is taken into account when predicting the copy number states of individual windows. The tool assumes a purity of 1.0 if no value is provided.
Next, options that can be used to filter CNVs are available (figure 3.30):
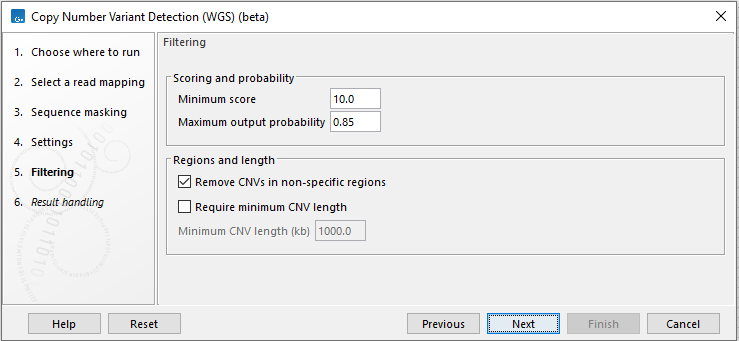
Figure 3.30: Specify filtering for CNV detection.
- Minimum score Remove CNVs with a CNV score below this cutoff (see how the CNV scores are calculated by the HMM above).
- Maximum output probability The maximum copy number state output probabilities calculated by the HMM can be limited to this threshold. The threshold also sets a minimum output probability that is equal to 1.0 - maximum output probability. Decreasing the maximum output probability will typically result in fewer and shorter CNVs, and increasing the maximum output probability will typically result in more and longer CNVs.
- Remove CNVs in non-specific regions Enabling this option will remove CNVs where more than half of the underlying windows contain a high number of non-specifically mapped reads.
- Require minimum CNV length CNVs shorter than a specified threshold will be removed.
- Minimum CNV length (kb) Specify the required minimum length of CNVs.
The Copy Number Variant Detection (WGS) (beta) tool has the following limitations:
- Only chromosomes larger than 10Mb are considered.
- Broken reads are ignored because they can accumulate in specific places, e.g. at the boundaries of deletions.
- If the majority of chromosomes are affected by chromosome-wide CNVs, the expected coverage for diploid regions might be suboptimally estimated as affected chromosomes may define the cluster used to estimate the expected coverage.
Subsections
