Annotate CDS with Pfam Domains
The Annotate CDS with Pfam Domains tool will allow you to annotate a set of contigs containing CDS annotations with Pfam and GO terms.
To start the analysis, go to:
Microbial Genomics Module (![]() ) | Metagenomics (
) | Metagenomics (![]() ) | Functional Analysis (
) | Functional Analysis (![]() ) | Annotate CDS with Pfam Domains (
) | Annotate CDS with Pfam Domains (![]() )
)
The following parameters are available:
- Genetic code. The genetic code used for translating CDS to proteins.
- Pfam database. The Pfam database. This database can be downloaded using the "Download Pfam Database" tool.
- Use profile's gathering cutoffs. Use cutoffs specifically assigned to each family by the curator instead of manually assigning the Significance cutoff.
- Significance cutoff. The E-value (expectation value) describes the number of hits one would expect to see by chance when searching a database of a particular size.
- Remove overlapping matches from the same clan. Perform post-processing of the results where overlaps between hits are resolved by keeping the hit with the smallest e-value.
- GO database. The GO database, used to map between Pfam domains and GO terms. The GO database can be downloaded using the Download GO Database tool ((see section "Download GO database" ). If the database is not specified, no GO annotation will be added.
- GO subset. A subset of the GO database. Since many GO terms are too general or too specific, several meaningful subsets of GO terms are provided. See http://geneontology.org/page/go-slim-and-subset-guide.
If you select Create report, the tool will create a summary report table. The report is divided in three parts
- Input. Contains information about the size of the contigs and CDS used as input.
- Output. The total number (and percent) of CDS that were annotated with a Pfam domain or a GO term, as well as the total number of Pfam domains and GO terms added.
- Pfam database.The Pfam database used in the search together with its version and size.
- GO database. The GO database (or subset) used in the search together with its version, size, and the number of Pfam domains mapping to at least one term.
When a Pfam domain is found in a CDS, the tool adds a new Pfam annotation, as shown in figure 6.3. The annotation contains the following fields:
- Description. A description of the Pfam domain.
- Accession. The accession number of the Pfam domain.
- Clan. The clan that the domain belong to (if any).
- Score. The score
- E-value. The E-value of the match.
- CDS. The CDS that contains this domain.
- Protein. The protein region (in aa coordinates) that encodes for the domain.
- GO cellular component. GO terms of the cellular component domain which are related to the Pfam domain.
- GO molecular function. GO terms of the molecular function domain which are related to the Pfam domain.
- GO biological process. GO terms of the biological process domain which are related to the Pfam domain.
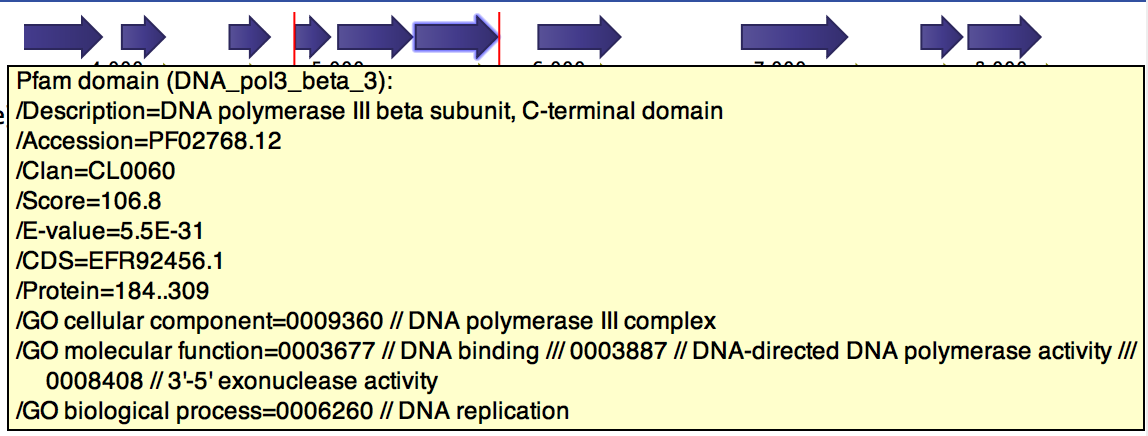
Figure 6.3: Pfam and GO annotations added to gene cds4 of h. pylori.
