Cell Clonotypes alignments
The alignments view (
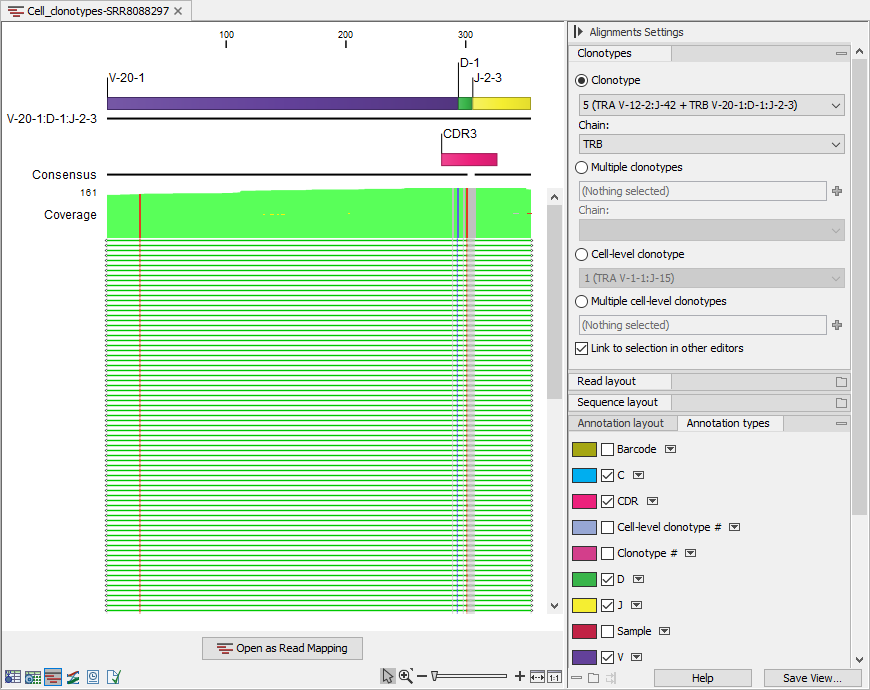
Figure 13.5: Read mapping for the TRB clonotype from a clonotype containing both TRA and TRB. V, D, J and C segments are annotated on the reference sequence and the CDR3 is annotated on the consensus.
The alignment contains:
- The reference sequence consisting of the identified V(D)JC segments. Annotations indicate the location of the different segment types. For clonotypes with ambiguous segments, only one of the identified segments is used.
- The consensus sequence with an annotation indicating the CDR3 region.
- The aligned contigs.
The clonotypes for which the alignment should be shown can be selected from the drop-down menus in the Side Panel, or from one of the clonotype tables (Cell Clonotypes tables) while using a split view (figure 13.6).
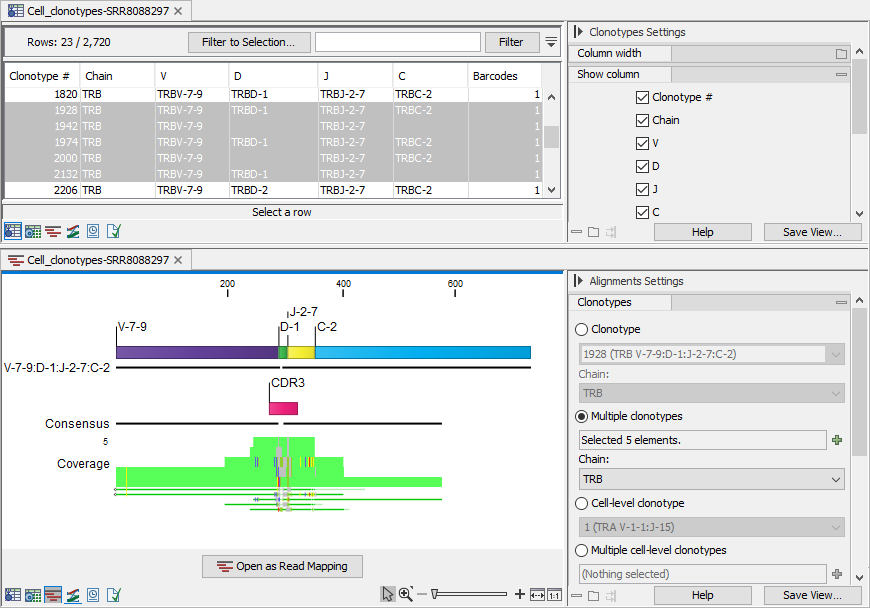
Figure 13.6: Clonotypes split view. Top: multiple clonotypes sharing reference segments are selected in the table view. Bottom: Alignment view for the clonotypes selected in the table view.
Alignments for multiple clonotypes can be shown together provided that they have the same chain, V and J segments and the D / C segments are not contradictory: either the D / C segment is identified and the same, or it is missing (figure 13.6).
When viewing alignments for multiple clonotypes, it can be useful to change "Compactness" to "Not compact" and tick the "Sample", "Barcode", "Cell-level clonotype #" and "Clonotype #" from the Side Panel. This way, it is easy to see this information for each of the aligned contigs (figure 13.7)).
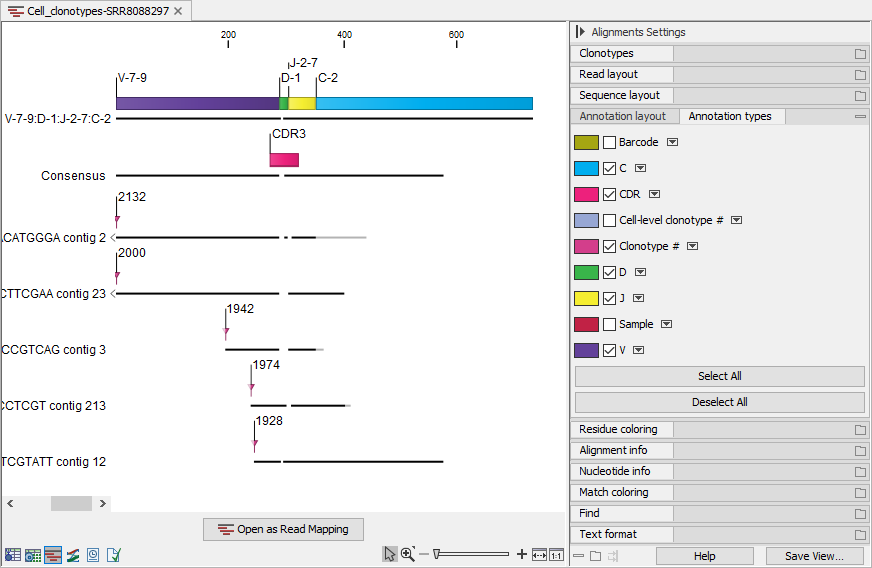
Figure 13.7: Alignment view for multiple clonotypes where "Compactness" is set to "Not compact" and "Clonotype #" is ticked.
Figure 13.6 shows an alignment for multiple clonotypes. Some of the contigs do not span past the J segment and using the "Clonotype #" annotation (figure 13.7)), we can confirm that these contigs belong to clonotypes for which the C segment has not been identified. Some of the clonotypes share the D segment, while others do not have an identified D segment. They all have different CDR3 sequences. Using the alignment view, it is straightforward to spot the differences between the CDR3 sequences.
For further processing, the alignments can be opened and saved as a stand-alone read mapping by using the "Open as Read Mapping" button. Using the Extract Reads tool (see http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Extract_Reads.html), the contigs can be extracted from the stand-alone read mapping as a Sequence List (![]() ), which can be used as input to Single Cell V(D)J-Seq Analysis. The tool will then skip the assembly and trimming and only clonotype the contigs (see The clonotype identification algorithm). This allows for custom processing of the contigs, where additional trimming can be performed before clonotyping.
), which can be used as input to Single Cell V(D)J-Seq Analysis. The tool will then skip the assembly and trimming and only clonotype the contigs (see The clonotype identification algorithm). This allows for custom processing of the contigs, where additional trimming can be performed before clonotyping.
Various settings controlling how the alignment, consensus and reference are displayed can be configured in the Side Panel, see http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=View_settings_in_Side_Panel.html.
