Convert from Tracks
Tracks are useful for comparative analysis and visualization, but sometimes it is necessary to convert a track to a normal sequence or mapping. This can be done with the Convert from Tracks tool that can be found here:
Tools | Utility Tools (![]() ) | Tracks (
) | Tracks (![]() ) | Convert Tracks (
) | Convert Tracks (![]() ) | Convert from Tracks (
) | Convert from Tracks (![]() )
)
One or more tracks can be used as input. In the example given in figure 27.30 a reads track and two annotation tracks are converted simultaneously to an annotated read mapping (figure 27.31).
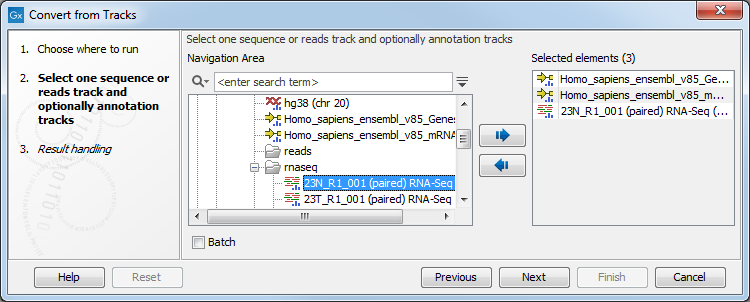
Figure 27.30: A reads track and two annotation tracks are converted from track format to stand-alone format.
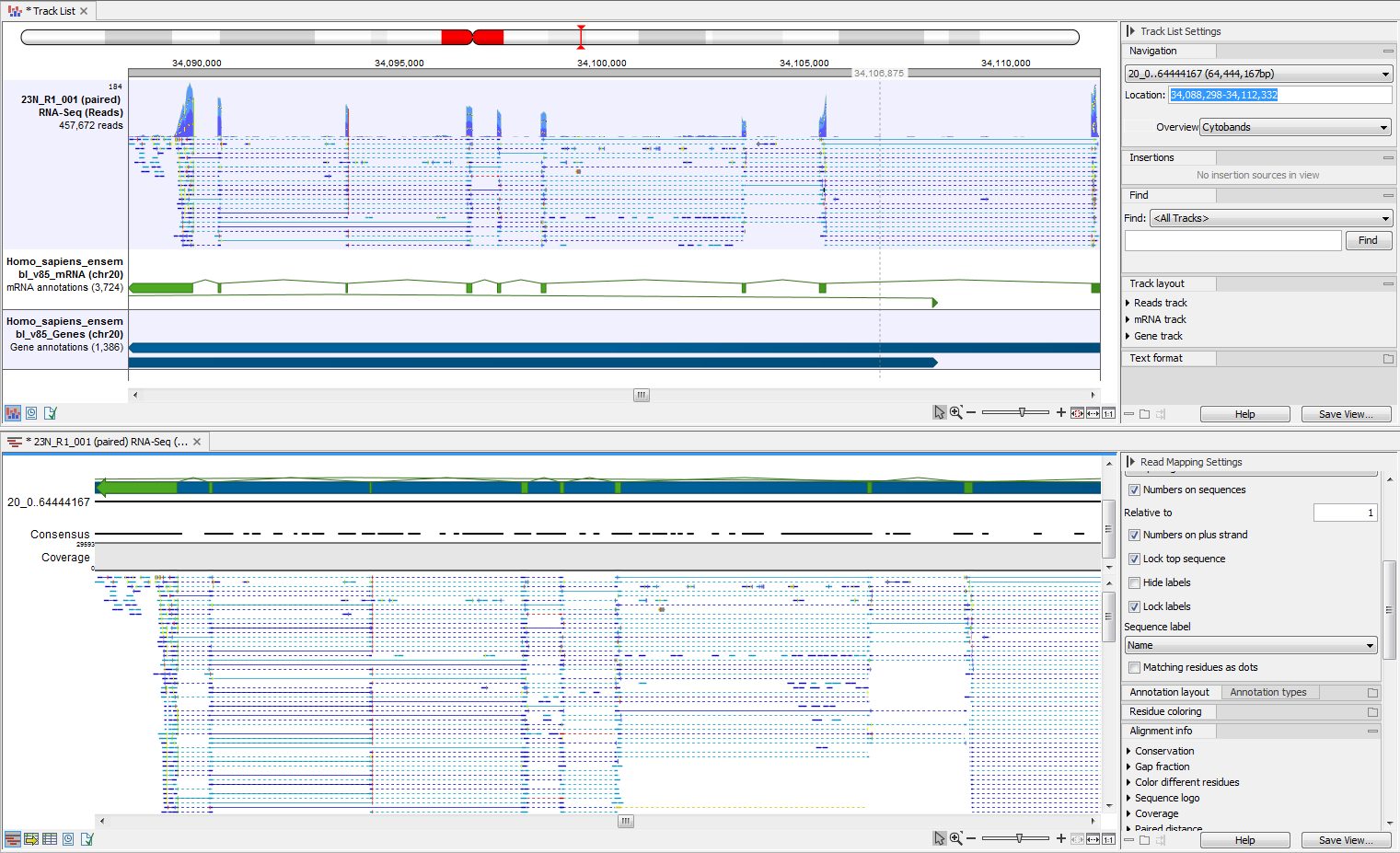
Figure 27.31: The upper part of the figure shows the three individual input tracks, arranged for simplicity in a track list. The lower part of the figure shows the resulting stand-alone annotated read mapping.
Likewise it is possible to create an annotated, stand-alone reference from a reference track and the desired number of annotation tracks. This is shown in figure 27.32 where one reference and two annotation tracks are used as input.
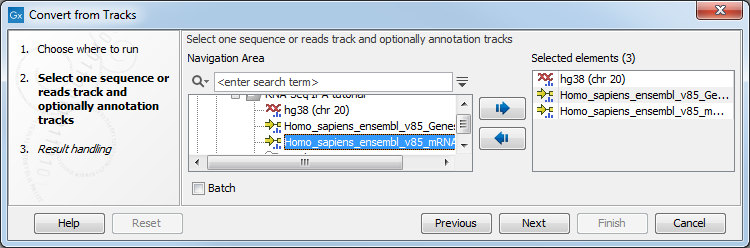
Figure 27.32: A reference track and two annotation tracks are converted from track format to stand-alone format.
The output is shown in figure 27.33. The reference sequence has been transformed to stand-alone format with the two annotations "CDS" and "Gene".
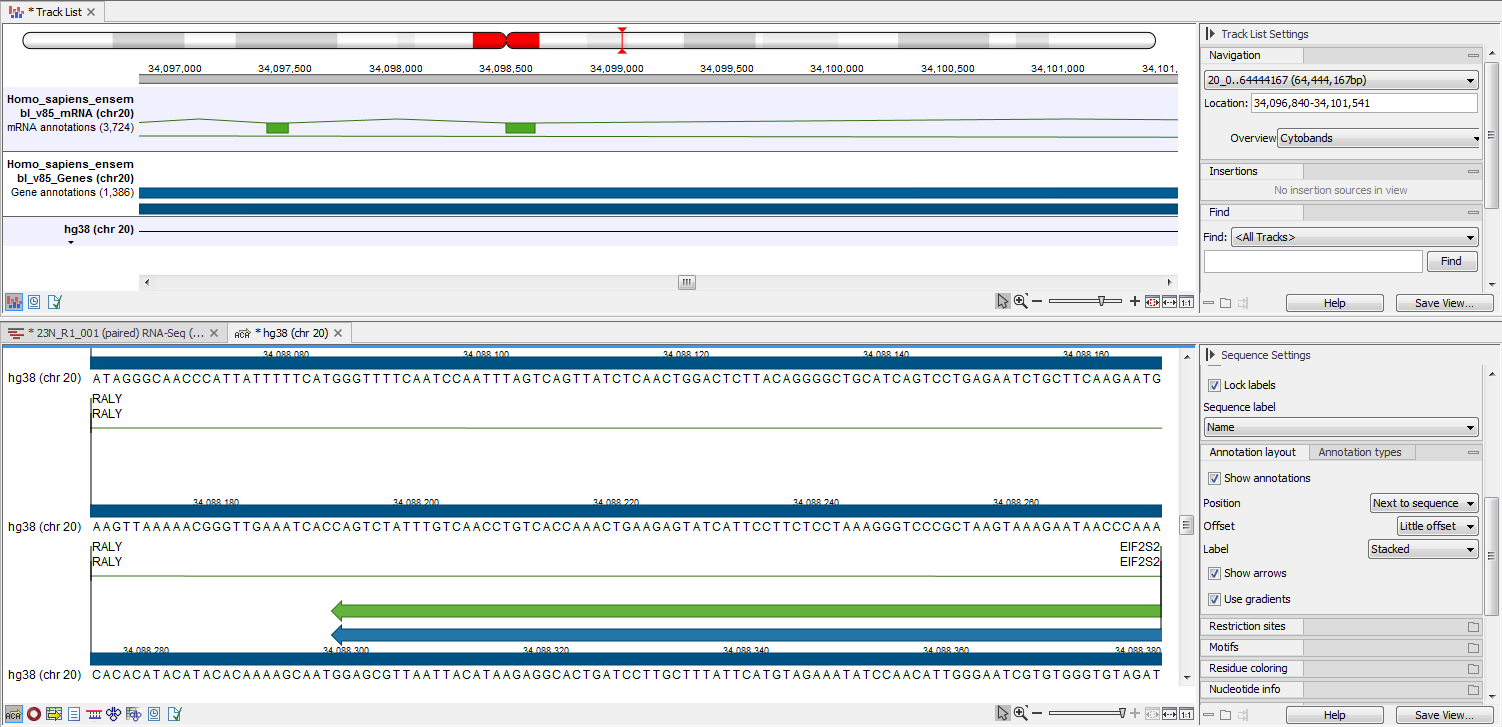
Figure 27.33: The upper part of the figure shows the three input tracks, shown for simplicity in a track list. The lower part of the figure shows the resulting stand-alone annotated reference sequence.
Depending on the input provided, the tool will create one of the following types of output:
- Sequence (
 )
) - Will be created when a sequence track (
 ) with a genome with only one sequence (one chromosome) is provided as input
) with a genome with only one sequence (one chromosome) is provided as input
- Sequence list (
 )
) - Will be created when a sequence track (
 ) with a genome with several sequences (several chromosomes) is provided as input
) with a genome with several sequences (several chromosomes) is provided as input
- Mapping (
 )
) - Will be created when a reads track (
 ) with a genome with only one sequence (one chromosome) is provided as input.
) with a genome with only one sequence (one chromosome) is provided as input.
- Mapping table (
 )
) - Will be created when a reads track (
 ) with a genome with several sequences (several chromosomes) is provided as input.
) with a genome with several sequences (several chromosomes) is provided as input.
