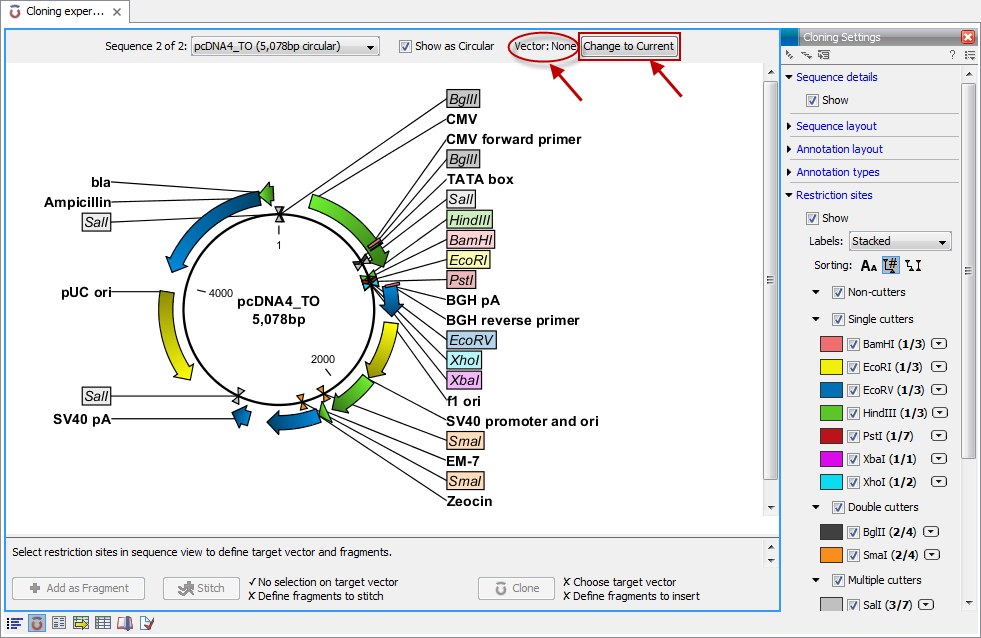
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a very important tool in the quest to
understand gene function and regulation. Through molecular cloning
it is possible to study individual genes in a controlled
environment. Using molecular cloning it is possible to build
complete libraries of fragments of DNA inserted into appropriate
cloning vectors.
The in silico cloning process in Biomedical Genomics Workbench begins with the selection of sequences to be used:
Toolbox | Cloning and Restriction Sites (![]() )| Cloning (
)| Cloning (![]() )
)
This will open a dialog where you can select the sequences containing the fragments you want to clone as well as sequences to be used as vector (figure 30.1).
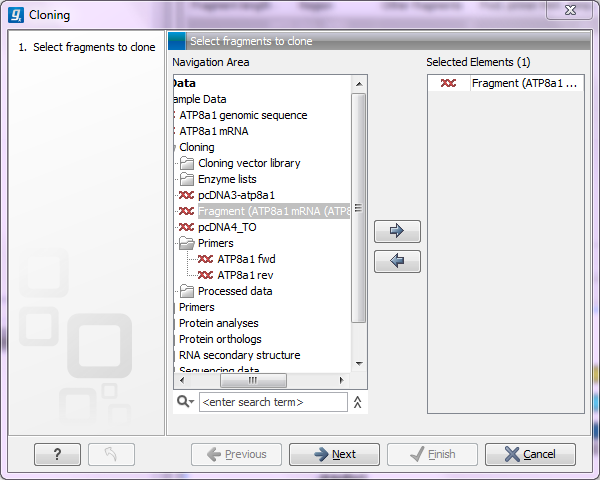
Figure 30.1: Selecting one or more sequences containing the fragments you want to clone.
The Biomedical Genomics Workbench will now create a sequence list of the selected fragments and vector sequences (if you have selected both fragments and vectors) and open it in the cloning editor as shown in figure 30.2.
When you save the cloning experiment, it is saved as a
Sequence list. See Sequence lists
for more information about sequence lists. If you need to open the list later for cloning work, simply switch to the Cloning (![]() ) editor at the bottom of the view.
) editor at the bottom of the view.
If you later in the process need additional sequences, you can easily add more sequences to the view. Just:
right-click anywhere on the empty white area | Add Sequences
Subsections