Map Long Reads to Reference output
Outputs are selected from the dialog shown in figure 5.3.

Figure 5.3: Map Long Reads to Reference output settings.
The main choice in output format is at the top of the dialog - the read mapping can either be stored as a track or as a stand-alone read mapping. Both options have distinct features and advantages:
- Reads track. A reads track is best used in the context of a Track List, where additional information about the reference, consensus sequence or annotations can be added and viewed alongside the reads. Unless any specific functionality of the stand-alone read mapping is required, we recommend to using the tracks output for the additional flexibility it brings in further analysis.
- Stand-alone read mapping. This output is more elaborate than the reads track and includes the full reference sequence with annotations. A consensus sequence is created as part of the output. Furthermore, the possibilities for detailed visualization and editing are richer than for the reads track. However, stand-alone read mappings do not lend themselves well to comparative analyses. Note that if multiple reference sequences are used as input, a read mapping table is created.
Read more about both output types at http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Reads_tracks_stand_alone_read_mappings.html.
In addition to the choice between the two main output options, the following output options are available:
- Create report. Creates a summary report.
- Collect unmapped reads. Collects all the reads that could not be mapped to the reference into a sequence list.
Map Long Reads to Reference report
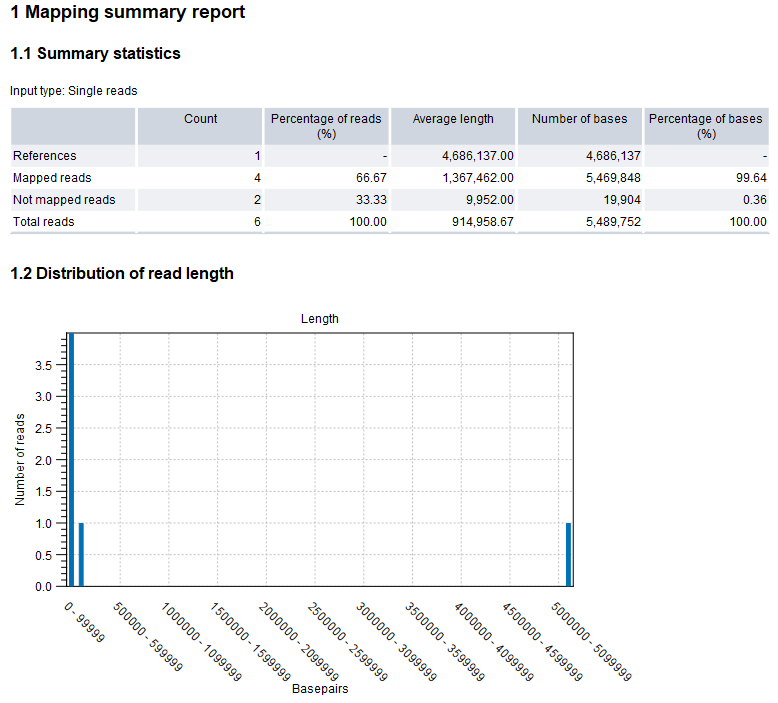
Figure 5.1: Map Long Reads to Reference summary report
The report will summarize the results of the mapping process. An example of the first part of the report is shown in figure 5.4.
The information included in the report is:
- Summary statistics. A summary of the mapping statistics:
- References. The count of reference sequences, the average length, and the total number of bases.
- Mapped reads. The count of mapped reads, the percentage of mapped reads relative to total reads, the average read length, the total number of bases, and the percentage of bases relative to the total read count.
- Not mapped reads. The count of un-mapped reads, the percentage of un-mapped reads relative to total reads, the average read length, the total number of bases, and the percentage of bases relative to the total read count.
- Total reads. The total count of reads, the average read length, and the total number of bases.
- Distribution of read length. A visual representation of the occurrence of each specific read length, offering insights into the overall pattern and variability in the dataset.
- Distribution of mapped reads lengths. Equivalent to the above, but including mapped reads only.
- Distribution of un-mapped reads lengths. Equivalent to the above, but including un-mapped reads only.
