Bin Pangenomes by Sequence
Binning by sequence is done irrespective of a database, only depending on content and coverage. To have both sources of information available, the Bin Pangenomes by Sequence tool takes read mappings to contigs as input, where there should be one read mapping per technical replicate (each mapping to the same contigs) in order to make most use of coverage information across all samples. However, if read mappings are not available, the Bin Pangenomes by Sequence tool also takes plain sequence lists of contigs as input.
The Bin Pangenomes by Sequence takes one or several single or paired-end read files as input (figure 6.4).
In the next dialog (figure 6.5), the several parameters can be specified:
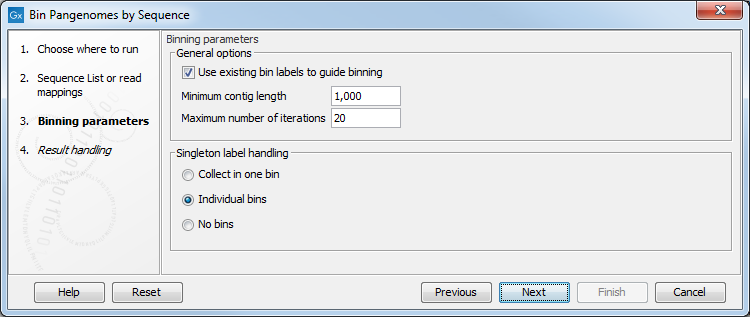
Figure 6.5: Configuration of the Bin Pangenomes by Sequence.
- Use existing labels to guide binning may be used to improve binning quality and speed. For read mapping inputs, (Assembly ID) labels assigned to reads are used, while for sequence list inputs the labels assigned to the contigs are used.
- Minimum contig length specifies the minimal length for contigs to be considered (should be at least 1000 to obtain decent bin qualities
- Maximum number of iterations specifies how many purification steps at most should be made.
- Singleton label handling decides whether singletons should be collected in one bin, kept in individuals bin, or not included in any bins.
Finally, in the "Result handling" dialog, it may be specified whether the reads of the binned contigs should be labelled and collected.
The standard output of the Bin Pangenomes by Sequence tool consists of a Sequence binning report, a contig list with their assigned bin listed in the Assembly_ID column, and as many read lists as read mappings were used as input in the tool, where reads have been assigned the bin of the contig they belong to.