Suboptimal structures determination
A number of known factors violate the assumptions that are implicit in MFE structure prediction. [Schroeder et al., 1999] and [Chen et al., 2004] have shown experimental indications that the thermodynamic parameters are sequence dependent. Moreover, [Longfellow et al., 1990] and [Kierzek et al., 1999], have demonstrated that some structural elements show non-nearest neighbor effects. Finally, single stranded nucleotides in multi loops are known to influence stability [Mathews and Turner, 2002].
These phenomena can be expected to limit the accuracy of RNA secondary structure prediction by free energy minimization and it should be clear that the predicted MFE structure may deviate somewhat from the actual preferred structure of the molecule. This means that it may be informative to inspect the landscape of suboptimal structures which surround the MFE structure to look for general structural properties which seem to be robust to minor variations in the total free energy of the structure.
An effective procedure for generating a sample of suboptimal structures is given in [Zuker, 1989a]. This algorithm works by going through all possible Watson-Crick base pair in the molecule. For each of these base pairs, the algorithm computes the most optimal structure among all the structures that contain this pair, see figure 21.28.
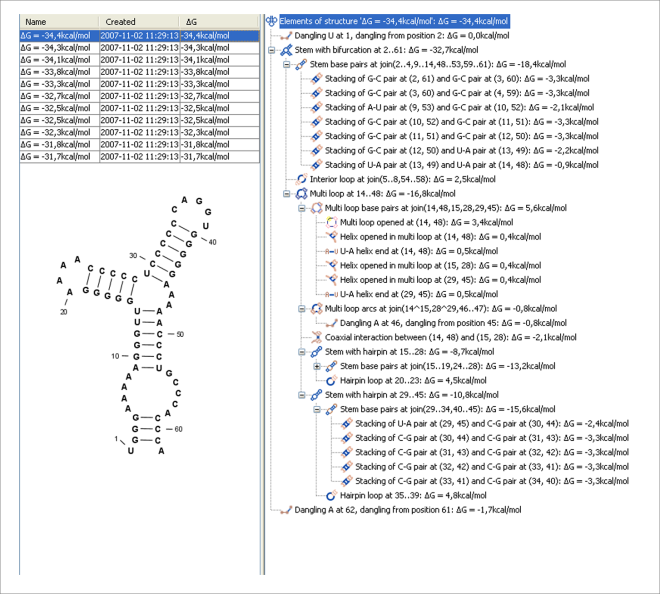
Figure 21.28: A number of suboptimal structures have been predicted using CLC Genomics Workbench and are listed at the top left. At the right hand side, the structural components of the selected structure are listed in a hierarchical structure and on the left hand side the structure is displayed.
