Map Reads to Contigs
The Map Reads to Contigs tool allows mapping of reads to contigs. This can be relevant in situations where the reference of a mapping is contigs, such as when:
- Contigs have been imported from an external source
- The output from a de novo assembly is contigs with no read mapping
- You wish to map a new set of reads or a subset of reads to the contigs
The Map Reads to Contigs tool is similar to the Map Reads to Reference tool in that both tools accept the same input reads, and make use of the same read mapper in accordance to the reads input (see the introduction of Map Reads to Reference).
The main difference between the two tools is the output. The output from the Map reads to contigs tool is a de novo object that can be edited, in contrast to the reference sequence used when mapping reads to a reference.
To run the Map Reads to Contigs tool:
Tools | De Novo Sequencing (![]() ) | Map Reads to Contigs (
) | Map Reads to Contigs (![]() )
)
This opens up the dialog in figure 35.25 where you select the reads you want to map to the contigs. Click Next.
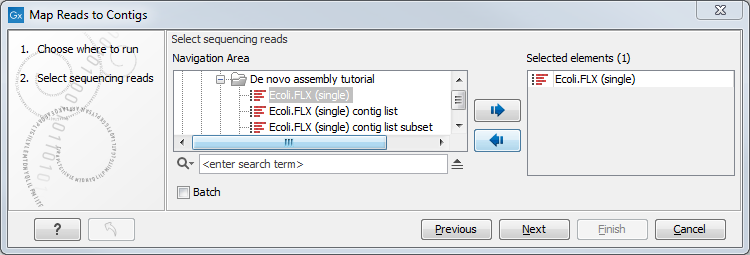
Figure 35.25: Select reads. The contigs will be selected in the next step.
Select the contigs to map the reads against (figure 35.26).
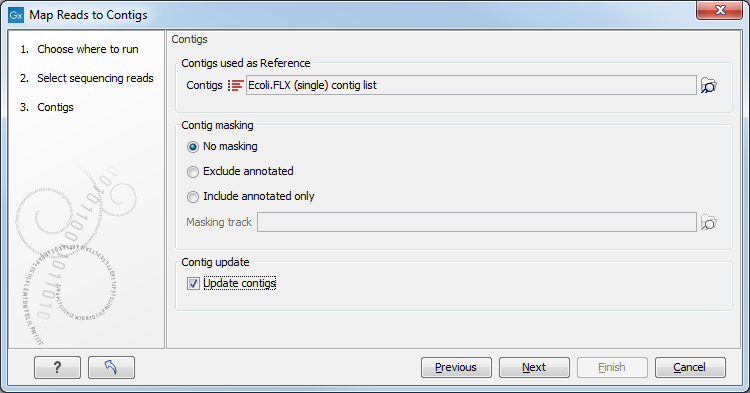
Figure 35.26: Select contigs and specify whether to use masking and the "Update contigs" function.
Under "Contig masking", specify whether to include or exclude specific regions (for a description of this see Including or excluding regions (masking)).
The contigs can be updated by selecting "Update contigs". The advantage of using this option during read mapping is that the read mapper is better than the de novo assembler at handling errors in reads. Specifically, the actions taken when contigs are updated are:
- Regions of a contig reference, where no reads map, are removed. This leads to a joining of the surrounding regions of the contig as shown in the example in figure 35.27).
- In the case of locations where reads map to a contig reference, but there are some mismatches to that contig, the contig sequence is updated to reflect the majority base at that location among the reads mapped there. If more than half of the reads contain a gap at that location, the contig sequence will be updated to include the gap.
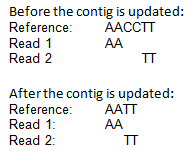
Figure 35.27: When selecting "Update Contig" in the wizard, contigs will be updated according to the reads. This means that regions of a contig where no reads map will be removed.
In the Mapping options dialog, the parameters of the Map Reads to Contigs tool are identical to the ones described for the Map Reads to Reference tool (see Mapping parameters).
The output from the Map Reads to Contigs tool can be a track or stand-alone read mappings. If the option to update contigs has been enabled, the track-based output cannot be selected.
When stand-alone read mappings have been selected as output, it is possible to edit and delete contig sequences.
Figure 35.28 shows two stand-alone read mappings generated by using Map Reads to Reference (top) and Map Reads to Contigs (bottom) on the exact same reads and contigs as input. Contig 1 from both analyses have been opened from their respective Contig Tables. The differences are highlighted with red arrows. The output from the Map Reads to Reference has a consensus sequence; in the output from Map Reads to Contigs, the Contig itself is the consensus sequence if "Update contigs" was selected.
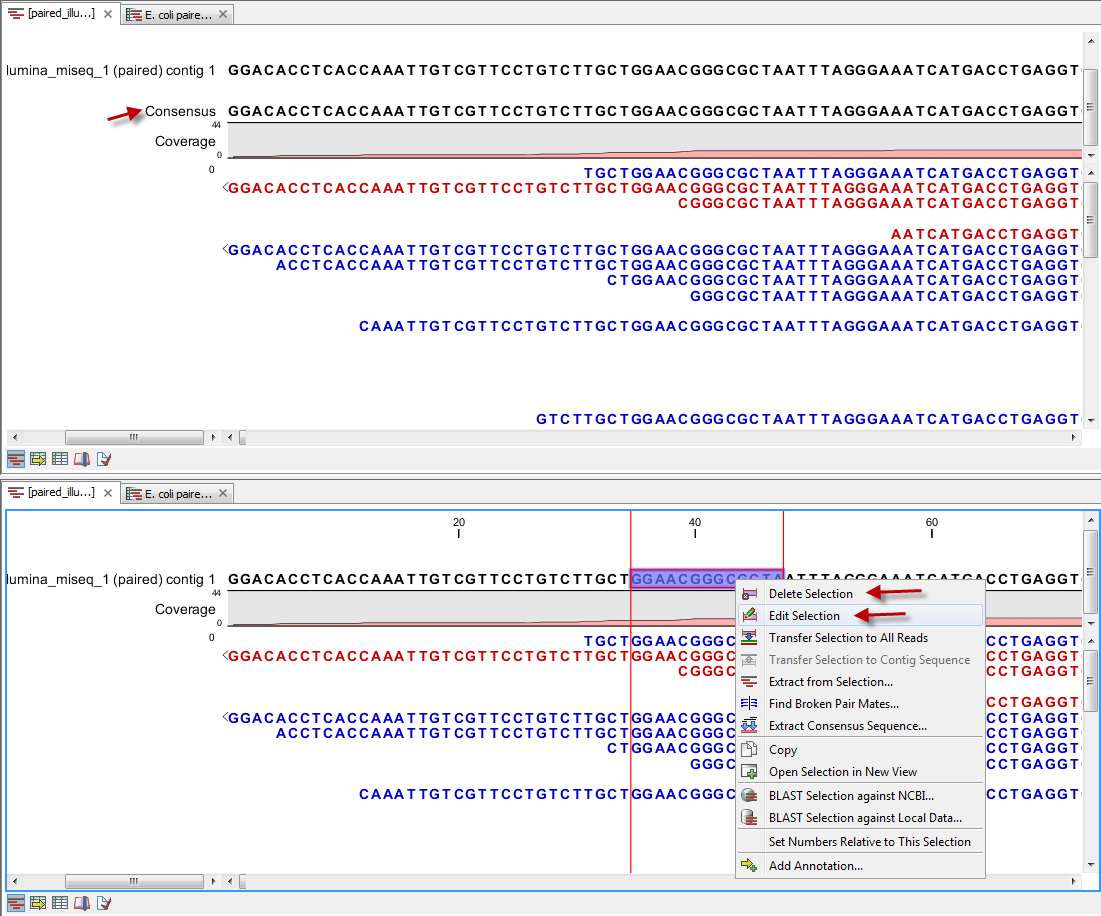
Figure 35.28: Two different read mappings performed with Map Reads to Reference (top) and Map Reads to Contigs (bottom). The differences are highlighted with red arrows.
