Translation of DNA or RNA to protein
To translate a nucleotide sequence into a protein sequence use the Translate to Protein tool, available at:
Tools | Nucleotide Analysis (![]() )| Translate to Protein (
)| Translate to Protein (![]() )
)
This opens the dialog displayed in figure 19.4:
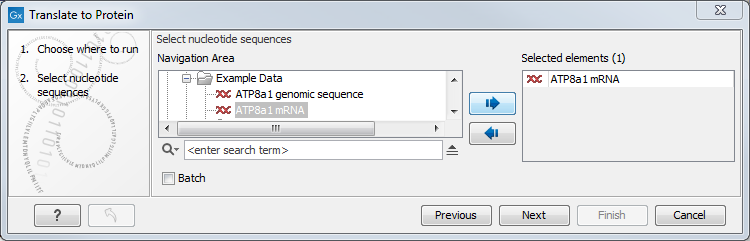
Figure 19.4: Choosing sequences for translation.
Use the arrows to add or remove sequences or sequence lists from the selected elements list.
Clicking Next generates the dialog seen in figure 19.5:
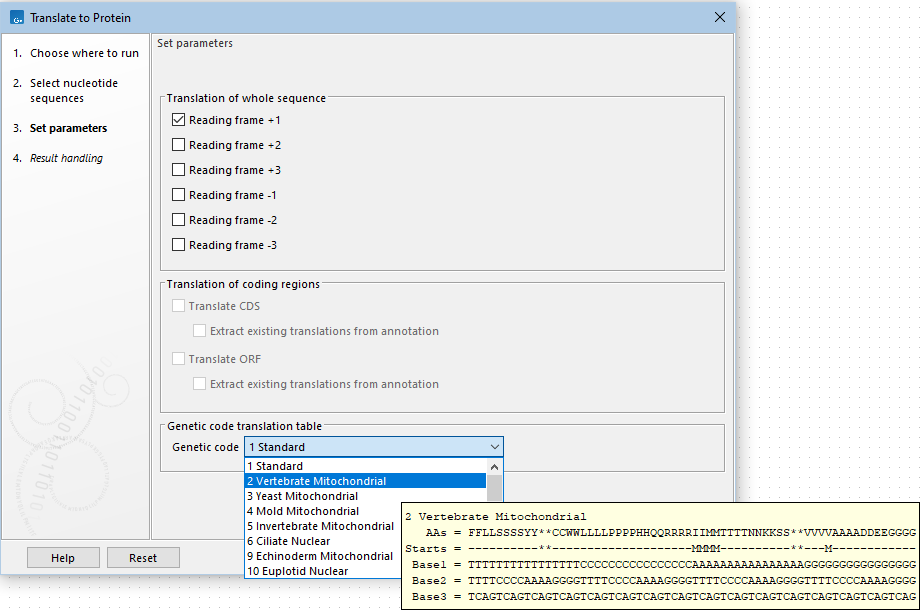
Figure 19.5: Configure the translation options. Hover the mouse cursor over a genetic code option to reveal a tooltip containing the relevant translation table.
Here you have the following options:
- Reading frames
- If you wish to translate the whole sequence, you must specify the reading frame for the translation. If you select e.g. two reading frames, two protein sequences are generated.
- Translate CDS
- You can choose to translate regions marked by and CDS or ORF annotation. This will generate a protein sequence for each CDS or ORF annotation on the sequence. The "Extract existing translations from annotation" allows to list the amino acid CDS sequence shown in the tool tip annotation (e.g. interstate from NCBI download) and does therefore not represent a translation of the actual nt sequence.
- Genetic code
- Specify the genetic code to use. Hover the mouse cursor over an item in this list to reveal a tooltip containing the relevant translation table (figure 19.5). The translation tables are sourced from the NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Utils/wprintgc.cgi).
Stop codons result in an asterisk being inserted in the protein sequence at the corresponding position.
Click Finish to start the tool. The newly created protein is shown, but is not saved automatically.
To save a protein sequence, drag it into the Navigation Area or press Ctrl + S (![]() + S on Mac) to activate a save dialog.
+ S on Mac) to activate a save dialog.
The name for a coding region translation consists of the name of the input sequence followed by the annotation type and finally the annotation name.
Translate part of a nucleotide sequence
If you want to make separate translations of all the coding regions of a nucleotide sequence, you can check the option: "Translate CDS/ORF..." in the translation dialog (see figure 19.5).
If you want to translate a specific coding region, which is annotated on the sequence, use the following procedure:
Open the nucleotide sequence | right-click the
ORF or CDS annotation | Translate
CDS/ORF... (![]() )
)
A dialog opens to offer you the following choices (figure 19.6):
- Select a genetic code translation table Translates the ORF/CDS to protein using the selected translation table. Hover the mouse cursor over an item in this list to reveal a tooltip containing the relevant translation table (figure 19.5). The translation tables are sourced from the NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Utils/wprintgc.cgi).
- Extract existing translation from annotation Translates the ORF/CDS to protein using existing translation information available in the annotation.
Choose the option needed and click Translate.
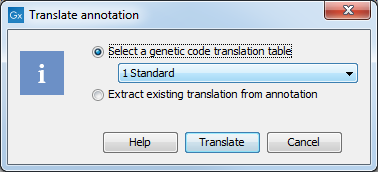
Figure 19.6: Choosing how to translate CDS or ORF annotations.
The CDS and ORF annotations are colored yellow as default.
