Ion Torrent
Choosing the Ion Torrent import will open the dialog shown in figure 6.15.
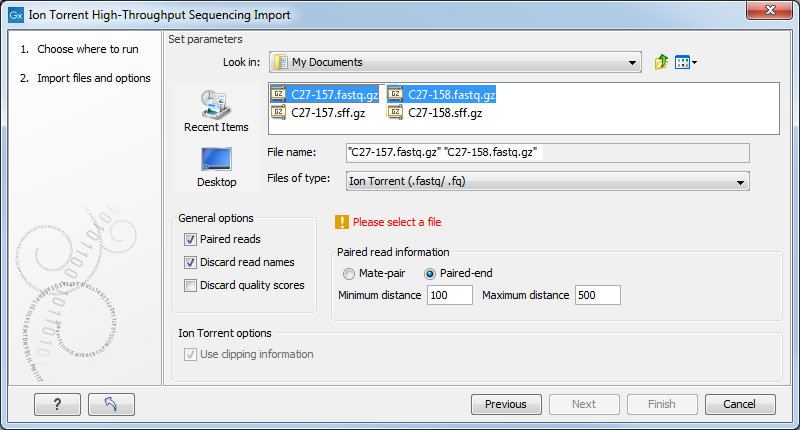
Figure 6.15: Importing data from Ion Torrent.
We support import of two kinds of data from the Ion Torrent system:
- SFF files (.sff ) providing extra information on adapters or regions of low quality
- Fastq files (
.fastq). Quality scores are expected to be in the NCBI/Sanger format (see Quality scores in the Illumina platform). Compressed data in gzip format is also supported (.gz).
The General options to the left are:
- Paired reads. The Biomedical Genomics Workbench supports both paired end and mate pair protocols.
- Paired end
- Paired end data from Ion Torrent comes in two files per data set. The first file in is assumed to contain the first reads of the pair, and the second file is assumed to contain the second read in a pair. On import, the orientation of the reads is set to forward - reverse. When the reads have been imported, there will be one file with intact pairs, and one file where one part of the pair is missing (in this case, "single" is appended to the file name). The Workbench connects the right sequences together in the pair based on the read name. Read more about handling paired data.
- Mate pair
- Mate pair reads from Ion torrent are Reverse-Forward and usually between 2,000 and 10,000 bp. The mate pair protocol for Ion Torrent entails that the two reads are separated by a linker sequence. During import of paired data, the linker sequence is removed and the two reads are separated and put into the same sequence list. You can change the linker sequence in the Preferences (in the Edit menu) under Data. When looking for the linker sequence, the Workbench requires 80 % of the maximum alignment score, using the following scoring scheme: matches = 1, mismatches = -2 and indels = -3.
Some of the sequences may not have the linker in the middle of the sequence, and in that case the partial linker sequence is still removed, and the single read is put into a separate sequence list. Thus when you import Ion Torrent mate pair data, you may end up with two sequence lists: one for paired reads and one for single reads. Note that for de novo assembly projects, only the paired list should be used since the single reads list may contain reads where there is still a linker sequence present but only partially due to sequencing errors. Read more about handling paired data.
- Discard read names. For high-throughput sequencing data, the naming of the individual reads is often irrelevant given the huge amount of reads. This option allows you to discard this option to save disk space.
- Discard quality scores. Quality scores are visualized in the mapping view and they are used for SNP detection. If this is not relevant for your work, you can choose to Discard quality scores. One of the benefits from discarding quality scores is that you will gain a lot in terms of reduced disk space usage and memory consumption. If you have selected the fna/qual option and choose to discard quality scores, you do not need to select a .qual file.
For sff files, you can also decide whether to use the clipping information in the file or not.
