Extract Reads Matching Primers
Contamination of next generation sequencing data is a common problem. Some of the problems when analyzing RNA sequencing data are caused by the presence of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) or genomic DNA (gDNA) in the sample. Likewise, RNA contamination can be a problem in DNA sequencing data.
Depletion of rRNA from RNA sequencing experiments is often performed using polyA enrichment for retaining RNA molecules with a polyA tail, a common feature of protein coding transcripts, and in this way eliminating rRNA sequences. Although the positive polyA selection usually is an efficient way to get rid of rRNA, polyA rich rRNA sequences do exist, and this type of rRNA may remain in sample.
A number of QIAseq RNA sequencing protocols can benefit from cleaning up the reads prior to mapping to remove contaminating rRNA reads. Using panel primer sequences as anchor, to only keep reads that match a primer sequence, can eliminate potential rRNA sequences. This is of particular importance when detecting gene fusions as polyA rich rRNA sequences can produce false positive gene fusions. Removal of these polyA rich rRNA sequences not only increases the quality of the fusion call but also decreases the run time as less fusion events are formed and analyzed.
In multi-modal applications, the presence of contaminating RNA in the DNA samples can also lead to false positive variant calls due to the different nature of the read composition where especially InDels are problematic, but also RNA editing can introduce variants that are RNA editing artifacts.
To improve the sample purity and thereby potentially decreasing the number of false positive calls it can be useful to remove reads that do not match any primers. The tool "Extract Reads Matching Primers" extracts reads that match a primer and discards reads that do not match a primer. The tool takes unmapped DNA or RNA sequencing reads as input. We recommend using the "Extract Reads Matching Primers" tool on the raw sequencing reads before analyzing the data.
To run the Extract Reads Matching Primers tool, go to:
Toolbox | Biomedical Genomics Analysis (![]() ) | Biomedical Utility Tools (
) | Biomedical Utility Tools (![]() ) | Extract Reads Matching Primers (
) | Extract Reads Matching Primers (![]() )
)
After you have specified whether you want to run the job locally or connected to a server, you are asked to select sequencing reads (figure 6.1).
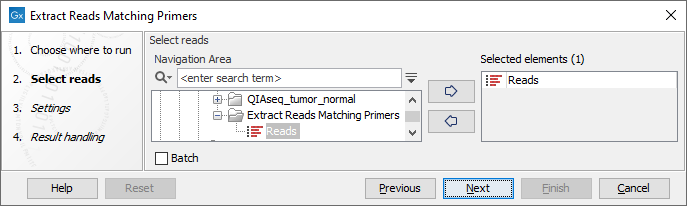
Figure 6.1: Select unmapped sequencing reads.
In the next dialog a number of different settings can be adjusted (figure 6.2).
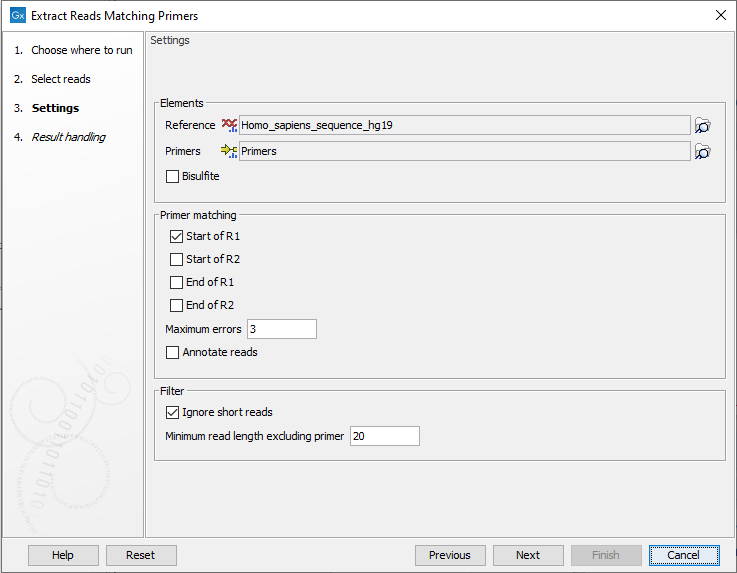
Figure 6.2: In addition to selecting reference sequence and the relevant primer track, different settings can be adjusted in this dialog.
The settings you can specify or adjust are:
- Elements
- Reference A reference sequence track (
 ) compatible with the selected primer track.
) compatible with the selected primer track.
- Primers A track containing the original primers and their intended primer locations (
 ). A description of how to import pairs of primers can be found in the Import Primer Pairs section of the CLC Genomics Workbench manual:
http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Import_Primer_Pairs.html. A description of how to import QIAGEN primers can be found in Import QIAGEN Primers.
). A description of how to import pairs of primers can be found in the Import Primer Pairs section of the CLC Genomics Workbench manual:
http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Import_Primer_Pairs.html. A description of how to import QIAGEN primers can be found in Import QIAGEN Primers.
- Bisulfite Check this box if you are analyzing methylation data using bisulfite converted primer sequences.
- Reference A reference sequence track (
- Primer matching
- Primer location Allows specification of where the primers are located on the input reads. One or more of the following options can be selected:
- Start of R1 The primers are found in the beginning of the R1 reads for paired-end reads or in the beginning of all reads for single-end reads.
- Start of R2 The primers are found in the beginning of the R2 reads for paired-end reads or in the beginning of all reads for single-end reads.
- End of R1 The primers are found at the end of R1 reads for paired-end reads or at the end of all reads for single-end reads.
- End of R2 The primers are found at the end of R2 reads for paired-end reads or at the end of all reads for single-end reads.
- Maximum errors The maximum number of mismatches allowed between the primer sequence and the read sequence. A read and a primer are not matched if the number of mismatches between primer and read exceeds the specified number of Maximum errors.
- Annotate reads Annotates each extracted read with information about whether it should be used for detection of fusions, detection of variants, and quantification of gene expression. This option only has an effect when this information is present on the primers.
- Primer location Allows specification of where the primers are located on the input reads. One or more of the following options can be selected:
- Filter
- Ignore short reads Allows exclusion of short reads that match a primer but where the length of the read excluding the primer sequence is below a length that can be specified under "Minimum read length excluding primer".
- Minimum read length excluding primer. When "Ignore short reads" is checked the "Minimum read length excluding primer" can be specified. Reads matching a primer but where the read excluding the primer sequence is shorter than this value will be discarded.
The output from the "Extract Reads Matching Primers" tool is a list of sequencing reads that match a primer and that have a length that is at least the length of what was specified under "Minimum read length excluding primer" if the option "Ignore short reads" was selected.
