Extract Multiple Sequence Alignment
Extract Multiple Sequence Alignment traverses all aligned blocks in a Whole Genome Alignment and creates a linear concatenated Multiple Sequence Alignment. In contrast to the Whole Genome Alignment, a Multiple Sequence Alignment has all aligned blocks occurring in the same order and orientation.
Note: if the extracted Multiple Sequence Alignment contains long sequences, viewing the Multiple Sequence Alignment may be slow. The purpose of this tool is to make it possible to export the extracted alignment in Nexus format for example, so it can be used in third-party software that cannot process whole genome alignments formats (MAF and XMFA).
To run Extract Multiple Sequence Alignment, go to:
Tools | Whole Genome Alignment (![]() ) | Extract Multiple Sequence Alignment (
) | Extract Multiple Sequence Alignment (![]() )
)
Once the tool wizard has opened (figure 7.1), choose the Whole Genome Alignment you would like to use.
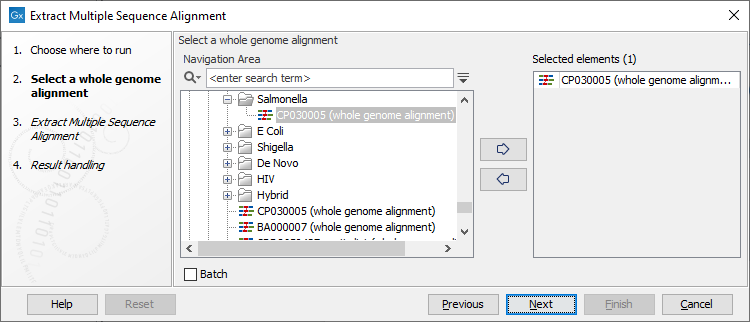
Figure 7.1: Select a Whole Genome Alignment.
In the next dialog (figure 7.2), you can set the following parameters:
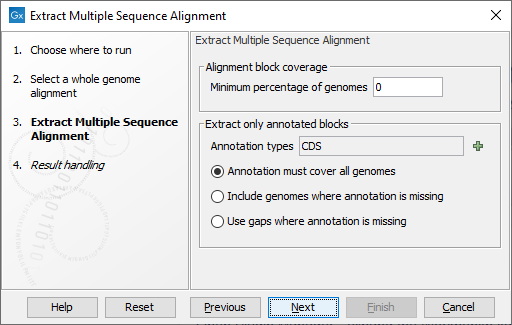
Figure 7.2: Select the table types and clusters construction methods you would like to use for building the heat maps.
- Minimum percentage of genomes An alignment block is only included if it is present on at least this fraction of the genomes. Setting this value to 100 means that only alignment blocks covering all genomes are included.
- Extract only annotated blocks It is possible to restrict the extraction only to regions of the genome covered by an annotation (such as the CDS annotations for protein coding regions). If an alignment block is partly covered by an annotation, only the intersection of the annotation region and alignment region is included. Choose among the following options:
- Annotation types Which annotations types to restrict the extraction to, such as CDS or Gene types.
- Annotation must cover all genomes The intersection of the alignment block and the annotations is extracted only if the block intersects an annotation on all genomes the alignment block covers.
- Include genomes where annotation is missing An alignment block only needs to intersect an annotation for some of the genomes it covers in order for the intersection of the block and the annotations to be extracted.
- Use gaps where annotation is missing If an alignment block covers a region of a genome without an annotation, that region will be represented as gaps in the extracted alignment.
