Compare Immune Repertoires
The Compare Immune Repertoires tool contrasts properties of immune repertoires, such as diversity and similarity.
To run Compare Immune Repertoires go to the Toolbox and select:
Tools | QIAseq Panel Expert Tools (![]() ) | Immune Repertoire Expert Tools (
) | Immune Repertoire Expert Tools (![]() ) | Compare Immune Repertoires (
) | Compare Immune Repertoires (![]() )
)
This opens a dialog where TCR clonotypes (![]() ) or BCR clonotypes (
) or BCR clonotypes (![]() ) to be compared can be selected. Note that TCR and BCR clonotypes cannot be mixed and only one type should be used at a time.
) to be compared can be selected. Note that TCR and BCR clonotypes cannot be mixed and only one type should be used at a time.
Output from Compare Immune Repertoires tool
Three outputs can be generated by the tool:
- Compare Immune Repertoires (CIR) report (
 ). A report containing comparisons of repertoire properties.
). A report containing comparisons of repertoire properties.
- Heat map (
 ). A heat map with similar repertoires clustered.
). A heat map with similar repertoires clustered.
- Similarity table (
 ). A table showing the similarity of the immune repertoires for each pair of inputs.
). A table showing the similarity of the immune repertoires for each pair of inputs.
CIR Report
The report contains the following sections:
- Summary. A summary table showing, for each input, the total number of clonotyped fragments, as well as the clonotyped fragments from each chain type. A fragment represents one single read or a pair of reads.
The remaining information in the report is give per chain type and only for those chain types for which clonotypes have been identified for at least two of the inputs.
- Diversity indices. A table showing the diversity metrics 'Observed diversity', 'Extrapolated diversity (chaoE)' and 'Extrapolated Shannon-Wiener index (chaoE)', see report. Additionally, the table contains the diversity metric 'Interpolated to lowest sample diversity', showing an estimate of the diversity if all the inputs had the same number of clonotyped fragments as the input with the lowest number of clonotyped fragments.
- Scatter plots. If exactly two inputs are compared, this section will contain scatter plots with the clonotypes frequency in the two inputs.
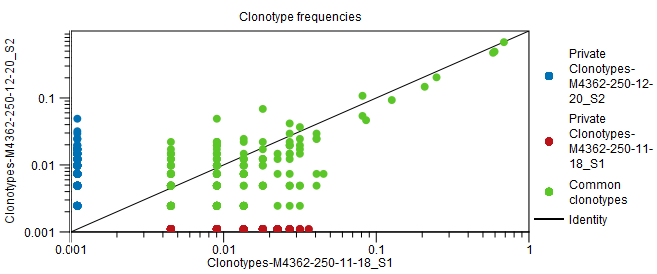
Figure 8.14: Scatter plot with clonotype frequencies for a particular chain type. Note that private clonotypes have frequencies 0 in one of the samples. Due to the log scale, they cannot be plotted at frequency 0. - Rarefaction. A plot with rarefaction curves, also known as species accumulation curve.
It shows the expected number of different clonotypes discovered as a function of the total number of clonotyped fragments for a particular chain.
The curve is extrapolated to twice the total number of clonotyped fragments for the most abundant input.
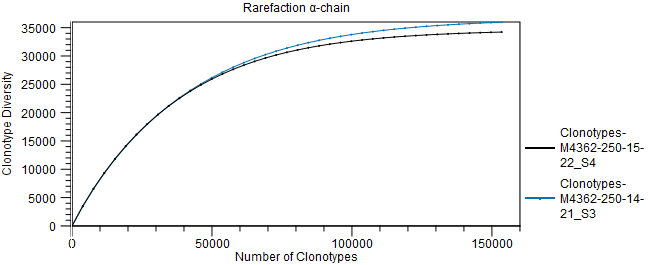
Figure 8.15: Rarefaction or species accumulation curve. - CDR3 length. A table comparing CDR3 length summary statistics for the different inputs, across all chains. For each chain type, the CDR3 length distribution is also shown as a box plot.
- V, D, J and C usage. Bar plots showing the V, D, J and C segment usage for each input.
Heat map
For each pair of inputs, the weighted Jaccard similarity between the two is computed.
Let ![]() ,
, ![]() denote the relative frequencies of the
denote the relative frequencies of the ![]() 'th clonotype in the first and second input respectively.
The weighted Jaccard similarity is defined as,
'th clonotype in the first and second input respectively.
The weighted Jaccard similarity is defined as,
The weighted Jaccard distance is defined as,
The heat map shows the Jaccard distance with inputs clustered hierarchically.
Similarity table
A table showing the Jaccard similarity (eq. 8.1) between each pair of inputs.
