How to run the Identify Known Variants in One Sample (WES) workflow
- Go to the toolbox and double-click on
Toolbox | Ready-to-Use Workflows | Whole Exome Sequencing (
 ) | General Workflows (WES) | Identify Known Variants from One Sample (WES) (
) | General Workflows (WES) | Identify Known Variants from One Sample (WES) ( )
)
- This will open the wizard step shown in
figure 16.8 where you can
select the reads of the sample that should be tested for presence or absence
of your known variants.
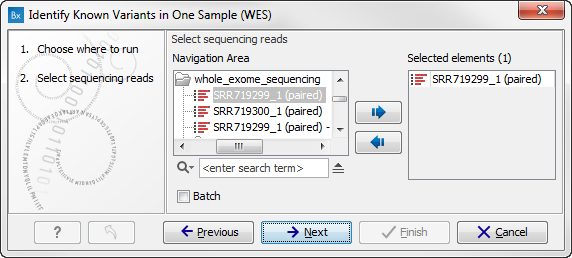
Figure 16.8: Select the sequencing reads from the sample you would like to test for your known variants.If several samples from different folders should be analyzed, the tool has to be run in batch mode. This is done by selecting "Batch" and specifying the folders that hold the data you wish to analyse.
Click on the button labeled Next.
- Specify the target region for the Indels and Structural Variants tool (figure 16.9). This step is optional and will speed the completion time of the workflow by running the tool only on the selected target regions. If you do not have a targeted region file to provide, simply click Next.
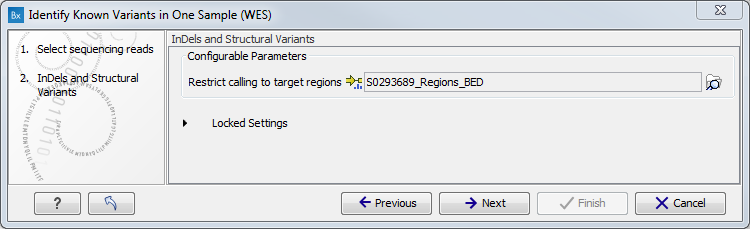
Figure 16.9: Specify the targeted region file for the Indels and Structural Variants tool. - Specify the parameters for the QC for Target Sequencing tool (figure 16.10).
When working with targeted data (WES or TAS data), quality checks for the targeted sequencing is included in the workflows. This step is not optional, and you need to specify the targeted regions file adapted to the sequencing technology you used. Choose to use the default settings or to adjust the parameters.
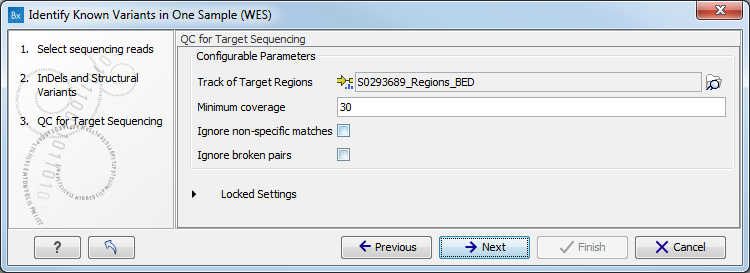
Figure 16.10: Specify the parameters for the QC for Target Sequencing tool.The parameters that can be set are:
- Minimum coverage provides the length of each target region that has at least this coverage.
- Ignore non-specific matches: reads that are non-specifically mapped will be ignored.
- Ignore broken pairs: reads that belong to broken pairs will be ignored.
For more information about the tool, see QC for Target Sequencing.
- Click on the button labeled Next and specify the track with the known variants that should be identified in your sample (figure 16.11).
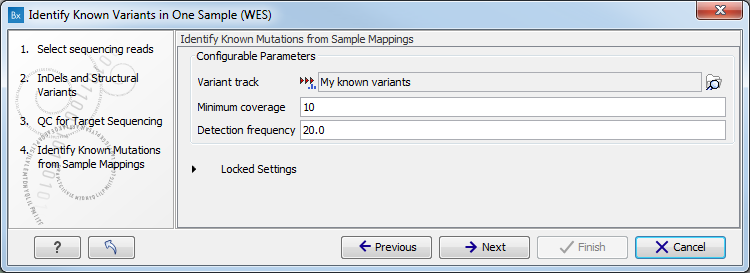
Figure 16.11: Specify the track with the known variants that should be identified.The parameters that can be set are:
- Minimum coverage The minimum number of reads that covers the position of the variant, which is required to set "Sufficient Coverage" to YES.
- Detection frequency The minimum allele frequency that is required to annotate a variant as being present in the sample. The same threshold will also be used to determine if a variant is homozygous or heterozygous. In case the most frequent alternative allele at the position of the considered variant has a frequency of less than this value, the zygosity of the considered variant will be reported as being homozygous.
The parameter "Detection Frequency" will be used in the calculation twice. First, it will report in the result if a variant has been detected (observed frequency > specified frequency) or not (observed frequency <= specified frequency). Moreover, it will determine if a variant should be labeled as heterozygous (frequency of another allele identified at a position of a variant in the alignment > specified frequency) or homozygous (frequency of all other alleles identified at a position of a variant in the alignment < specified frequency).
Click on the button labeled Next.
- In the last wizard step (figure 16.12)you can check the selected settings by clicking on the button labeled Preview All Parameters.
Figure 16.12: Check the settings and save your results.At the bottom of this wizard there are two buttons regarding export functions; one button allows specification of the export format, and the other button (the one labeled "Export Parameters") allows specification of the export destination.
- Click on the button labeled OK to go back to the previous dialog box and choose to Save your results.
Note! If you choose to open the results, the results will not be saved automatically. You can always save the results at a later point.
