Create Consensus Sequences from Variants
Using the Create Consensus Sequences from Variants tool, consensus sequences can be created from a Variant track (![]() ) and the matching reference genome (
) and the matching reference genome (![]() ). In addition, it is an option to mask out low coverage regions (
). In addition, it is an option to mask out low coverage regions (![]() ) with N's when a coverage track is provided.
) with N's when a coverage track is provided.
Note: To create a low coverage region track use the Create Mapping Graph (![]() ) tool to identify coverage in your sample followed by filtering on specified frequency using the Identify Graph Threshold Areas (
) tool to identify coverage in your sample followed by filtering on specified frequency using the Identify Graph Threshold Areas (![]() ) tool.
) tool.
The Create Consensus Sequences from Variants tool offers a number of filtering options:
- Minimum frequency for inclusion - Include variants above a selected frequency in the consensus.
- Ambiguity threshold - Mask out positions where the most commonly observed nucleotide is seen in fewer than the specified fraction of reads.
- Ignore frameshift variants - Filter out Indels of size 1,2,4,5 etc. A minimum frequency can be specified for when to include a variant.
Running the Create Consensus Sequences from Variants tool
To run the Create Consensus Sequences from Variants tool, go to:
Toolbox | Resequencing Analysis (![]() ) | Create Consensus Sequences from Variants (
) | Create Consensus Sequences from Variants (![]() )
)
In the first step, select the variant track that contains the variants from which the consensus should be created.
The next step provides options for how to construct the consensus sequences (see figure 25.1).
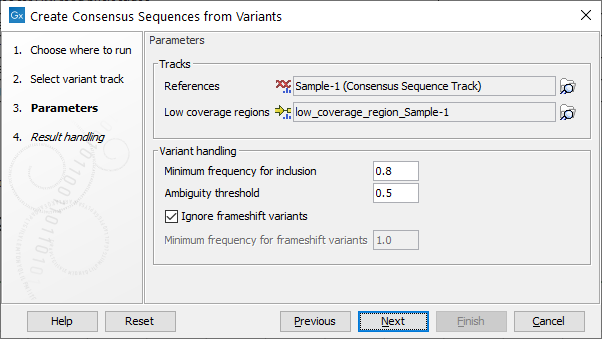
Figure 25.1: Options available to configure when running the Create Consensus Sequences from Variants tool.
In the Tracks parameters, specify the reference genome and optionally provide an annotation track containing low coverage regions.
Variant handling parameters include:
- Minimum frequency for inclusion ranging from 0.0 to 1.0 (Default 0.8).
- Ambiguity threshold for masking variants with N's range from 0.0 to minimum frequency for inclusion (Default is 0.5). When generating the consensus, positions with variants that have a frequency between the ambiguity threshold and the minimum frequency for inclusion are replaced with N's. Positions with variants below the ambiguity threshold use the nucleotide from the reference. Note: only none-Indel variants can be masked using this threshold.
- Ignore frameshift variants. Enabled when ticked, otherwise a frequency can be specified in order to include frameshift at a certain frequency (default is 1.0). Note, frameshift variants are here defined to cover Indels not fitting with a 3 codon base structure in its simplest form. This feature is especially relevant for Virus consensus creation where frameshift variants are unlikely.
In the final step, specify the output type and a save data location.
The tool offers two types of consensus sequence format:
- Sequence Track A Consensus Genome Track.
- Sequence List A Consensus Sequence list.
To get an overview of the variants and masking in the consensus sequences an option for smaller genomes is to map the Consensus Sequence List against the reference sequence using Map Reads to Reference (![]() ) and look at the Sample mapping and table. An example for the SARS-CoV-2 (MN908947.3) consensus and reference is given in figure 25.2 and 25.3).
) and look at the Sample mapping and table. An example for the SARS-CoV-2 (MN908947.3) consensus and reference is given in figure 25.2 and 25.3).
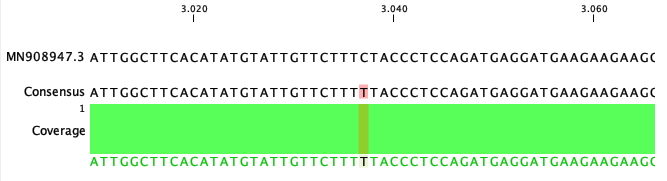
Figure 25.2: Alignment of a mapped SARS-CoV-2 consensus against MN908947.3 reference genome.
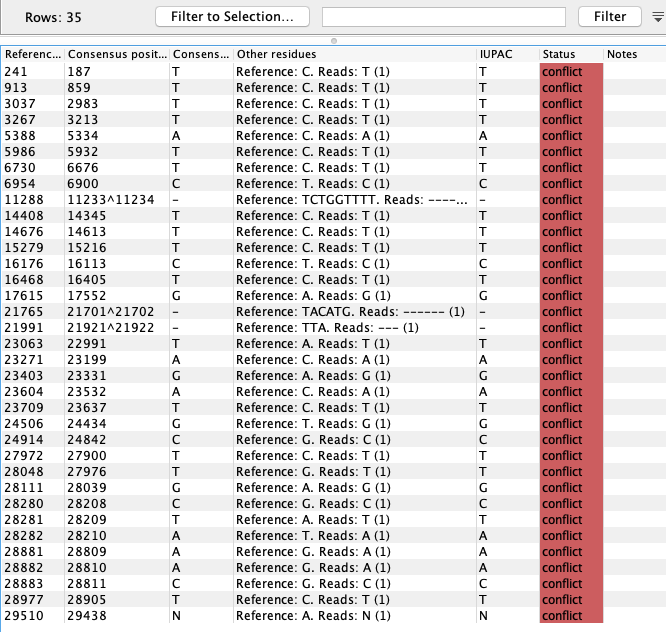
Figure 25.3: Variant representation of the alignment shown in figure 25.2
The Map Long Read to Reference (![]() ) tool should be used for bigger genomes. The Map Long Read to Reference (
) tool should be used for bigger genomes. The Map Long Read to Reference (![]() ) is part of the Long Read Support Plugin and can be downloaded from the Plugins Manager (see
http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/longreadsupport/current/index.php?manual=Map_Long_Reads_Reference.html for further details).
) is part of the Long Read Support Plugin and can be downloaded from the Plugins Manager (see
http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/longreadsupport/current/index.php?manual=Map_Long_Reads_Reference.html for further details).
