Detect and Refine Fusion Genes
Detect and Refine Fusion Genes uses information from unaligned read ends in a read mapping (![]() ) to detect potential fusions between gene pairs. Candidate fusions are selected among these, and are refined by mapping the input reads (
) to detect potential fusions between gene pairs. Candidate fusions are selected among these, and are refined by mapping the input reads (![]() ) to both the original wildtype reference genome and an artificial fusion genome (figure 33.55). The tool produces comprehensive outputs (see Output from Detect and Refine Fusion Genes), enabling detailed analysis of the evidence for fusions.
) to both the original wildtype reference genome and an artificial fusion genome (figure 33.55). The tool produces comprehensive outputs (see Output from Detect and Refine Fusion Genes), enabling detailed analysis of the evidence for fusions.
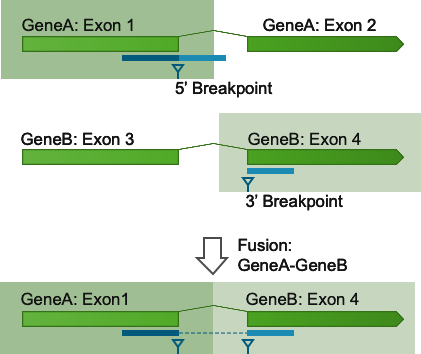
Figure 33.55: A read is mapped to GeneA in the input read mapping, with an unaligned end. The unaligned end is then remapped to GeneB. An artificial fusion chromosome is created for a candidate fusion between GeneA and GeneB. This fusion has its 5' breakpoint at the exon boundary of GeneA and its 3' breakpoint at the exon boundary of GeneB.
Known limitations
The tool is not suitable for detection of fusions involving:
- CircRNAs, as it disregards evidence of back-splicing.
- A mix of sense and antisense exons.
- More than two genes.
- A region before the first annotated exon or after the last annotated exon.
Subsections
- Running Detect and Refine Fusion Genes
- Exclude lists
- Output from Detect and Refine Fusion Genes
- Interpretation of fusion results
