Import QIAGEN Primers
When creating a custom analysis workflow, it is possible to specify a Primer annotation track using the import button to the right of the relevant field in the Add custom panel dialog. Importing such a file can also be done ahead of time using the Import QIAGEN Primers tool.
The Import QIAGEN Primers importer can import a QIAseq Panel primer file previously saved on your computer. During import, the primers used for targeted resequencing are saved in the Navigation Area of the workbench as a Primer track. Note: the Import QIAGEN Primers tool is different from the Import Primer Pairs tool because of the formats of the primer files it can handle (see below for a detailed description of the formats).
The Import QIAGEN Primers tool can be found in the toolbar:
Import (![]() ) | Import QIAGEN Primers (
) | Import QIAGEN Primers (![]() )
)
The import wizard is shown in figure 5.13. The first step is to select the primers to import and a reference sequence.
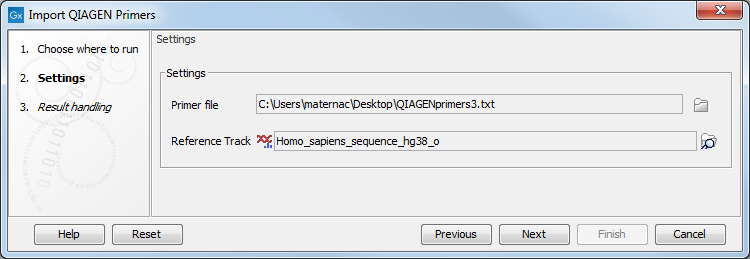
Figure 5.13: Select files to import.
- Primer File Click on the folder icon to select the file you received upon purchase of a QIAseq Panel. The name of the file should include
primer3.txtoramplicons. - Reference Track Choose the hg19 or the hg38 reference sequence that are saved in the Workbench after you have downloaded hg19 (or hg38) in the Reference Data Manager. The sequence can be found in the CLC_References folder in the Navigation Area tab, or using the QIAGEN Active sets folders in the Reference Data tab.
Click Next to go to the wizard step and choose to Save the imported primer location file.
Once the import completes, it is recommended to check the imported primers in the table view. If present, the "Matches reference sequence" column will have one of the following values: "Yes", "No", and in the case of QIAseq Targeted Methyl panels "Yes - after bisulfite conversion". A "No" indicates that the primer may have been designed against a more recent genome version, which has a corrected base compared to the reference. If there are many "No"s, it most likely indicates that an incorrect reference genome was supplied during import (figure 5.14).
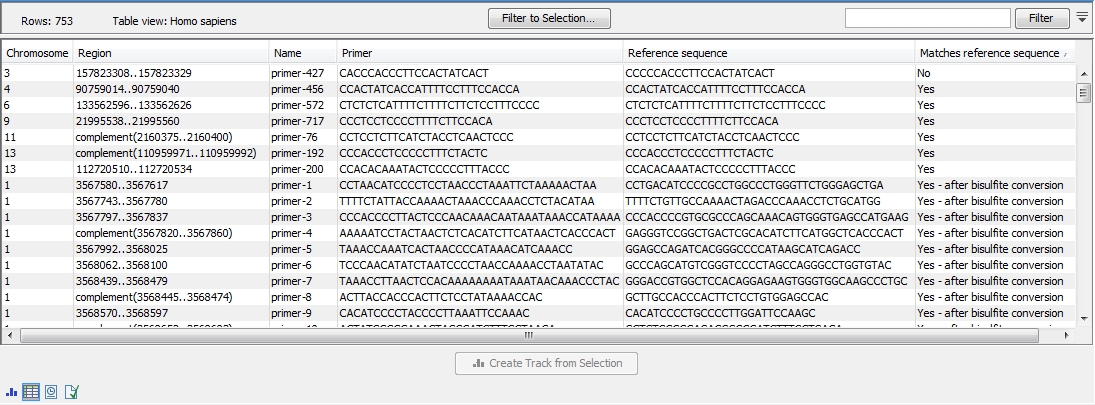
Figure 5.14: The imported QIAGEN primers.
QIAseq panel primer formats
The QIAseq panel primers are provided upon purchase of a kit, and the file can have the following formats:
The first file format is a tab-separated file with 4 columns defining:
- Chromosome
- Primer start/end position (0-indexed)
- Whether the primer is on the plus strand indicated by an "L" or a "0", or on the minus strand indicated by an "R" or a "1".
- The bases of the primer.
For example, the lines
chr1 1887011 L AGAATATTTTCTTGCTTAACCGTCACTTAACATCGA
chr1 1900114 R GGGACAAGACCTGGAACTACATTTCTGACT
define the primers:
On chr1, from 1886977 to 1887012 (both are 0-indexed, inclusive), on the plus strand.
On chr1, from 1900114 to 1900144 (both are 0-indexed, inclusive), on the minus strand.
The second file format is a tab-separated file with 6 or 7 columns defining:
- Primer count (this value is ignored during import)
- Chromosome
- Start position (0-indexed) when on the "+" strand or End position (0-indexed) when on the "-" strand
- End position (0-indexed) when on the "-" strand or Start position (0-indexed) when on the "+" strand
- Strand ("+" or "-")
- The bases of the primer
- Target annotation (optional)
For example, the lines:
14 chr1 1886977 1887012 + AGAATATTTTCTTGCTTAACCGTCACTTAACATCGA COPA
2 chr1 1900114 1900144 - GGGACAAGACCTGGAACTACATTTCTGACT RCSD1
define the primers from the previous example, with their target annotation.
The third file format is a tab-separated file with 11 or 14 columns defining:
- Gene identifier
- gene symbol
- Chromosome
- 5' primer location (0-based)
- 3' primer location (0-based)
- Genome strand (0 for binding to "-" but matching "+", and 1 for the opposite case)
- The bases of the primer
- Control primer flag (0 - not a control; 1 - reference gene expression control; 2-gDNA contamination control)
- Genome blocks
- Block sizes (comma-delimited)
- Block starts (comma-delimited)
- Whether the primer is designed for fusion calling (optional, 0 - no, 1 - yes)
- Whether the primer is designed to target a SNP or indel (optional, 0 - no, 1 - yes)
- Whether the primer is designed for use in gene expression (optional, 0 - no, 1 - yes)
For example, the lines:
ENSG00000000457 SCYL3 chr1 169859157 169859065 1 CTTCAATTCTGGATTCTTTACT 0 1 28 0
ENSG00000000457 SCYL3 chr1 169859969 169859079 1 GAGAACTTAGATCGATCGATTCCTG 0 1 30 0
define the primers from a RNAscan panel using the 11 column format.
The lines:
ENSG00000109685 WHSC1 chr4 1918581 1918613 0 GCATCCCAGTTTTTGGTCTTCTGTCAAAAACAC 33 0 0 0 0 1
ENSG00000109685 WHSC1 chr4 1959733 1961059 0 CAGAAAGGGAGAATTTGTTAACGAGTACGTTGG 7,26 0,1301 0 0 1 1
define the primers from a Fusion XP panel using the 14 column format.
All three file formats will be imported as paired primers when there is an even number of primers per chromosome and the lines are ordered with strands L, R, .. or R, L, .. (where L/R can also be +/- or 0/1 depending on the file format). Imported paired primers have an extra column "PrimerId" in the table view and work with Trim Primers and their Dimers from Mapping.
The fourth file format is a tab-separated file with 12 columns defining amplicons. Each amplicon implicitly defines two primers, and the same primer will be present multiple times if it amplifies multiple amplicons. The columns are:
- Chromosome
- 5' primer location (0-based)
- 3' primer location (0-based)
- Name of the left and right primers, separated by a "|"
- This value is ignored during import
- This value is ignored during import
- 5' primer location (0-based)
- 3' primer location (0-based)
- This value is ignored during import
- Block count - always "2" because each amplicon consists of two primers
- Block sizes (comma-delimited)
- Block starts (comma-delimited)
Primers from this fourth format will be paired primers with an extra column "PrimerId" in the table view. They will work with Trim Primers and their Dimers from Mapping.
The lines:
MN908947.3 3177 3412 QIAseq_23_LEFT|QIAseq_23_RIGHT 1 . 3177 3412 0 2 26,22 0,213
MN908947.3 3177 3425 QIAseq_23_LEFT|QIAseq_23-2_RIGHT 1 . 3177 3425 0 2 26,26 0,222
define primers from a QIAseq DIRECT SARS CoV-2 panel using this fourth format.
