How to run the Add reads to contigs
Toolbox | Genome Finishing Module (![]() ) |
Add reads to contigs (
) |
Add reads to contigs (![]() )
)
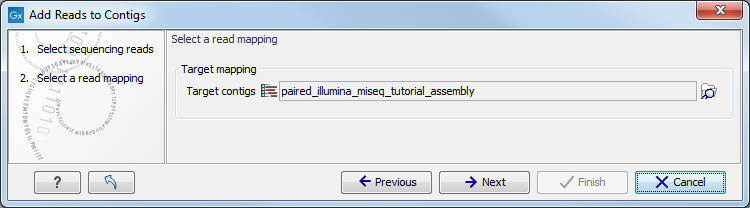
This opens the dialog shown in figure 6.2.
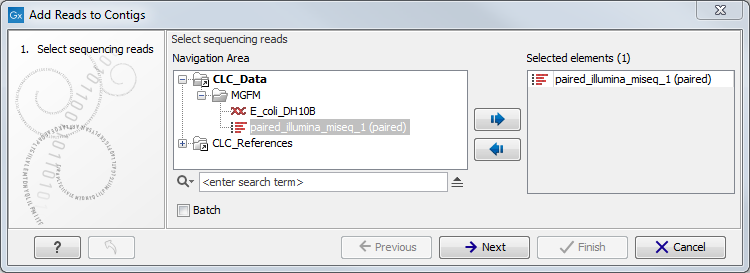
Figure 6.2: Select sequence reads.
Select sequence reads and click Next. This opens the dialog shown in figure 6.3.
Select the contig or the list of contigs that you want to add by clicking on the folder (![]() ).
Next, set the mapping options (figure 6.4).
).
Next, set the mapping options (figure 6.4).
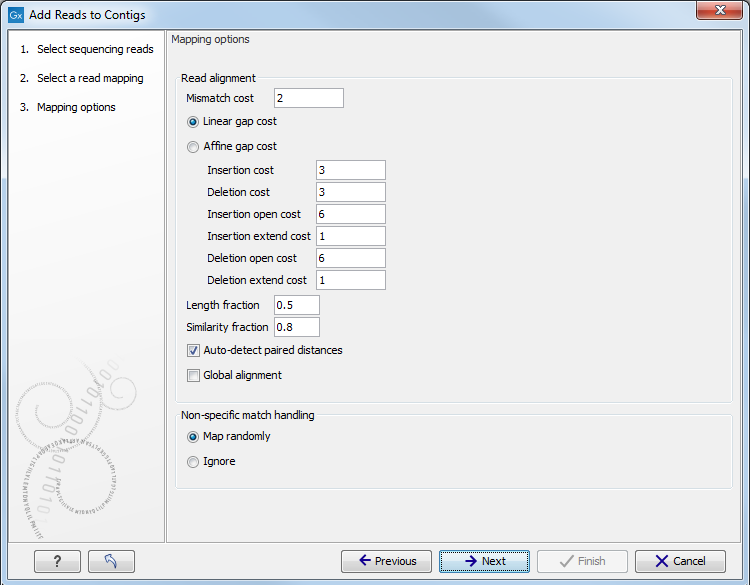
Figure 6.4: Set mapping options.
- Read alignment
- Mismatch cost. The cost of a mismatch between the read and the reference sequence. Ambiguous nucleotides such as "N", "R" or "Y" in read or reference sequences are treated as a mismatches and any column with one of these symbols will therefore be penalized with the mismatch cost.
- Linear gap cost. The cost of a gap is computed directly from the
length of the gap and the insertion or deletion cost. This model
often favors small, fragmented gaps over long contiguous gaps.
- Insertion cost. Can be set at 1, 2, or 3.
- Deletion cost. Can be set at 1, 2, or 3.
- Affine gap cost. An extra cost associated with opening a gap is
introduced such that long contiguous gaps are favored over short
gaps.
- Insertion open cost. Cost of opening an insertion in the read (a gap in the reference sequence).
- Insertion extend cost. Cost of extending an insertion in the read (a gap in the reference sequence) by one column.
- Deletion open cost. Cost of a opening a deletion in the read (gap in the read sequence).
- Deletion extend cost. Cost of extending a deletion in the read (gap in the read sequence) by one column.
- Length fraction. Minimum length fraction of a read that must match the reference sequence.
- Similarity fraction. Minimum fraction of similarity between read and reference sequence.
- Auto-detect paired distances. Determine the insert size of paired data sets.
- Global alignment. If selected, end gaps are treated as mismatches. If not checked, end gaps have no cost. Auto-detect paired distances is only accessible when using the relevant data sets.
- Non-specific match handling
- Map randomly. Reads with more than one match are assigned randomly.
- Ignore. Reads with more than one match are ignored.
After clicking Finish in the Result handling step, the reads will be added to the existing mapping of reads to contigs.