Export in VCF format
Using this tool, variants, CNV and fusion data are exported to a VCF 4.2 format file.
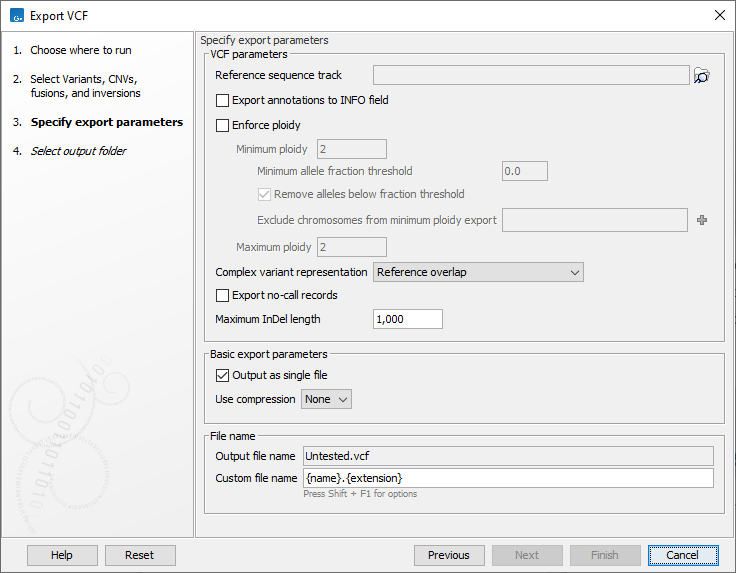
Figure 8.8: Several options are available when exporting to a VCF format file.
A number of configuration options are available (figure 8.8). Those specific to exporting to a VCF format file are:
- Reference sequence track
- Since the VCF format specifies that reference and allele sequences cannot be empty, deletions and insertions have to be padded with bases from the reference sequence. The export needs access to the reference sequence track in order to find the neighboring bases.
- Export annotations to INFO field
- Checking this option will export annotations on variant alleles as individual entries in the INFO field. Each annotation gets its own INFO ID. Various annotation tools can be found under Resequencing Analysis | Variant Annotation. Undesired annotations can be removed prior to export using Remove Information from Track, see Remove Information from Track. Some variant annotations corresponding to database identifiers, such as dbSNP and db_xref, will also be exported in the ID field of the VCF data line.
- Enforce ploidy
- Enforce minimum and maximum ploidy by modifying the number of alleles in the exported VCF genotype (GT) field. The two steps "Enforce minimum ploidy" and "Enforce maximum ploidy" are carried out separately during export in the mentioned order. Note that "Enforce minimum ploidy" can be disabled by setting both Minimum ploidy and Minimum allele fraction threshold to zero. "Enforce maximum ploidy" can be disabled by setting Maximum ploidy to 1000 or more.
- Minimum and Maximum ploidy. Minimum and maximum number of alleles to be written in the genotype field of the VCF. Enforcing minimum and maximum ploidy only affects the VCF genotype field. Both are set by default to 2, resulting in a VCF file in which the allele values in the Genotype (GT) field for haploid variants are reported following the format for diploid variants (i.e., the GT allele values reported could be 1/1). This is to allow compatibility of the exported VCF file with programs for downstream variant analysis that expect strictly diploid genomes. Note that it is proper to enforce diploid if the sample is diploid, and two alleles are expected to be present at all positions in the variant track (except excluded chromosomes). But if the variants have been filtered in a way that positions are no longer expected to have two alleles (e.g. all reference alleles have been removed), then it becomes wrong to enforce diploid.
- Minimum allele fraction threshold and Remove alleles below fraction threshold. Only alleles with an allele fraction above this threshold are considered as contributing to the minimum ploidy alleles. Alleles with a fraction below the threshold may still be reported in the VCF genotype field if the "Remove alleles below fraction threshold" option is disabled and the maximum ploidy allows it. The effect of this threshold depends on the minimum and maximum ploidy values set: For a minimum ploidy set at 2, a maximum ploidy set at 4 and the "Remove alleles below fraction threshold" option disabled, a case of 3 alleles where one (A) is above the threshold and two (C and T) are below will lead to the VCF genotype A/A/C/T. If the "Remove alleles below fraction threshold" option is enabled, or the maximum ploidy is set to 2, the VCF genotype field becomes A/A.
- Exclude chromosomes from minimum ploidy export. The user can specify that the Enforce minimum ploidy option is only applied to certain chromosomes, while others will be reported without enforcing a minimum ploidy.
Some chromosomes can be excepted from the enforced diploid export. For a human genome, that would be relevant for the mitochondrion and for male X and Y chromosomes. For this option, you can select which chromosomes should be excepted. They will be exported in the standard way without assuming there should be two genotypes, and homozygous calls will just have one value in the GT field.
- Minimum and Maximum ploidy. Minimum and maximum number of alleles to be written in the genotype field of the VCF. Enforcing minimum and maximum ploidy only affects the VCF genotype field. Both are set by default to 2, resulting in a VCF file in which the allele values in the Genotype (GT) field for haploid variants are reported following the format for diploid variants (i.e., the GT allele values reported could be 1/1). This is to allow compatibility of the exported VCF file with programs for downstream variant analysis that expect strictly diploid genomes. Note that it is proper to enforce diploid if the sample is diploid, and two alleles are expected to be present at all positions in the variant track (except excluded chromosomes). But if the variants have been filtered in a way that positions are no longer expected to have two alleles (e.g. all reference alleles have been removed), then it becomes wrong to enforce diploid.
- Complex variant representation
- Complex variants are allelic variants that overlap but do not cover the same range. In exporting, a VCF line will be written for each complex variant. Choose from the drop down menu:
- Reference overlap: Accurate representation where reference alleles are added to the genotype field to specify complex overlapping alleles.
- Reference overlap and depth estimate: More widely compatible and less accurate representation where a reference allele will be added, and the allele depth will be estimated from the alternate allele depth and coverage.
- Star alleles: Accurate representation where star alleles are used to specify complex overlapping alleles.
- Without overlap specification: this is how complex variants used to be handled in previous versions of the CLC Genomics Workbench, where complex overlap does not affect how variants are specified.
- Export no-call records
- Some export parameter settings can result in removal of all alleles at a given locus present in the exported variant track.
Enable this option to export such loci where no alleles are called.
In the generated no-call record, the genotype will be specified as missing, however the original variant annotations will be available.
No-call records may occur when 'Remove alleles below fraction threshold' is enabled, when enforcing a maximum ploidy, or when using the 'Reference overlap and depth estimate' complex variant representation.
- Maximum InDel length
- The maximum length at which insertions and deletions (InDels) are represented with full sequence in the VCF. Variants that are longer than the threshold, will instead be included in the VCF as symbolic alleles.
For full compatibility with QIAGEN Clinical Insight Interpret (QCI Interpret), the threshold should be set to 1000.
- Output as single file
- When this option is checked, data from multiple input tracks, including CNV tracks and fusion tracks, are exported together to a single VCF file.
Important details about VCF export
- When working with fusion data, only fusions with "PASS" in the "Filter" column will be exported.
- Where the same variant is reported multiple times, which is especially relevant when providing multiple variant tracks as input, the VCF file will include only one of these, the copy with the highest QUAL value.
- Counts from the variant track are put in CLCAD2 or AD fields depending on the chosen complex variant representation, and coverage is placed in the DP field. The values of the CLCAD2 tag follow the order of REF and ALT, with one value for the REF and for each ALT. For example, if there has been a homozygote variant identified at a certain position, the value of the GT field is 1/1 and the corresponding CLCAD2 value for the reference allele will be 0, which is always the first number in the CLCAD2 field. Please note that this does not mean the original mapping did not have any reads with that sequence, but it means that the variant track being exported does not contain the reference allele.
For descriptions of general export settings, see and .
Subsections
