Quantify miRNA
The Quantify miRNA tool counts and annotates miRNAs using miRBase. It maps the reads against the full precursor miRNA and further processes the mapping to produce expression values for:
- Mature miRNAs. Note that the same mature miRNA may be produced from different precursor miRNAs.
- Seeds. Note that the same seed sequence may be found in different mature miRNAs.
The tool performs the mapping using unique search sequences, i.e. collapsed identical reads. This significantly reduces the computational time. The report contains values for both reads and unique search sequences.
The tool will take:
- Trimmed reads (UMI or normal). Reads shorter than 15 bp are ignored.
- A miRBase database. Custom databases that include isoforms of small RNA, such as isopiRNA databases, are not supported.
- Spike-ins (optional): A list of sequences that have been spiked-in. Mapping against this set of sequences will be performed before mapping of the reads against miRBase and other databases. The spike-ins are counted as exact matches and stored in the report for further analysis by the Combined miRNA Report tool.
To run the tool, go to:
Tools | RNA-Seq and Small RNA Analysis (![]() )| miRNA Analysis (
)| miRNA Analysis (![]() ) | Quantify miRNA (
) | Quantify miRNA (![]() )
)
First select the trimmed reads as in figure 33.15.
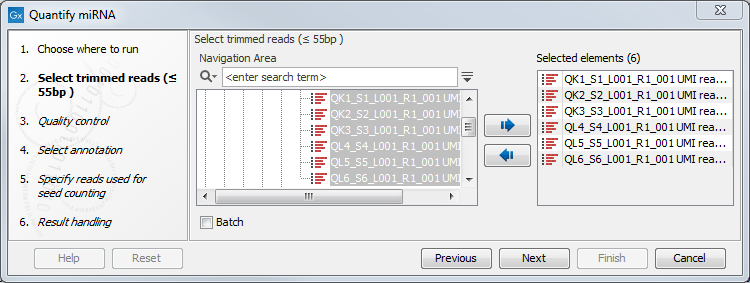
Figure 33.15: Select the reads.
If the sequencing was performed using Spike-ins controls, the option "Enable spike-ins" can be enabled in the Quality control dialog (figure 33.16), and a spike-ins file can be specified. You can also change the Low expression "Minimum supporting count", i.e., the minimum number of supporting reads for a small RNA to be considered expressed.
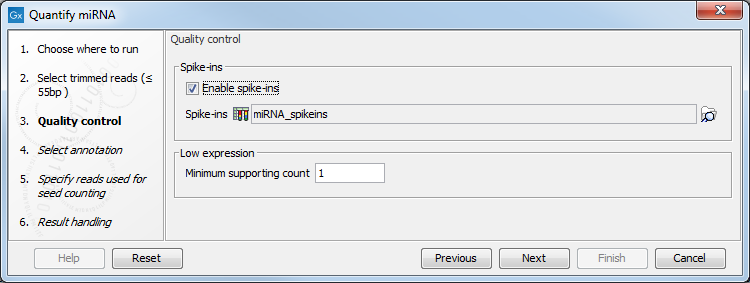
Figure 33.16: Specifying spike-ins is optional, and you can change the threshold under which a small RNA will be considered expressed.
In the annotation dialog, several configurations are available.
In the miRBase annotations section, specify a single reference - miRBase in most cases.
miRBase can be downloaded using the Reference Data Manager under QIAGEN Sets | Reference Data Elements | mirBase (figure 33.17).
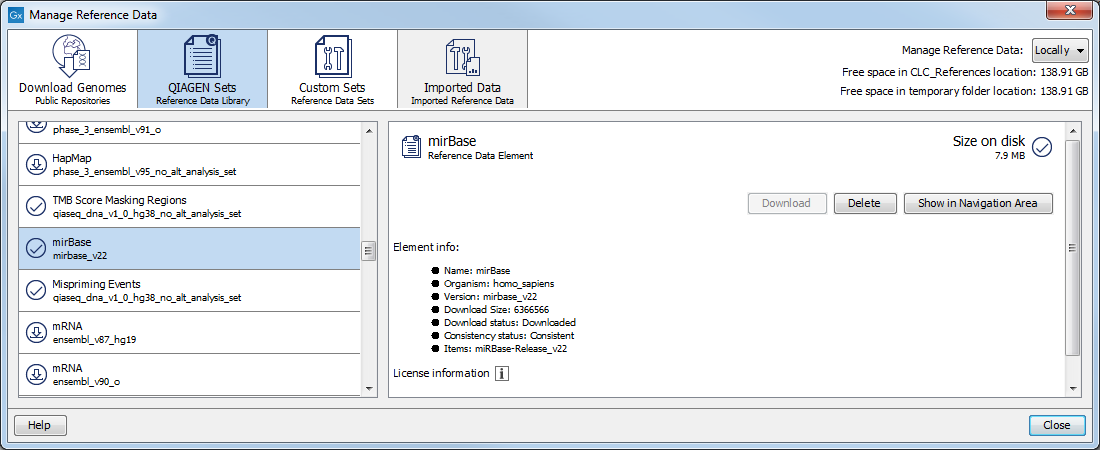
Figure 33.17: Download the latest miRBase database in the Workbench.
You can also import miRBase into the CLC Genomics Workbench using Standard Import (![]() ). The miRBase data file can be downloaded from ftp://mirbase.org/pub/mirbase/CURRENT/miRNA.dat.gz. Select
). The miRBase data file can be downloaded from ftp://mirbase.org/pub/mirbase/CURRENT/miRNA.dat.gz. Select MiRBase (.dat) in the Force import as type menu of the Standard Import dialog. Information about the miRBase dat format is provided in miRBase data file format.
Once miRBase has been selected, click the green plus sign to see the list of species available. It can take a while for all species to load. Species to be used for annotation should be selected using the left and right arrows, and prioritized using the up and down arrows, with the species sequenced always selected as top priority in the list (figure 33.18). The naming of the miRNA will depend on this prioritization.
In addition, it is possible to configure how specific the association between the isomiRs and the reads has to be by allowing mismatches and additional or missing bases upstream and downstream of the isomiR.
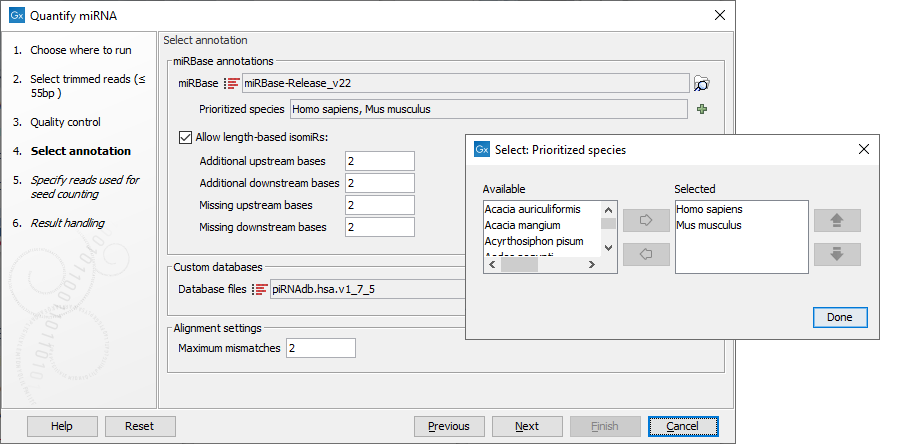
Figure 33.18: Specify and prioritize species to use for annotation, and how stringent the annotation should be.
In the Custom databases, you can optionally add sequence lists with additional smallRNA reference databases, e.g. piRNAs, tRNAs, rRNAs, mRNAs, lncRNAs. An output with quantification against the custom databases can be generated, which can be used for subsequent expression analyses. Reads count towards the reference to which they map best, regardless of which database (miRBase or custom) the reference is from.
Finally, configure the Alignment settings by defining how many "Maximum mismatches" are allowed between the reads and the references, i.e. miRBase and custom databases. Reads matching more than 100 references are ignored.
In the next dialog (figure 33.19), specify the length of the reads used for seed counting. Reads of the specified length, corresponding to the length of mature miRNA (18-25 bp by default, but this parameter can be configured) are used for seed counting. The seed is a 7 nucleotide sequence from positions 2-8 on the mature miRNA. The "Grouped on seed" output table includes a row for every seed that is observed in miRBase together with the expression of the same seed in the sample. In addition, the 20 most highly expressed novel seeds are output in the report.
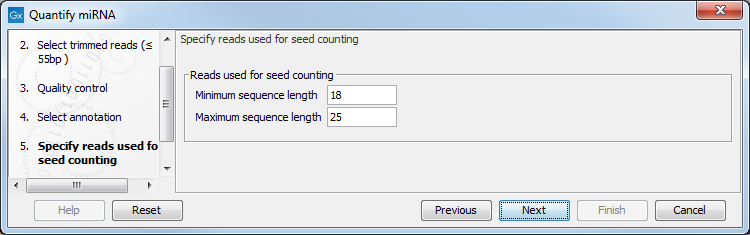
Figure 33.19: This dialog defines the length of the reads that will be merged according to their seed.
The tool will output the following expression tables:
- Grouped on mature, with a row for each mature miRNA in the database
- Grouped on seed, with a row for each seed sequence
- Grouped on custom databases, if one or more custom databases is provided.
Subsections
