Annotate CDS with Best BLAST Hit
The Annotate CDS with Best BLAST Hit tool will allow you to annotate a set of contigs containing CDS annotations with their best BLAST hit.
To start the analysis, go to:
Microbial Genomics Module (![]() ) | Metagenomics (
) | Metagenomics (![]() ) | Functional Analysis (
) | Functional Analysis (![]() ) | Annotate CDS with Best BLAST Hit (
) | Annotate CDS with Best BLAST Hit (![]() )
)
Several parameters are available:
- Genetic code. The genetic code used for translating CDS to proteins.
- BLAST database. A protein BLAST database. Popular BLAST protein databases can be downloaded using the Download BLAST Database tool or created using a the Create BLAST Database tool.
- Expectation value. The minimum expectation value (E) threshold to use.
Note that choosing a very large BLAST database with millions of sequences (e.g. the nt, nr and refeseq_protein databases from the NCBI) will slow down the algorithm considerably, especially when there are many CDS in the input. Therefore, we recommend to use a medium-sized database such as "swissprot".
In the wizard, you can choose between databases stored locally (![]() ) or remotely on the server (
) or remotely on the server (![]() ). If you create a workflow that you plan to run on a server, you should avoid locking the BLAST database parameter as the chosen database may not exist on the server.
). If you create a workflow that you plan to run on a server, you should avoid locking the BLAST database parameter as the chosen database may not exist on the server.
If you select Create Report, the tool will create a summary report table. The report is divided in three parts:
- Input. Contains information about the size of the contigs and CDS used as input.
- BLAST database. The protein BLAST database used in the search, together with its description, location, and size.
- Output. The total number (and percent) of CDS that were annotated with their best BLAST hit.
When a hit for a CDS is found, the tool adds three fields to the CDS annotation, as shown in figure 6.2:
- BLAST Hit. Accession number of the best BLAST Hit in the BLAST database.
- BLAST Hit Description. Description of the matching protein, as present in the BLAST database.
- BLAST Hit E-value. The E-value of the match.
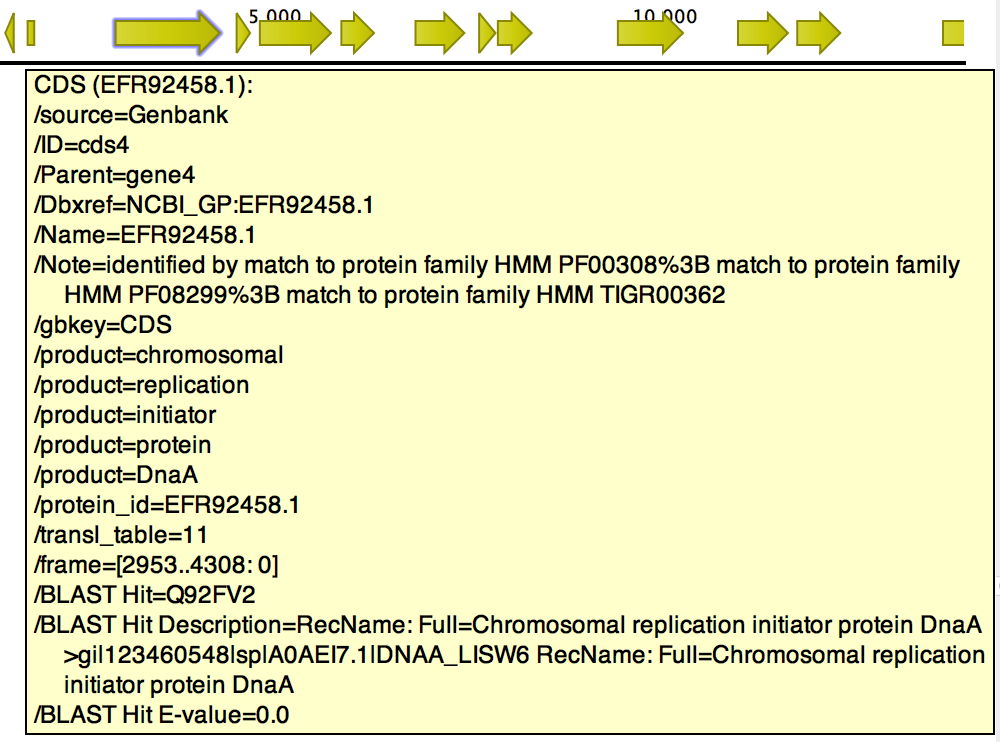
Figure 6.2: BLAST Best Hit annotations added to gene cds4 of h. pylori.
