Beta Diversity
Beta diversity examines the change in species diversity between ecosystems.
The analysis is done in two steps. First, the tool estimates a distance between each pair of samples (see the list of available distances below). Once the distance matrix is calculated, the beta diversity analysis tool performs Principal Coordinate Analysis (PCoA) on the distance matrices. These can be visualized by selecting the PCoA icon (![]() ) in the bottom of the Beta Diversity results (
) in the bottom of the Beta Diversity results (![]() ).
As in the case of Alpha Diversity, you must have previously aligned the OTUs and constructed a phylogeny that can be used as input in the Beta Diversity tool.
).
As in the case of Alpha Diversity, you must have previously aligned the OTUs and constructed a phylogeny that can be used as input in the Beta Diversity tool.
To run the tool, open
Toolbox | Microbial Genomics Module (![]() ) | OTU clustering (
) | OTU clustering (![]() ) | Beta Diversity (
) | Beta Diversity (![]() )
)
Select an OTU abundance table before clicking on the button labeled Next.
You can now set the parameters for the beta diversity analysis as shown in figure 4.4.
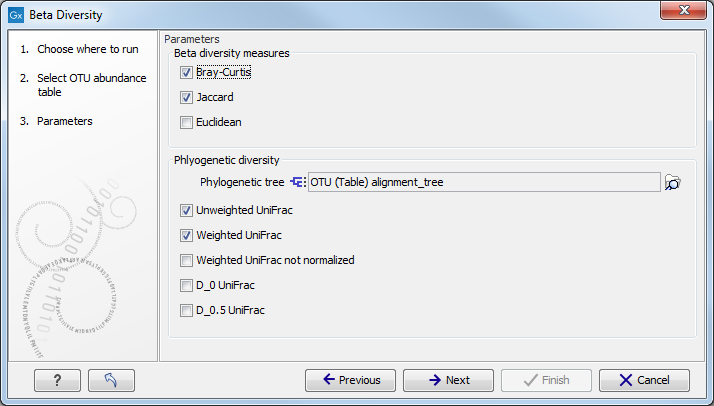
Figure 4.4:
Set up parameters for the Beta diversity tool.
The unweighted UniFrac distance gives comparatively more importance to rare lineages, while the weighted UniFrac distance gives more important to abundant lineages. The generalized UniFrac distance ![]() offers a robust tradeoff [Chen et al., 2012].
offers a robust tradeoff [Chen et al., 2012].
The output of the tool is a PCoA that can also be seen as a table (figure 4.5).
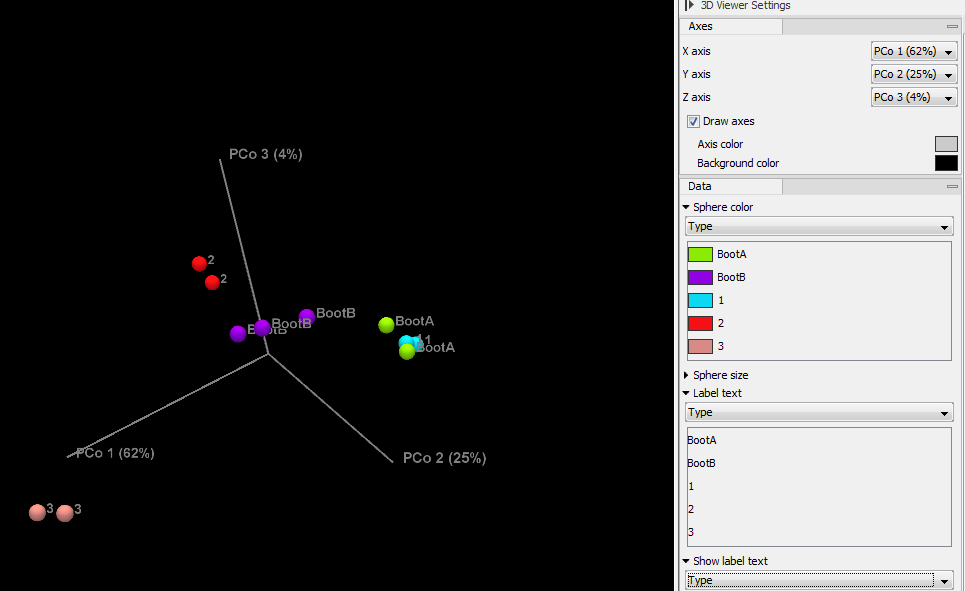
Figure 4.5:
Beta diversity results seen as a 3D PCoA.
Use the settings in the right hand side panel to explore the results and visualize them adequately.
Subsections
