Calculate TMB Score
Calculate TMB Score takes a variant track and a matching target regions track, and calculates a TMB score, i.e. the number of somatic mutations per megabase (Mb).
The Calculate TMB Score tool considers only SNVs - and discards variants of any other type. First, it filters variants, keeping only variants that lie within exons, within target regions, and outside the masking regions. It then successively applies various quality, germline, and non-synonymous filters before calculating the TMB score as the number of somatic variants divided by the length of the assessed regions in Mb.
Calculate TMB Score is available from the Tools menu at:
Tools | Biomedical Genomics Analysis (![]() ) | Oncology Score Estimation (
) | Oncology Score Estimation (![]() ) | Calculate TMB Score (
) | Calculate TMB Score (![]() )
)
The tool takes a variant track as input.
In the next dialog, the following tracks are specified (figure 8.1):
- Target regions A track containing target regions with sufficient coverage in all positions. See details below for how to generate such regions.
- Exon regions An mRNA track containing the exons of interest.
- Masking regions Regions that should not be considered.
Only variants inside target regions and exons, and not within regions annotated on the masking track, are considered when calculating the TMB score.

Figure 8.1: Specifying tracks and parameters for calculating a TMB score.
In addition, it is possible to enable the calculation of a TMB status based on a low and a high threshold. The TMB status will appear as an additional item on the TMB report. The default values of 10 and 15, respectively, have been chosen based on internal benchmark analyses of lung cancer cell lines and different tissue cancer samples. Given the lack of standardization of methods and the heterogeneity of tumor mutation burden across many tumor types, it is difficult to establish cutoff values. Thresholds should be set according to the samples analyzed.
In the next dialog, quality filters, germline filters, and a non-synonymous filter can be configured (figure 8.2):

Figure 8.2: Specifying filters for calculating a TMB score.
- Quality filters
- Minimum average quality The average quality score of reads calculates the amount of sequences that feature individual PHRED-scores in 64 bins from 0 to 63. The quality score of a sequence is calculated as arithmetic mean of its base qualities. PHRED-scores of 30 and above are considered high quality.
- Minimum QUAL Measure of the significance of a variant, i.e., a quantification of the evidence (read count) supporting the variant, relative to the coverage and what could be expected to be seen by chance, given the error rates in the data.
The mathematical derivation depends on the set of probabilities of generating the nucleotide pattern observed at the variant site (1) by sequencing errors alone and (2) under the different allele models the variant caller allows.
QUAL is calculated as
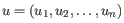 ,
, 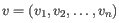 being the probability that a particular variant exists in the sample.
QUAL is capped at 200 for
being the probability that a particular variant exists in the sample.
QUAL is capped at 200 for 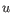 (200 is highly significant, 0 is insignificant).
In rare cases, the QUAL value cannot be calculated for a specific variant and as a result the QUAL field will be empty. This value is necessary for certain downstream analyses of the data after export in VCF format. A QUAL value of 10 indicates a 1 in 10 chance that the called variant is an error, while a QUAL of 100 indicates a 1 in
(200 is highly significant, 0 is insignificant).
In rare cases, the QUAL value cannot be calculated for a specific variant and as a result the QUAL field will be empty. This value is necessary for certain downstream analyses of the data after export in VCF format. A QUAL value of 10 indicates a 1 in 10 chance that the called variant is an error, while a QUAL of 100 indicates a 1 in 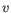 chance that the called variant is an error.
chance that the called variant is an error.
- Minimum coverage Only variants in regions covered by at least this many reads are used for TMB calculation. The minimum coverage filter used here should match the minimum coverage of target regions provided in the Specify settings step (figure 8.1).
- Minimum count Only variants that are present in at least this many reads are used for TMB calculation.
- Minimum frequency (%) Only variants with a detected frequency above this value are used for TMB calculation.
- Minimum read position test probability Tests whether the distribution of the read positions in the variant-carrying reads is different from that of all the reads covering the variant position (1 is well-balanced, 0 is unbalanced).
- Minimum read direction test probability Tests whether the distribution among forward and reverse reads of the variant-carrying reads is different from that of all the reads covering the variant position. This value reflects a balanced presence of the variant in forward and reverse reads (1 is well-balanced, 0 is unbalanced).
- Minimum average quality The average quality score of reads calculates the amount of sequences that feature individual PHRED-scores in 64 bins from 0 to 63. The quality score of a sequence is calculated as arithmetic mean of its base qualities. PHRED-scores of 30 and above are considered high quality.
- Germline filters
- Maximum frequency Only variants whose frequency is equal to or lower than the specified value will be considered. Variants with a frequency above this value are considered germline.
- Variant databases Specify a variant database such as dbSNP. Although dbSNP is thought to contain many erroneous calls, these may still be useful for removing variants that are not somatic, for example if they arise from common sequencing artifacts.
- Non-synonymous filter When enabled, only variants causing amino acid changes are considered for the TMB score calculation. Input variants must be annotated using Amino Acid Changes in order to filter non-synonymous variants.
Note that the default TMB filtering parameters are set conservatively. This is because for panels of 1Mb size, a single false positive variant may increase the TMB score substantially.
Generate target regions with sufficient coverage
Since the TMB score is calculated as the number of mutations per Mb, the minimum coverage used to filter somatic variants must also be used for calculating the length of assessed regions. By default, the minimum coverage threshold is set to 100x.
We recommend running Calculate TMB Score from a workflow including the tools Create Mapping Graph and Identify Graph Threshold Areas to generate target regions with sufficient coverage (figure 8.3). The same coverage threshold should then be used for Identify Graph Threshold Area and for Calculate TMB Score.

Figure 8.3: Workflow for identifying target regions with sufficient coverage and calculating a TMB score.
Output from Calculate TMB Score
The Calculate TMB Score tool generates two outputs:
- TMB report A report containing the TMB score and information about variant filtering (figure 8.4).
- Somatic variants A filtered variant track with variants used for calculating the TMB score.
The TMB report includes the TMB status when enabled in the Specify settings step (figure 8.1). By default, the TMB status is considered low if the TMB score is lower than 10; intermediate if the TMB score is between 10 and 15; and high if the TMB score is larger than 15.

Figure 8.4: A TMB report where the option to detect TMB status was enabled with default threshold values.
The Length of assessed regions (bp) is the length of the provided target regions overlapping exons and not included in the masking regions. The TMB status is assessed with a confidence level based on the length of the assessed regions. This is illustrated by the color of the TMB status table cell in the report. If the length of the assessed regions is below 900,000bp the cell will be colored in red, if it is between 900,000bp and 1,000,000bp it will be colored in yellow and if it is above 1,000,000bp it will not be colored. Note that if low coverage regions are not excluded from the target regions before TMB score calculation (as shown in figure 8.3), the TMB status confidence level may wrongly be displayed as high.
Additionally, the report lists the number of various types of variants based on germline, non-coding, and non-synonymous filter.
The Quality filters statistics section recapitulates how many variants were removed by the various filters applied by the tool, along with the frequency distributions of input and somatic variants.
