Transcript-level expression
In order to switch to the transcript-level expression, click the Transcript-level expression (
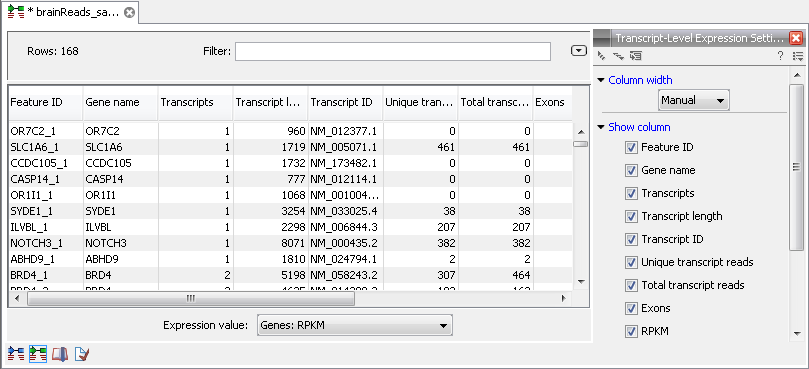
Figure 27.14: A subset of a result of an RNA-Seq analysis on the transcript level. Not all columns are shown in this figure
The following information is available in this table:
- Feature ID. This is the gene name with a number appended to differentiate between transcripts.
- Expression values. This is based on the expression measure chosen in figure 27.9.
- Gene name. The unique gene name.
- Transcripts annotated. The number of transcripts based on the mRNA annotations on the reference. Note that this is not based on the sequencing data - only on the annotations already on the reference sequence(s).
- Transcript length. The total length of all exons of that particular transcript.
- Transcript ID. This information is retrieved from transcript_ID key on the mRNA annotation.
- Unique transcript reads. This is the number of reads in the mapping for the gene that are uniquely assignable to the transcript. This number is calculated after the reads have been mapped and both single and multi-hit reads from the read mapping may be unique transcript reads.
- Total transcript reads. Once the 'Unique transcript read's have been identified and their counts calculated for each transcript, the remaining (non-unique) transcript reads are assigned randomly to one of the transcripts to which they match. The 'Total transcript reads' counts are the total number of reads that are assigned to the transcript once this random assignment has been done. As for the random assignment of reads among genes, the random assignment of reads within a gene but among transcripts, is done proportionally to the 'unique transcript counts' normalized by transcript length, that is, using the RPKM (see the description of the 'Maximum number of hits for a read' option', 27.1.1). Unique transcript counts of 0 are not replaced by 1 for this proportional assignment of non-unique reads among transcripts.
- Ratio of unique to total (exon reads). This will show the ratio of the two columns described above. This can be convenient for filtering the results to exclude the ones where you have low confidence because of a relatively high number of non-unique transcript reads.
- Exons. The number of exons for this transcript. Note that this is not based on the sequencing data - only on the annotations already on the reference sequence(s).
- RPKM. The RPKM value for the transcript, that is, the number of reads assigned to the transcript divided by the transcript length and normalized by 'Mapped reads' (see below).
- Relative RPKM. The RPKM value for the transcript divided by the maximum of the RPKM values for transcripts for this gene.
- Chromosome region start. Start position of the annotated gene.
- Chromosome region end. End position of the annotated gene.
