Multi-job processing on grid
Certain types of CLC Server jobs, known as "non-exclusive" jobs, can be scheduled to run concurrently on the same grid node when appropriate. Non-exclusive jobs are those that have reasonably low demands for system resources. A list of such jobs is provided in the Appendix, Non-exclusive Algorithms.
There are two ways non-exclusive jobs can be configured to run concurrently on a grid node:
- In the context of a workflow or workflow block executed on a single grid node
If the server has been configured to send all tasks in a workflow to a single node, or to send tasks in a workflow block to a single node, as described in Workflow queuing options, and the workflow or workflow block includes parallel non-exclusive tasks, then if these may run concurrently on the grid node.By default, up to 10 such non-exclusive jobs can be run concurrently. This value can be changed in the "Maximum number of concurrent jobs" field, available in the "Server setup" area of the Job Distribution tab. That field is visible when the server mode "Single server" has been selected, as shown in figure 6.7. The value configured is passed through to the CLC Server queue with the grid worker.
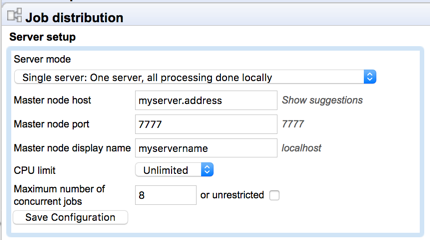
Figure 6.7: The Maximum number of concurrent jobs setting is visible when the Single server mode is selected.A grid setup can be run with the Single server or Master node setting selected. To adjust the "Maximum number of concurrent jobs" if the Master node option is selected, temporarily change the mode to Single server, set the desired value, and then change the mode back to Master node.
Limitation: The maximum value that can be entered in the "Maximum number of concurrent jobs" field is the number of cores on the master server. Setting that maximum value is the equivalent of checking the unlimited box. If this value is smaller than the desired value, as might happen when grid nodes have many more cpu than the master server, then we recommend leaving this field blank so that the default value of 10 is used.
- In any other context
Information about the CPU or thread requirements of the jobs must be passed to the grid scheduler. Non-exclusive algorithms expose their CPU or thread usage, and this information can be passed on to the grid scheduler via the COMMAND_THREAD_MIN and COMMAND_THREAD_MAX variables in the Shared native specification of a grid preset. The variableCOMMAND_THREAD_MAXwould be used alone as an argument when a single value should be specified, or both the variablesCOMMAND_THREAD_MINandCOMMAND_THREAD_MAXcan be provided when a range is required. An example of specifying a range is shown in the image of a grid present in Configure and save grid presets.One can also use the functions
take_lower_ofandtake_higher_offor settings relevant to configuring multiple job processing. For example, to specify 4 as the maximum number of cores to be used by a non-exclusive job, the following could be used as the argument to the relevant parameter in the Shared native specification of a grid preset:{#take_lower_of COMMAND_THREAD_MAX, 4}. As the non-exclusive job passes on its thread usage requirements via theCOMMAND_THREAD_MAXvariable, this evaluates to 4 if that requirement is higher than 4 or the value specified by the job if is lower than 4.Further details about grid preset configuration, including Shared native specifications, functions and variables, can be found in Configure grid presets.
Licensing notes
Each CLC Grid Worker launched, whether it is to run alone on a node or run alongside a job already running on a particular node, will attempt to get a license from the CLC License Server. Once the job is complete, the license will be returned.
If the server has been configured to send all tasks in a workflow to a single node, only a single CLC Grid Worker will be launched for a given workflow run. Thus, irrespective of the number of concurrently running jobs in such a workflow run, only a single gridworker license is used.
If the server has been configured so that each task in a workflow is submitted separately, then a CLC Grid Worker will be launched for each task, resulting in the use of a gridworker license for each task, including non-exclusive jobs executed concurrently. When no licenses are available, jobs wait in the queue until a license becomes available.
If the server has been configured so that each block of a workflow is submitted to run on a single node, a CLC Grid Worker will be launched for each block. If the workflow contains no iteration blocks, then it, by definition, consists of a single block and will use a single gridworker license. If a workflow contains one or more iteration blocks, it will consume a number of licenses equal to the number of iterations of these blocks plus one for each additional, non-iterated block. See figure 6.13 in Workflow queuing options for more detail about workflow blocks.
