Identify and Interpret Causal Variants in a Trio using IVA (WGS)
To run this workflow, go to:
Toolbox | Ready-to-Use Workflows | Whole Genome Sequencing (![]() ) | Hereditary Disease (
) | Hereditary Disease (![]() ) | Identify and Annotate Variants in a Trio using IVA (WGS) (
) | Identify and Annotate Variants in a Trio using IVA (WGS) (![]() )
)
- Double-click on the Identify and Annotate Variants in a Trio using IVA (WGS) tool to start the analysis. If you are connected to a server, you will first be asked where you would like to run the analysis.
- Select the sequencing reads for the proband, father and mother respectively (figure 4.2). You can do that by double-clicking on the reads file name or clicking once on the file and then clicking on the arrow pointing to the right side in the middle of the wizard. Click Next between each family member.
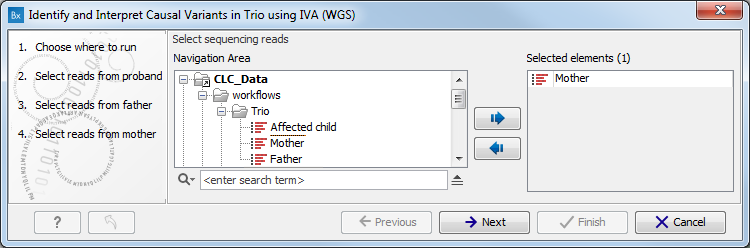
Figure 4.2: Specify the sequencing reads for each family member successively. - Specify the parameters for the Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection tool for the proband, father and mother successively (figure 4.3).
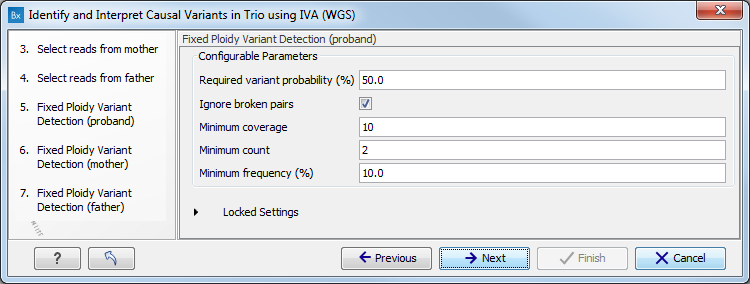
Figure 4.3: Specifying the parameters for the Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection tool.The parameters that can be set are:
- Required variant probability is the minimum probability value of the 'variant site' required for the variant to be called. Note that it is not the minimum value of the probability of the individual variant. For the Fixed Ploidy Variant detector, if a variant site - and not the variant itself - passes the variant probability threshold, then the variant with the highest probability at that site will be reported even if the probability of that particular variant might be less than the threshold. For example if the required variant probability is set to 0.9 then the individual probability of the variant called might be less than 0.9 as long as the probability of the entire variant site is greater than 0.9.
- Ignore broken pairs: When ticked, reads from broken pairs are ignored. Broken pairs may arise for a number of reasons, one being erroneous mapping of the reads. In general, variants based on broken pair reads are likely to be less reliable, so ignoring them may reduce the number of spurious variants called. However, broken pairs may also arise for biological reasons (e.g. due to structural variants) and if they are ignored some true variants may go undetected. Please note that ignored broken pair reads will not be considered for any non-specific match filters.
- Minimum coverage: Only variants in regions covered by at least this many reads are called.
- Minimum count: Only variants that are present in at least this many reads are called.
- Minimum frequency: Only variants that are present at least at the specified frequency (calculated as 'count'/'coverage') are called.
- In the Ingenuity Variant Analysis for Hereditary Diseases window, you need to specify your login information to Ingenuity Variant Analysis (figure 4.4).
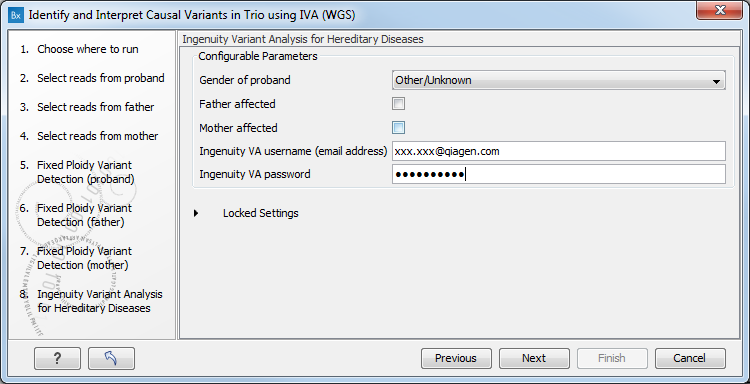
Figure 4.4: Specify login information to Ingenuity Variant AnalysisIt is also possible to configure the following parameters:
- Gender of proband: you can choose between male, female, ambiguous (for babies born with sex chromosomes anomalies or sexual organs that are not yet fully developed) and unknown.
- Check if another family member is affected: the mother or the father.
- Ingenuity VA username: usually the email address you used to sign in the Ingenuity Variant Analysis.
- Ingenuity VA password: the password you chose when you signed in on the Ingenuity website.
- On the last wizard window, pressing the button Preview All Parameters allows you to preview all parameters. At this step you can only view the parameters, it is not possible to make any changes. Choose to save the results and click on the button labeled Finish.
The following outputs are generated:
- 3 Reads Track, one for each family member
- 3 Filtered Variant Track, one for each family member
- A Genome Browser View
- A URL file
- A Recessive-Compound Heterozygous track
- A Recessive-Homozygous track
- A De novo track
- A Dominant track
