Surfaces
(Molecular surfaces can be visualized.
Five color schemes are available for surfaces:
- Color by Charge. Charged amino acids close to the surface will show as red (negative) or blue (positive) areas on the surface, with a color gradient that depends on the distance of the charged atom to the surface.
- Color by Element. Smoothed out coloring based on the classic CPK coloring of the heteroatoms close to the surface.
- Color by Temperature. Smoothed out coloring based on the temperature values assigned to atoms close to the surface (See the "Wireframe, Stick, Ball and stick, Space-filling/CPK" section above).
- Color by Entry. Each surface is assigned its own specific color.
- Custom Color. The user selects a surface color from a palette.
A surface spanning multiple molecules can be visualized by creating a custom atom group that includes all atoms from the molecules (see Create atom group).
It is possible to adjust the opacity of a surface by adjusting the transparency slider at the bottom of the menu.
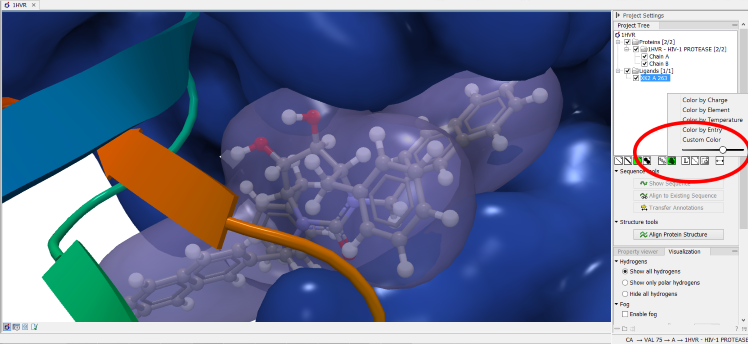
Figure 13.8: Transparent surfaces
Notice that visual artifacts may appear when rotating a transparent surface. These artifacts disappear as soon as the mouse is released.
