The differential accessibility algorithm
The Differential Accessibility for Single Cell tool performs different types of tests for the different data types.
Peaks
As peaks are either present or not in a cell and their counts are not relevant, only the peak presence / absence is used when performing the differential aceessbility test.
The observed presence / absence is modeled using logistic regression. Let ![]() be the presence / absence of the peak and
be the presence / absence of the peak and
![]() , then the form of the model for each peak is:
, then the form of the model for each peak is:
where for cell ![]() ,
, ![]() denotes the group it belongs to, and
denotes the group it belongs to, and ![]() its total peak count. The total peak count is used as a proxy for the total sequencing depth of the cell.
its total peak count. The total peak count is used as a proxy for the total sequencing depth of the cell.
Note that the logistic regression is applied in a pairwise fashion, where ![]() is either 0 or
is either 0 or ![]() .
.
The probability that the peak is present in a specific group
![]() is then estimated as
is then estimated as
where
![]() is the indicator function and
is the indicator function and
![]() is the average
is the average
![]() over all cells.
over all cells.
The following are reported:
- Max group mean. The maximum of the two estimated probabilities.
- Fold change. The ratio between the two estimated probabilities.
- P-value. The p-value that
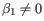 .
.
Nearby Genes and Transcription Factors
When comparing nearby genes or transcription factors, the count data is first normalized using a negative binomial (NB) generalized linear model.
The form of the model for each feature is:
where ![]() are the observed counts for the feature for a cell
are the observed counts for the feature for a cell ![]() . The dispersion parameter
. The dispersion parameter
![]() of the NB distribution is estimated during fitting using the Cox-Reid penalized adjusted likelihood [Robinson et al., 2010]. When
of the NB distribution is estimated during fitting using the Cox-Reid penalized adjusted likelihood [Robinson et al., 2010]. When ![]() (
(
![]() ), the NB distribution reduces to the Poisson distribution.
), the NB distribution reduces to the Poisson distribution.
To obtain the normalized values, the Pearson residuals are calculated as follows:
The Pearson residuals are, however, difficult to interpret, and therefore the following is used for calculating average counts for each group:
The following are reported for pairwise comparisons:
- Max group mean. The maximum of the average
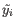 of the two groups.
of the two groups.
- Fold change. The ratio between the average
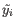 of the two groups.
of the two groups.
- P-value. The p-value obtained from a Mann-Whitney U test (also known as Wilcoxon rank-sum test) on the Pearson residuals.
Note that when identifying markers, the reported `Max group mean', `Fold change' and `P-value', regardless of the data type used for the test, are aggregated across all pairwise comparisons, as detailed in Differential Expression for Single Cell.
For more details on the outputs, see Interpreting the output of Differential Expression for Single Cell.
