Understanding the Bowtie Map configuration
After the bowtie-pp2.xml configuration file has been imported, click the CLC bio Bowtie Map name to see the configuration (figure 16.27).
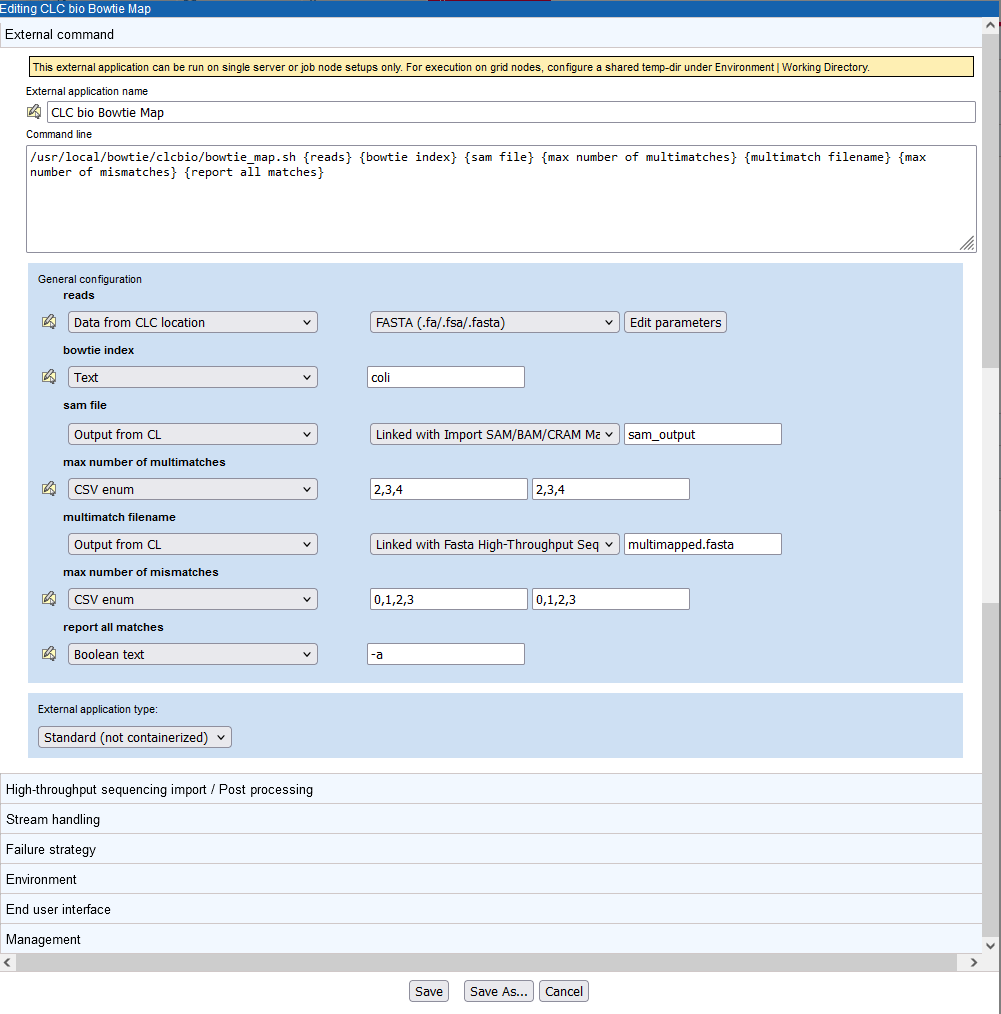
Figure 16.27: The External command tab of the CLC bio Bowtie Map configuration in the external application editor.
When the external application has been saved and is available to end-users, it will be listed under the External Applications menu in the Tools menu in Workbenches. Like for other tools, when an external application is launched, a wizard guides the user. In this case, they are prompted to select sequencing reads to be mapped, to identify the pre-built index file of the reference sequence to use and to configure other options, according to what options have been made available in the external application configuration. Once running, the bowtie executable is run on the server system and the results generated are imported into a CLC Server location using post-processing tools. The sam mapping file is imported using the Import SAM/BAM/CRAM Mapping Files tool. A fasta file of sequences mapping to multiple locations is imported using the Fasta High-Throughput Sequencing Import tool.
Below, we step through the General configuration panel and then explain the configuration of the post processing tools that handle the outputs from the bowtie analysis.
General configuration panel
Each of the parameters (items within curly brackets) written into the "Command line" box is presented as an item in the General configuration panel. There, we define the type of information each parameter expects or represents and default values, where relevant.
To understand how these parameters relate to the information that will be passed to the native bowtie executable, please refer to the bowtie_map.sh script in the clcbio folder that should now be in place in the bowtie distribution folder.
Stepping through the parameters in the order they appear in the "Command line" area of the configuration, and thus the order they appear in the General config panel:
- The reads parameter refers to the data that will be provided to bowtie to map.
The Data from CLC location option means users will be prompted to select data from a CLC location for analysis. This data will be exported, such that the bowtie tool can use it. The second element in this line specifies the format the data should be exported to. This is set to FASTA (.fa/.fsa/.fasta) as this is the format the bowtie tool expects sequencing read data.
- The bowtie index parameter expects the name of a bowtie index. Specifying the type Text for this parameter means a user will see a box in the Workbench wizard that they can type text into. Here, a default name, "coli" has been specified, which can be changed when launching this tool.
For options like this, a more user-friendly choice that would be less subject to user error would be CSV enum. With that type, a list of indices can be entered, which is then presented to the Workbench user as a drop-down list they can choose an item from. An example of a parameter using this type is max number of multimatches, described below.
- The sam file parameter refers to the sam mapping file that bowtie generates as one of its results file. Thus, the type is set to Output file from CL. Import of sam files into the CLC Server involves a tool that requires user input. Thus, a post processing tool is configured. This can be seen immediately by the text in the second drop-down box: "Linked with Import SAM/BAM/CRAM Mapping Files".
If a parameter with type Output file from CL is not mapped to a parameter of a post processing step, the text displayed is "Do not standard import / map to high-throughput sequencing importer". Mapping of outputs to post processing tools is described in more detail below.
The last entry in the configuration of the sam file parameter is the name of the sam output file that bowtie should generate. Here it is set to sam_output. This file name is used by the bowtie command. Those launching the external application do not see this file name..
- The max number of multimatches parameter allows a user to select the maximum number of locations a read can map equally well to for it to be included in the mapping. The type is set to CSV enum, which means a user will be able to select a value from a drop down list of the 3 values listed in the last field (2,3,4). The first value will be the default. The values in the middle field are those passed to the bowtie wrapper script and then onto bowtie. So, for example, if "2,3,4" were entered in the middle field, and "two, three, four" in the last field, a user could select the option "two", and bowtie would be sent the value 2.
- The multimatch filename parameter refers to another output from bowtie, this one containing fasta formatted reads that match to multiple locations of the reference equally well. Since it is a result file, the type is set to Output file from CL. We have decided to use a post processing tool to bring the results back into the CLC Server, the Fasta High-Throughput Sequencing Import tool.
- The max number of mismatches parameter allows a user to select the maximum number of mismatches to be allowed between a read and the reference in order for a read to be considered as matching the reference at that location. The type is set to CSV enum, and is presented to a user in the same way as the max number of multimatches parameter described above.
- The report all matches is set to type Boolean text. This is presented as a checkbox in the Workbench launch wizard. When checked, the value in the text field, here "-a", is passed to bowtie. When not checked, nothing is passed to bowtie relating to this setting.
Post processing - importing the results from Bowtie
Click on the High-throughput sequencing import /Post-processing tab to expand this area. Two post-processing tools are specified in this configuration: Import SAM/BAM/CRAM Mapping Files and Fasta High-Throughput Sequencing Import.
In each case, clicking on the Edit and map parameters... button below it opens the configuration window for that tool. Here, several types of configuration can be carried out.
- Mapping of outputs of the external application to inputs of the post processing tool.
- Locking or unlocking of parameters, determining which parameters users can alter when launching the tool via the Workbench or Command Line Tools.
- Setting default values for parameters of the external application.
Here, we step through the configuration of the Import SAM/BAM/CRAM Mapping Files tool. The configuration of the Fasta High-Throughput Sequencing Import is similar.
The parameters in the configuration window that opens when the "Edit and map parameters..." button for the Import SAM/BAM/CRAM Mapping Files tool are the same options available when that importer is run directly in a CLC Workbench.
A locked lock symbol by a parameter means that the user will not be given access to this option when launching the tool. Default settings for lock parameters are used. The locked parameters shown in figure 16.28 indicate that a track will be output rather than a stand-alone read mapping, unmapped reads will be saved, references will not be downloaded from an external source and, had they been, downloaded references will not be saved. Quality scores and sequence names will be kept (not discarded).
By contrast, the References parameter is unlocked. When using the Import SAM/BAM/CRAM Mapping Files tool, users need to specify where the relevant reference sequences are. Thus, this option should be made available for users to configure when the tool is being launched.
The input to the Import SAM/BAM/CRAM Mapping Files also needs to be defined. This is done by mapping the relevant output from the bowtie command to the input parameter for the Import SAM/BAM/CRAM Mapping Files tool. The output from bowtie is defined by the "sam file" parameter, and the relevant input parameter in the import tool is "Selected files". A drop down list of potentially relevant parameters appears to the left of the "Selected files" parameter. In our example, this has already been mapped to the "sam file" parameter of the command, as shown in figure 16.28.
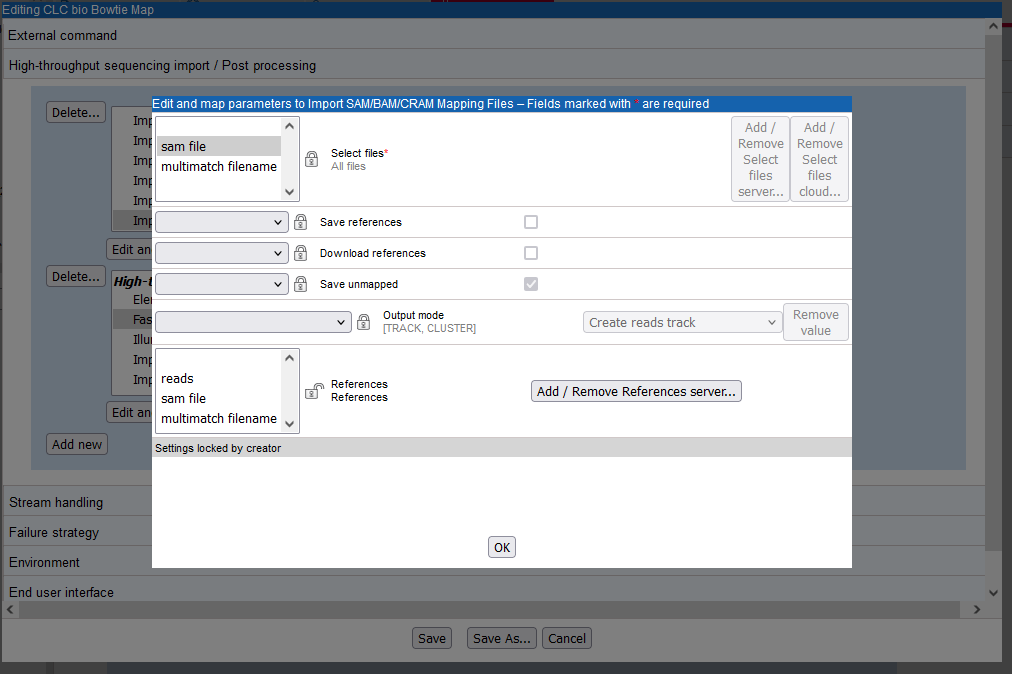
Figure 16.28: Configuration of Import SAM/BAM/CRAM Mapping Files for import of a sam file after mapping using Bowtie. The "Select file" option has been linked with the "sam file" setting in the external application configuration. The References setting is unlocked, so this option will be configurable by the end user.
Note: The drop-down lists of possibly relevant parameters provided in the post processing tool configuration window are populated based only on the types of parameters (in the General configuration pane). Any parameters of a type that could be relevant are presented. This means that some parameters appearing in these lists may not make sense contextually.
Configuring the execution environment
The Environment tab (figure 16.29) includes settings relating to the general environment when the tool is run. This includes the ability to define environmental variables, define the working directory for the external tool, specify how the tool should be executed, and specify whether parameter history should be added to imported objects.
In figure 16.29, a shared location has been specified for the working directory. A shared working directory is necessary when working on a master-node setup, as the files in this area must be accessible to both the master and execution nodes.
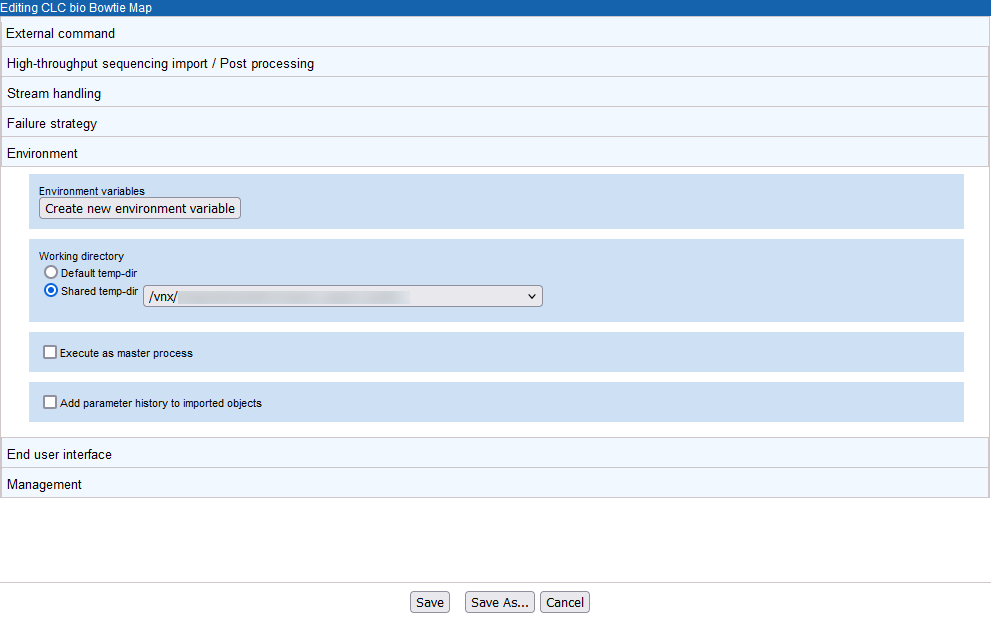
Figure 16.29: A shared directory has been specified as the working directory for bowtie
