Extract sequences from tracks
Note that the functionalities described in this page are valid for sequence or reads tracks. For similar functionalities on read mappings, see Extract reads from a mapping.
Extracting the sequence from a sequence track
It is possible to extract a DNA sequence from a sequence track included in a Track List with the Extract Sequence... option of the right-click menu on the sequence (menu to the right of figure 24.12). In this case, a pop up window proposes to Extract annotations, which will extract all the annotations present on the other tracks of the Track list, and add them to the extracted sequence.
Note that it is possible to extract the sequence of a single sequence track, but in this case (the track is not included in a track list), or when the sequence track is in a track list that does not contain annotation tracks, the option to Extract annotations is unavailable.
Extracting a single read/sequence from a reads track
Right-click on the sequence of interest and choose the Selected read... option to Copy, Open in a new view or Blast the selected sequence.
Extracting all reads/sequences from a track
Use the tool Extract Sequences from the Toolbox to extract sequences from the subset reads track as described in Extract sequences.
Extracting only selected reads/sequences from a track
The sequences of interest can be selected by dragging the mouse over the region of interest, followed by a right click on the reads (or on the sequences in the case of a sequence track) and a click on Create Reads Track from Selection (as can be seen on the menu to the left in figure 24.12).
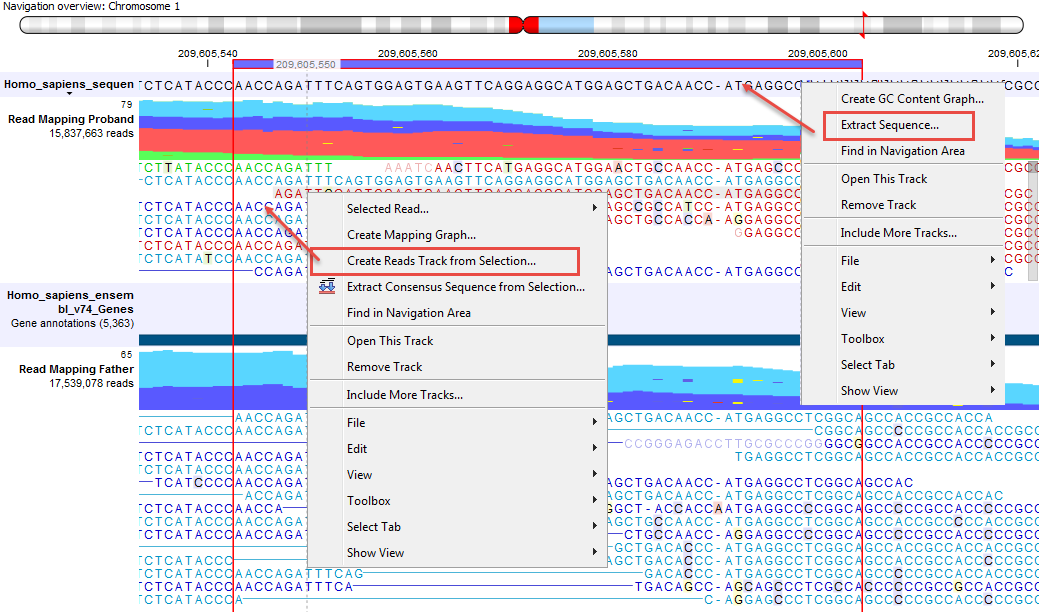
Figure 24.12: Extract sequences from a read mapping track. This screenshot shows the menus available when right-clicking on the reference sequence and the sequences/reads in the tracks below.
An Extract from Selection pop up dialog lets you specify what kind of reads you want to include in the subset of the original reads track (figure 24.13).
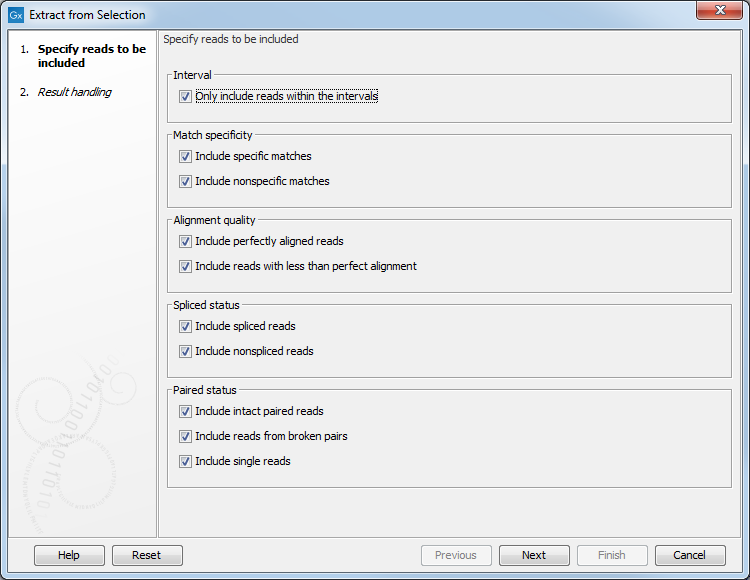
Figure 24.13: Selecting the reads to include.
Per default all reads are included. The options are:
- Paired status
- Include intact paired reads. When paired reads are placed within the paired distance specified, they will fall into this category. Per default, these reads are colored in blue.
- Include paired reads from broken pairs. When a pair is broken, either because only one read in the pair matches, or because the distance or relative orientation is wrong, the reads are placed and colored as single reads, but you can still extract them by checking this box.
- Include single reads. This will include reads that are marked as single reads (as opposed to paired reads). Note that paired reads that have been broken during assembly are not included in this category. Single reads that come from trimming paired sequence lists are included in this category.
- Match specificity
- Include specific matches. Reads that only are mapped to one position.
- Include non-specific matches. Reads that have multiple equally good alignments to the reference. These reads are colored yellow per default.
- Alignment quality
- Include perfectly aligned reads. Reads where the full read is perfectly aligned to the reference sequence (or consensus sequence for de novo assemblies). Note that at the end of the contig, reads may extend beyond the contig (this is not visible unless you make a selection on the read and observe the position numbering in the status bar). Such reads are not considered perfectly aligned reads because they don't align in their entire length.
- Include reads with less than perfect alignment. Reads with mismatches, insertions or deletions, or with unaligned nucleotides at the ends (the faded part of a read).
- Spliced status
- Include spliced reads. Reads that are across an intron.
- Include non spliced reads. Reads that are not across an intron.
