Shuffle sequence
In some cases, it is beneficial to shuffle a sequence, for example, when for statistical analyses when comparing an alignment score with the distribution of scores of shuffled sequences.
Shuffling a sequence removes all annotations that relate to the residues. To launch the Shuffle Sequence tool, go to:
Tools | General Sequence Analysis (![]() )| Shuffle Sequence (
)| Shuffle Sequence (![]() )
)
Use the arrows to add or remove sequences or sequence lists from the selected elements list.
Click Next to determine how the shuffling should be performed.
In this step, shown in figure 18.4:
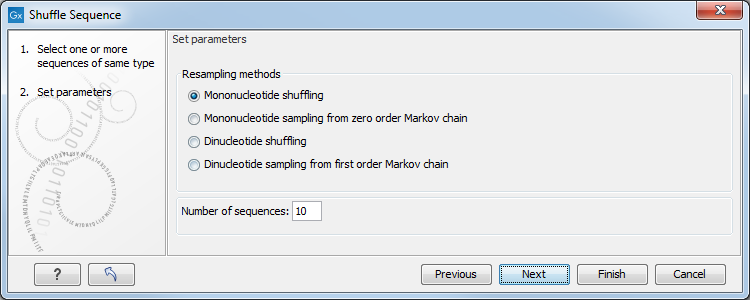
Figure 18.4: Parameters for shuffling.
For nucleotides, the following parameters can be set:
- Mononucleotide shuffling. Shuffle method generating a sequence of the exact same mononucleotide frequency
- Dinucleotide shuffling. Shuffle method generating a sequence of the exact same dinucleotide frequency
- Mononucleotide sampling from zero order Markov chain. Resampling method generating a sequence of the same expected mononucleotide frequency.
- Dinucleotide sampling from first order Markov chain. Resampling method generating a sequence of the same expected dinucleotide frequency.
For proteins, the following parameters can be set:
- Single amino acid shuffling. Shuffle method generating a sequence of the exact same amino acid frequency.
- Single amino acid sampling from zero order Markov chain. Resampling method generating a sequence of the same expected single amino acid frequency.
- Dipeptide shuffling. Shuffle method generating a sequence of the exact same dipeptide frequency.
- Dipeptide sampling from first order Markov chain. Resampling method generating a sequence of the same expected dipeptide frequency.
Click Finish to start the tool.
This will open a new view in the View Area displaying the
shuffled sequence. The new sequence is not saved automatically. To
save the sequence, drag it into the Navigation Area or press
ctrl + S (![]() + S on Mac) to activate a save dialog.
+ S on Mac) to activate a save dialog.
