Variant Detectors - overview
Biomedical Genomics Workbench offers three tools for detecting variants.
- Basic Variant Detection (
 ) - described in detail in section Basic Variant Detection
) - described in detail in section Basic Variant Detection
- Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection (
 ) - described in detail in section Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection
) - described in detail in section Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection
- Low Frequency Variant Detection (
 ) - described in detail in section Low Frequency Variant Detection.
) - described in detail in section Low Frequency Variant Detection.
They are designed for the analysis of different types of samples and they differ in their underlying assumptions about the data, and hence in their assessments of when there is enough information in the data for a variant to be called. An overview of these differences is given in figure 21.55.
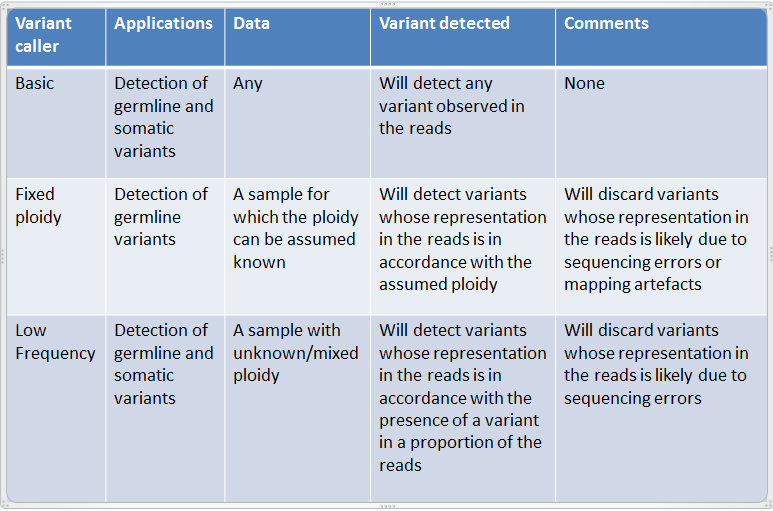
Figure 21.55: An overview of the variant detection tools.
Note that the 'Basic Variant Detection' and the 'Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection' tools are new versions of respectively the 'Quality-based Variant Detection' and the 'Probabilistic Variant Detection' tools, where the filtering options have been unified and extended. The 'Quality-based Variant Detection' and the 'Probabilistic Variant Detection' are now considered legacy tools and have been moved to the Legacy Tools section of the Workbench Toolbox. These tools will be retired in a later version of the software.
To run a variant detection tool, go to:
Toolbox | Resequencing Analysis (![]() ) | Variant Detectors
) | Variant Detectors
If you double-click on one of the tools, a dialog is opened where you can select the reads track or read mapping to analyze.
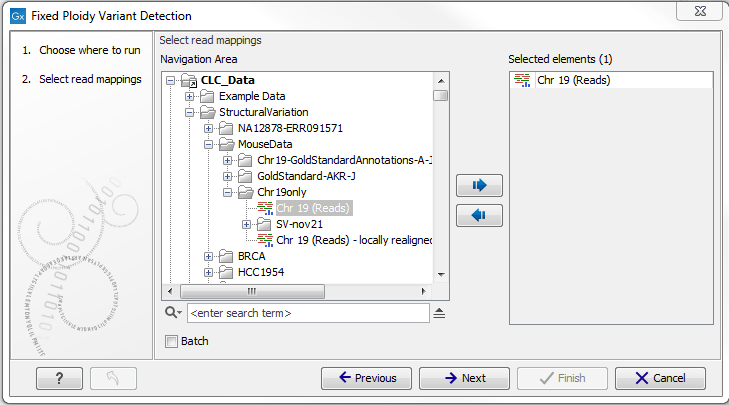
Figure 21.56: Select the read mapping that you want to analyze.
Click on the Next button when the reads track or mapping has been added to the right-hand side of the dialog.
The user is next asked to set the parameters that are specific for the variant detection tool. The three tools, their assumptions, and the tool-specific parameters are described later in their respective sections.
All variant detection tools will call:
- SNVs - single nucleotide variants
- MNVs - neighbording SNVs, where there is evidence they occur together
- small to medium-sized insertions and deletions - insertions and deletions fully represented within a single read
- replacements - neighboring SNVs and insertions or deletions
Subsections
