Metadata
Metadata refers to information about data. In the context of the CLC Main Workbench, this usually means information about samples. For example a set of reads could come from a particular specimen at a particular time point with particular characteristics. The specimen, time and characteristics would be metadata for that set of reads.
Examples in this chapter refer to tools present in the CLC Genomics Workbench, but the principles apply to other CLC Workbenches.
What is metadata used for?
Core uses of metadata in CLC software include:- Defining batch units when launching workflows in batch mode, described in Running workflows in batch mode.
- Distributing data to the relevant input channels in a workflow when using Collect and Distribute elements, described in the section about control flow elements.
- Finding and selecting data elements based on sample information (in a CLC Metadata Table). Workflow Result Metadata tables are of particular use when reviewing results generated by workflows run in batch mode and are described in Workflow outputs and workflow result metadata tables.
- Running tools where characteristics of the data elements are relevant. An example is Differential Expression for RNA-Seq in the CLC Genomics Workbench, described at http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Differential_Expression_RNA_Seq.html.
Metadata tables
An example of a CLC Metadata Table in the CLC Main Workbench is shown in figure 10.1. Each column represents a property of a sample (e.g., identifier, height, age, treatment) and each row contains information relevant to a sample. A single column can be designated the key column. That column must contain unique entries.
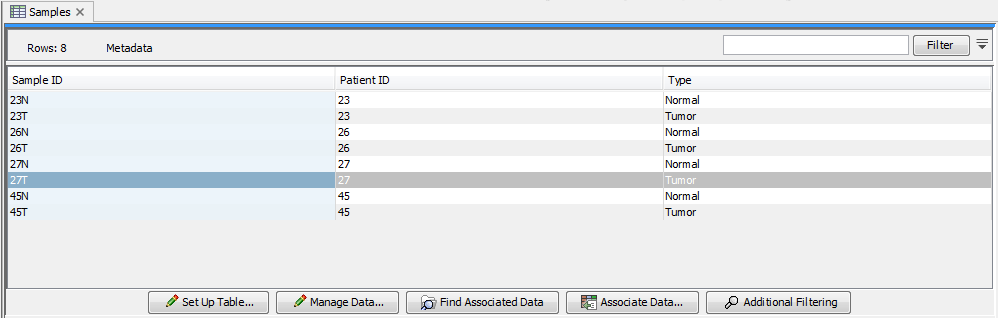
Figure 10.1: A simple metadata table, with the key column highlighted in blue.
Each row can have associations with one or more data elements, such as sequence lists, expression tracks, variant tracks, etc. Associating data elements with relevant metadata rows, automatically or manually, is covered in Associating data elements with metadata
Information from an Excel, CSV or TSV format file can be imported into a CLC Metadata Table, as described in Importing metadata. CLC Metadata Tables are also generated by workflows, as described in Workflow outputs and workflow result metadata tables.
Metadata Elements table
Data elements with an association to a row in a CLC Metadata Table can be listed by selecting the rows of interest and clicking on the Find Associated Data button. The Metadata Elements table opens, with a table of information about elements with associations to the selected rows (figure 10.2).
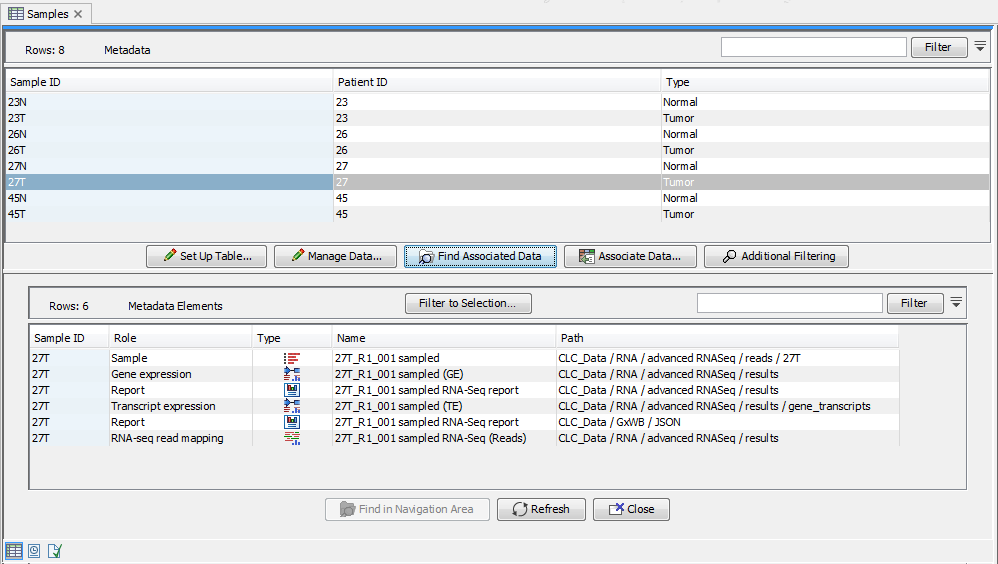
Figure 10.2: A CLC Metadata Table and corresponding Metadata Elements table showing elements associated with sample 27T.
When a data element is associated with a metadata row, the outputs of analyses involving that data usually inherit the metadata association automatically. For example, if a sequence list with an association to a CLC Metadata Table row is used as input to analyses, results of these analyses may also be associated with that row (figure 10.2).
Inheritance of associations to metadata requires that a single association can be unambiguously identified for an output when a tool is run. If an output is derived from two ore more inputs with different metadata associations, then no association will be inherited.
Subsections
- Creating metadata tables
- Associating data elements with metadata
- Working with data and metadata
- Moving, copying and exporting metadata
