Correct PacBio Reads
This tool will be retired in a future version of the software. It has been replaced by Correct Long Reads available from the Long Read Support plugin, see http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/longreadsupport/current/index.php?manual=Correct_Long_Reads.html.
Please note that the tools Correct PacBio Reads (legacy) and De Novo Assemble PacBio Reads (legacy) are optimized for the use of PacBio data and readily support data generated with different generations of PacBio chemistry. Due to such algorithm-optimizations the use of these tools for other data types is not supported. Moreover, for the tool Correct PacBio Reads (legacy) we are relying on certain methods which are the intellectual property of Pacific Biosciences. The use of the Correct PacBio Reads (legacy) tool or the template workflow PacBio De Novo Assembly Pipeline (legacy) with data other than that data generated on a PacBio instrument constitutes a violation of the end user license agreement that users of the CLC Genome Finishing Module agree to during installation.
The Correct PacBio Reads (legacy) tool should be used as a preprocessing step prior to assembly of SMRT sequencing reads with high error-rates with the De Novo Assemble PacBio reads (legacy) tool to increase the quality and thereby obtain a better assembly. Both tools are designed for assembly of microbial genomes and small Eukaryotic genomes (for example C. elegans).
SMRT sequencing technologies, as implemented by Pacific BiosciencesTM, have the potential to vastly improve the completeness of genome sequence assemblies, as read lengths often exceed the length of most repeats in the genome. A major obstacle is the high (10-15%) rate of sequencing errors in SMRT reads. A second obstacle is the presence of chimeric reads and sequences derived from untrimmed adapters, which can be hard to recognize given the rate of errors and truncations. However, because sequencing errors are mostly random and reads are randomly sampled across the genome, it is possible to i) correct SMRT sequencing reads if coverage is sufficiently high with the Correct PacBio Reads (legacy) tool and ii) assemble the error-corrected reads into high-quality contigs with the De Novo Assemble PacBio Reads (legacy) tool. Note that it is not necessary to correct PacBio reads when using these with the Join contigs tool with the "Use long reads" option selected. The error correction of PacBio reads is required only when one is performing de novo assembly using long reads.
The Correct PacBio Reads (legacy) tool takes raw PacBio reads as input and produces error-corrected reads as output. The overall strategy for correcting PacBio reads consists of the following four steps:
- Partition the reads into (long) seed reads and (shorter) correction reads.
- Map all correction reads to all seed reads.
- Detect and handle hairpin sequences (untrimmed adapters) and chimeras in the seed reads.
- For each seed read, compute a consensus sequence and output this sequence as a corrected read.
The longest reads are selected as seed reads, because they give the assembler most information to resolve large repeats.
Figures 14.1 to 14.3 illustrate the error-rates of an E. coli dataset before and after error-correction.
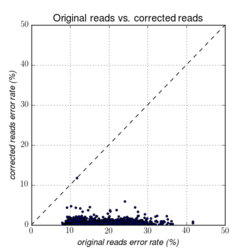
Figure 14.1: Error rates before and after error-correction on a whole genome E. coli dataset from PacBio RS II (P5/C3).
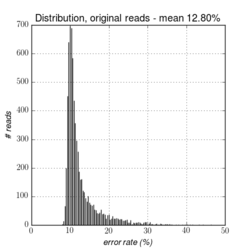
Figure 14.2: The distribution of error rates before error-correction on a whole genome E. coli dataset from PacBio RS II (P5/C3). The average error-rate is 12.80%
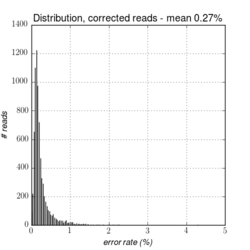
Figure 14.3: The distribution of error rates after error-correction on a whole genome E. coli dataset from PacBio RS II (P5/C3). The average error-rate is 0.27%
Subsections
